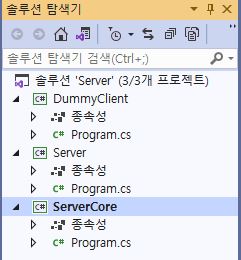
Project
Create Projects
- Server solution
- Create console app and name solution to
Server - Create project in
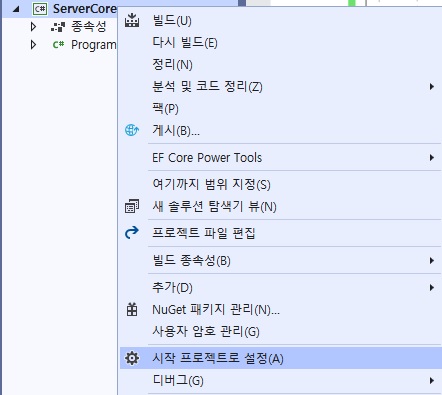
Serversolution namedDummyClientandServerCore - set
ServerCoreproject to starting project
- Create console app and name solution to
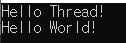
Thread
Create Thread
- ServerCore\Program.cs
- you have to make main thread function
- connect main thread function
Startlets main thread function start
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ServerCore
{
class Program
{
static void MainThread()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello Thread!");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread t = new Thread(MainThread);
t.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
}
}
}
Foreground Thread
- default is foreground thread in C#
-
if main thread has infinity funtion, then it will not finish forever
- ServerCore\Program.cs
static void MainThread()
{
while(true)
Console.WriteLine("Hello Thread!");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread t = new Thread(MainThread);
t.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
}Background Thread
- you can change main thread to background thread by
IsBackgoundmethod -
even there is infinity function in main thread, this thread will be finished because it is background thread
- ServerCore\Program.cs
static void MainThread()
{
while(true)
Console.WriteLine("Hello Thread!");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread t = new Thread(MainThread);
t.IsBackground = true;
t.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
}
Waiting Thread
- main can wait our main thread by
JoinMethod -
you can define Thread name by
NameMethod - ServerCore\Program.cs
static void MainThread()
{
while(true)
Console.WriteLine("Hello Thread!");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread t = new Thread(MainThread);
t.Name = "Test Thread";
t.IsBackground = true;
t.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Waiting for Thread!");
t.Join();
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
}
ThreadPool
- Thread is already made in C#
- So when we need this thread, just use
ThreadPool -
after their work, they are not removed, just changed to deactivate
- ServerCore\Program.cs
static void MainThread()
{
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
Console.WriteLine("Hello Thread!");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(MainThread);
while (true){ }
}
Set number of Threads
- you can set number of threads by
SetMinThreadsandSetMaxThreads
Test: existing waiting thread
-
if there is waiting thread, then this thread will excute
-
ServerCore\Program.cs
static void MainThread()
{
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
Console.WriteLine("Hello Thread!");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ThreadPool.SetMinThreads(1, 1);
ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(5, 5);
// There is left thread to work
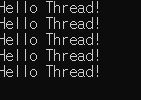
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem((obj) => { while (true) { } });
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(MainThread);
while (true){ }
}
Test: non existing waiting thread
-
but if there is no waiting thread because of infinity function in thread, then this project cannot be finished
-
ServerCore\Program.cs
static void MainThread()
{
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
