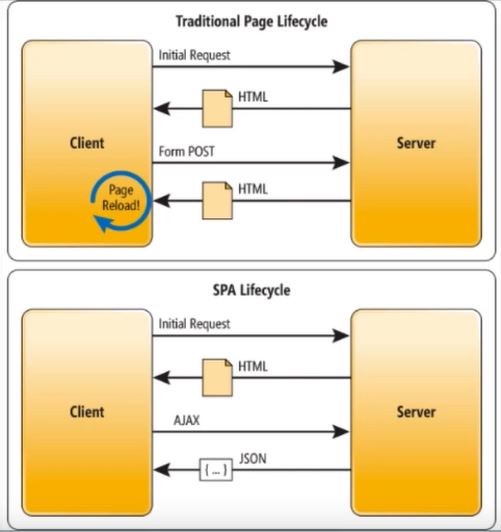
Blazor
- SPA
- Single Page Application
- Load HTML and extra files only one time
- After first Loading, request by Signal(ex. AJAX) with no-reloading
- .cshtml and .razor
- .cshtml: Razor page file
- .razor: Razor component file
Route
-
@page
- define how to match urls
- method is same with Razor pages
@page "/user"Binding
- @
- specifies to use C#
- You can make attribute or condition by this, also
button class="@_btnClass"
disabled="@(_users.Count()>=5)-
@key
- The @key directive attribute causes the components diffing algorithm to guarantee preservation of elements or components based on the key’s value.
<li @key="user" class="list-group-item">-
@bind-value
- bind value by variable name
@bind-value="_inputName"-
@code
- C# code in razor file
- seems like script in html file
Lambda
- ()=>
- is used for onclick method syntax
@onclick="(() => KickUser(user))"System.Threading
- System.Threading Namespace
- Provides classes and interfaces that enable multithreaded programming.
- In addition to classes for synchronizing thread activities and access to data (Mutex, Monitor, Interlocked, AutoResetEvent, and so on), this namespace includes a ThreadPool class that allows you to use a pool of system-supplied threads, and a Timer class that executes callback methods on thread pool threads.
- Timer Class
- Provides a mechanism for executing a method on a thread pool thread at specified intervals.
- This class cannot be inherited.
- InvokeAsync(Action)
- Executes the specified Action asynchronously on the thread the Dispatcher is associated with.
- StateHasChanged
- Notifies the component that its state has changed.
- When applicable, this will cause the component to be re-rendered.
@using System.Threading;
void AutoIncrement()
{
var timer = new Timer(x =>
{
InvokeAsync(() =>
{
IncrementCount();
StateHasChanged();
});
}, null, 1000, 1000);
}Parameter
- In this post,
ShowUser.cshtmlis child andUser.cshtmlis parent - To use parent’s variable or function in child
- Parent
- link the variable with child’s parameter name
<ShowUser Users="_users" CallbackTest="CallbackTestFunc" @ref="_showUser"></ShowUser>- Child
- define variable and spedify it is a parameter by
[Parameter]
- define variable and spedify it is a parameter by
[Parameter]
public List<UserData> Users { get; set; }ref
- In this post,
ShowUser.cshtmlis child andUser.cshtmlis parent - To use child’s variable or function in parent
- Parent
- define variable with child class name
<ShowUser Users="_users" CallbackTest="CallbackTestFunc" @ref="_showUser"></ShowUser>
ShowUser _showUser;EventCallBack
- EventCallback struckt
- A bound event handler delegate
public EventCallback CallbackTest { get; set; }- EventCallback.InvokeAsync Method
- Invokes the delegate associated with this binding and dispatches an event notification to the appropriate component.
public void KickUser(UserData user)
{
Users.Remove(user);
CallbackTest.InvokeAsync(null);
}- Diffence with
Action- Prefer the strongly typed EventCallback
, which provides better error feedback to users of the component. - Similar to other UI event handlers, specifying the event parameter is optional. Use EventCallback when there’s no value passed to the callback.
- Prefer the strongly typed EventCallback
public Action CallbackTest { get; set; }
public void KickUser(UserData user)
{
Users.Remove(user);
CallbackTest.Invoke();
StateHasChanged();
}Cascading Parameter
- CascadingValue
- You can assign parameter for children
- be applied in children’s children
- parent
- define
Nameto match with child - specify variable in
Valueto use parameter
- define
<CascadingValue Name="ThemeColor" Value="_selectedColor">
<ShowUser Users="_users" CallbackTest="CallbackTestFunc" @ref="_showUser"></ShowUser>
</CascadingValue>
string _selectedColor = "Green";- child
- link parameter by
Name
- link parameter by
[CascadingParameter(Name = "ThemeColor")]
string _color { get; set; }Select Binding
- Select Binding
- bind
@bindexpression andvalueattribute
- bind
<select class="form-control" @bind="_selectedColor">
@foreach(var option in _options)
{
<option value="@option">
@option
</option>
}
</select>Templated Component
- Templated Component
- Razor Component constructed with
RenderFragment
- Razor Component constructed with
- RenderFragment Delegate
- Represents a segment of UI content, implemented as a delegate that writes the content to a RenderTreeBuilder.
- Template
- You can use your parameters
- You can pass data with
Context
<TableTemplate Items="forecasts" TItem="WeatherForecast">
<Header>
<th>Date</th>
<th>Temp. (C)</th>
<th>Temp. (F)</th>
<th>Summary</th>
</Header>
<Row Context="forecast">
<td>@forecast.Date.ToShortDateString()</td>
<td>@forecast.TemperatureC</td>
<td>@forecast.TemperatureF</td>
<td>@forecast.Summary</td>
</Row>
</TableTemplate>
private WeatherForecast[] forecasts;- Usage
- IReadOnlyList
Interface: Represents a read-only collection of elements that can be accessed by index. - You can make Generic Type in razor with
@typeparam
- IReadOnlyList
@typeparam TItem
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
@Header
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var item in Items)
{
<tr>
@Row(item)
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
[Parameter]
public RenderFragment Header { get; set; }
[Parameter]
public RenderFragment<TItem> Row { get; set; }
[Parameter]
public IReadOnlyList<TItem> Items { get; set; }Partial
- Partial
- If you want to separate razor and code, make class file for code by same name with razor
- input
partialbetweenpublicandclass
public partial class FetchData{...}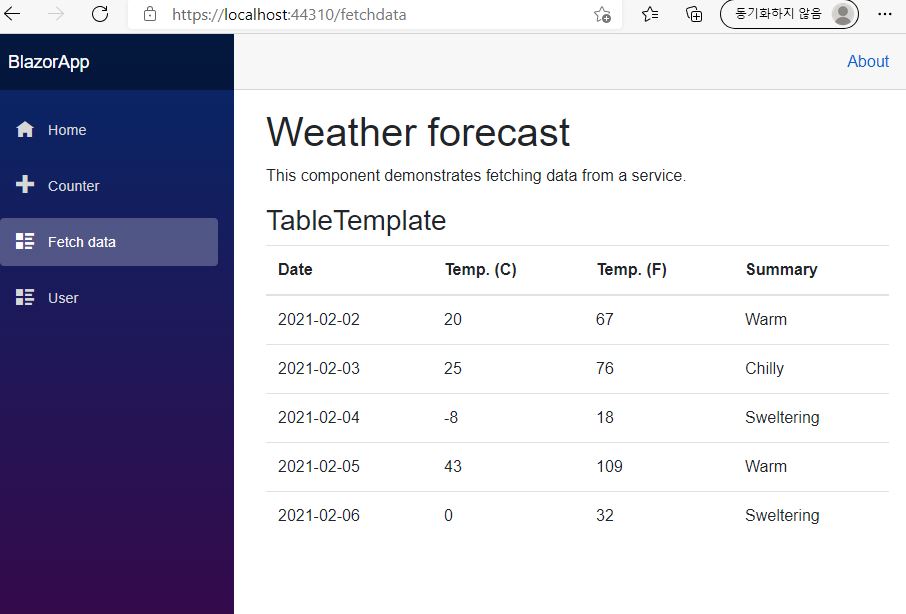
Dependency Injection
- Dependency
- In OOP, the lower the dependence, the better
- Rather than entering the class directly into the code, injecting dependencies using Startup.cs can reduce dependencies
- cs
- Create Interface
- Create Class that inherit the interface
public interface IFoodService
{
IEnumerable<Food> GetFoods();
}
public class FoodService : IFoodService
{
public IEnumerable<Food> GetFoods()
{
List<Food> foods = new List<Food>()
{
new Food(){Name = "Bibimbap", Price=7000},
new Food(){Name = "Kimbap", Price=3000},
new Food(){Name = "Bossam", Price=9000}
};
return foods;
}
}- Startup.cs
- Start service in
ConfigureServices
- Start service in
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddSingleton<IFoodService, FastFoodService>();
}- cshtml
- Inject the interface to use
@inject IFoodService foodService- Difference with C++
- When you use same interfacein different class, you don’t need to service the interface again
- Asp.Net will connect it atomatically
public class PaymentService
{
IFoodService _service;
public PaymentService(IFoodService service)
{
_service = service;
}
} services.AddSingleton<PaymentService>(); @inject PaymentService paymentService
Service lifetimes
Singleton
- Update every time server restart
public class SingletonService : IDisposable
{
public Guid ID { get; set; }
public SingletonService()
{
ID = Guid.NewGuid();
}
public void Dispose()
{
Console.WriteLine("SingletonService Disposed");
}
} services.AddSingleton<SingletonService>(); @inject SingletonService singleton
<h1>Singleton</h1>
Guid: @singleton.ID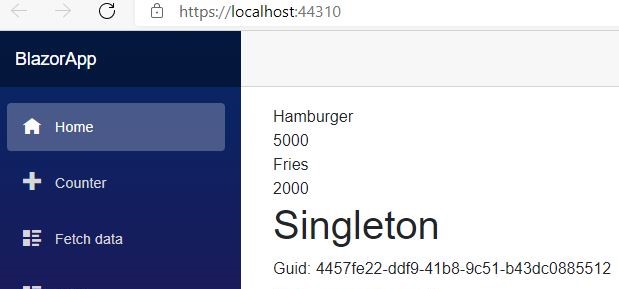
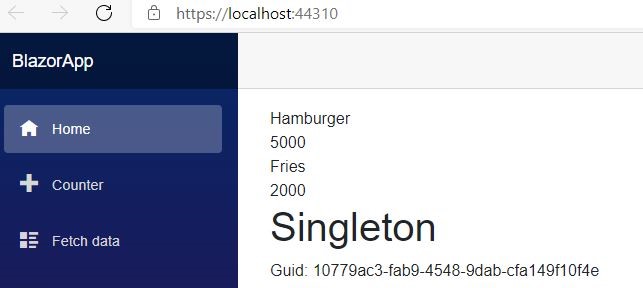
Transient
- Update every time the page is requested
public class TransientService : IDisposable
{
public Guid ID { get; set; }
public TransientService()
{
ID = Guid.NewGuid();
}
public void Dispose()
{
Console.WriteLine("SingletonService Disposed");
}
} services.AddTransient<TransientService>(); @inject TransientService transient
<h1>Transient</h1>
Guid: @transient.IDScoped
- Update every time web connect
public class ScopeService : IDisposable
{
public Guid ID { get; set; }
public ScopeService()
{
ID = Guid.NewGuid();
}
public void Dispose()
{
Console.WriteLine("SingletonService Disposed");
}
} services.AddScoped<ScopeService>(); @inject ScopeService scoped
<h1>Scoped</h1>
Guid: @scoped.IDForm
Array -> List
- WeatherForecastService.cs
- To add new object, change Array to List
public Task<List<WeatherForecast>> GetForecastAsync(DateTime startDate)
{
...
}).ToList());
} private List<WeatherForecast> _forecasts;Modal
- Modal
- To use popup in page
- Use
if-elselike modal-switch - For UI, just use specified classes in Bootstrap
if (_showPopup)
{
<div class="modal" style="display:block" role="dialog">
<div class="modal-dialog">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h3 class="modal-title">Add Forecast</h3>
<button type="button" class="close" @onclick="ClosePopup">
<span area-hidden="true">X</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
...
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
bool _showPopup = false;
WeatherForecast _addForecast;
void AddNewForecast()
{
_showPopup = true;
...
}
void ClosePopup()
{
_showPopup = false;
}Validation
class
- [Required]
- Specify variable must be not null
- You can put error message in
ErrorMessage
- [Range]
- Specify range of variable
- You can define type in
typeof, maximum, and minimum
- [StringLength]
- Specify length of string
- You can define length of maximum and mininum and put error message in
ErrorMessage
[Required(ErrorMessage = "NeedTemperatureC!")]
[Range(typeof(int), "-100", "100")]
public int TemperatureC { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Need Summary!")]
[StringLength(10, MinimumLength = 2, ErrorMessage = "2-10")]
public string Summary { get; set; }Razor Component
- EditForm
- To make Form
- Bind value in
Model - Bind function in
OnValidSubmitafter pressing button that type issubmit
- DataAnnotationsValidator
- Add Data Annotations Validation
- ValidationSummary
- Show ErrorMessage
- InputNumber
- Make
<input>tag with validation - Type is
int - Bind value in
@bind-value
- Make
- InputText
- Make
<input>tag with validation - Type is
string - Bind value in
@bind-value
- Make
<EditForm Model="_addForecast" OnValidSubmit="SaveForecast">
<DataAnnotationsValidator />
<ValidationSummary />
<label for="TemperatureC">TemperatureC</label>
<InputNumber class="form-control" placeholder="TemperatureC" @bind-Value="_addForecast.TemperatureC" />
<label for="Summary">Summary</label>
<InputText class="form-control" placeholder="Summary" @bind-Value="_addForecast.Summary" />
<br />
<button class="btn btn-primary" type="submit">Save</button>
</EditForm>Action
- Action Delegate
- Encapsulates a method that has no parameters and does not return a value
- You can change UI State by Invoke()
public Action OnStateChanged;Value
- value
- The value keyword is used to define the value being assigned by the set accessor.
public int Count
{
get
{
return _count;
}
set
{
_count = value;
Refresh();
}
}IDisposable
- Idisposable Interface
- Provides a mechanism for releasing unmanaged resources
- Dispose()
- Performs application-defined tasks associated with freeing, releasing, or resetting unmanaged resources
JavaScript
- Function
- To make a function, at first, you need to define variable
- define where you put your function. For example, window, document, and kind of tags
- define function’s name and contents like lambda function
- Call the function
var func = (function () {
window.testFunction = {
helloWorld: function () {
return alert('Hello World');
},
inputName: function (text) {
return prompt(text, 'Input Name');
}
};
});
func();- Script Binding
- You can link your script in
_Host.cshtmlby<sciprt>tag
- You can link your script in
<script src="test.js"></script>IJSRuntime
- IJSRuntime Interface
- Represents an instance of a JavaScript runtime to which calls may be dispatched
@inject IJSRuntime JSRuntime- InvokeAsync
- Invokes the specified JavaScript function asynchronously.
- Microsoft.JSInterop.JSRuntime will apply timeouts to this operation based on the value configured in Microsoft.JSInterop.JSRuntime.DefaultAsyncTimeout.
- To dispatch a call with a different timeout, or no timeout, consider using Microsoft.JSInterop.IJSRuntime.InvokeAsync
- An identifier for the function to invoke. For example, the value “someScope.someFunction” will invoke the function window.someScope.someFunction
_name = await JSRuntime.InvokeAsync<string>("testFunction.inputName", "Input Name");- InvokeVoidAsync
- Invokes the specified JavaScript function asynchronously
- An identifier for the function to invoke. For example, the value “someScope.someFunction” will invoke the function window.someScope.someFunction