Console.WriteLine("Hello Thread!");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ThreadPool.SetMinThreads(1, 1);
ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(5, 5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem((obj) => { while (true) { } });
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(MainThread);
while (true){ }
}Task
- Task is action
- Task is work of Thread
-
you can define this thread is infinity by
LongRunning - ServerCore\Program.cs
static void MainThread()
{
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
Console.WriteLine("Hello Thread!");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ThreadPool.SetMinThreads(1, 1);
ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(5, 5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Task t = new Task(() => { while (true) { } }, TaskCreationOptions.LongRunning);
t.Start();
}
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(MainThread);
while (true){ }
}
Compiler Optimization
- you can make stop duration by
Sleep Waitis same function withJoin, butWaitis for Task andJoinis for Thread-
you can wait main Task by
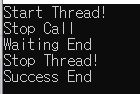
Wait - ServerCore\Program.cs
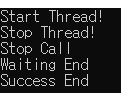
static bool _stop = false;
static void ThreadMain()
{
Console.WriteLine("Start Thread!");
while(_stop == false)
{
// wait stop signal
}
Console.WriteLine("Stop Thread!");
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Task t = new Task(ThreadMain);
t.Start();
Thread.Sleep(1000);
_stop = true;
Console.WriteLine("Stop Call");
Console.WriteLine("Waiting End");
t.Wait();
Console.WriteLine("Success End");
}
Release Mode
- release mode optimize our code

- So
whilemethod is optimized by Release mode - and this makes problem(like infinity program)
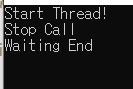
Disassembler
-
you can check your C# code to assembly language
-
Disassember
- make stop point in while method
- excute program by debugging mode
- click [Debug]-[Window]-[Disassembler]

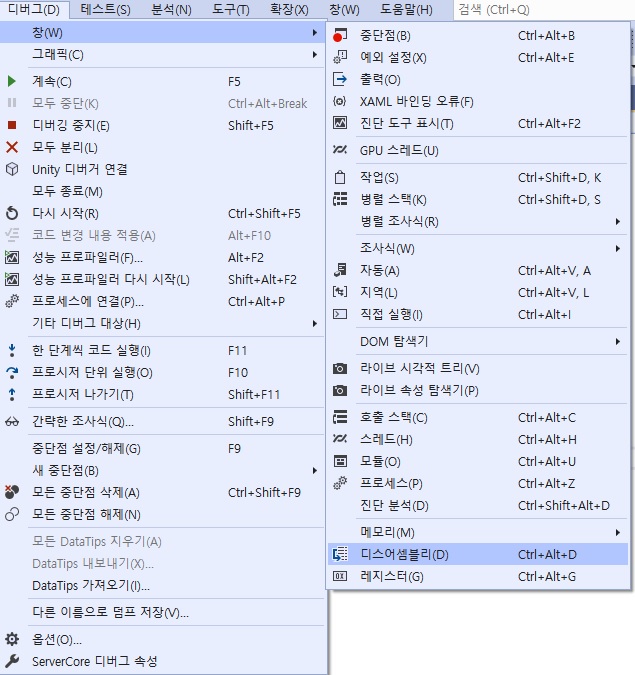
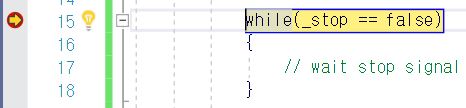
- Result
- by optimization, while method became infinity method
Volatile
-
you can avoid optimization by
volatile -
ServerCore\Program.cs
volatile static bool _stop = false;
...
Cache
- Temporal Locality
- recently used memory must have be used again
- Spacial Locality
- close memory with recently used memory must have be used
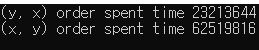
Test: Spacial Locality
- ServerCore\Program.cs
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[,] arr = new int [10000, 10000];
{
long now = DateTime.Now.Ticks;
for (int y = 0; y < 10000; y++)
for (int x = 0; x < 10000; x++)
arr[y, x] = 1;
long end = DateTime.Now.Ticks;
Console.WriteLine($"(y, x) order spent time {end-now}");
}
{
long now = DateTime.Now.Ticks;
for (int y = 0; y < 10000; y++)
for (int x = 0; x < 10000; x++)
arr[x, y] = 1;
long end = DateTime.Now.Ticks;
Console.WriteLine($"(x, y) order spent time {end-now}");
}
}
Memory Barrier
Hardware Optimization
- if there is no related with each code, ordering of code can be changed
Test
- ServerCore\Program.cs
class Program
{
static int x = 0;
static int y = 0;
static int r1 = 0;
static int r2 = 0;
static void Thread_1()
{
y = 1; //store y
r1 = x; // Load x
}
static void Thread_2()
{
x = 1; // Store x
r2 = y; // Load y
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int count = 0;
while (true)
{
count++;
x = y = r1 = r2 = 0;
Task t1 = new Task(Thread_1);
Task t2 = new Task(Thread_2);
t1.Start();
t2.Start();
Task.WaitAll(t1, t2);
if (r1 == 0 && r2 == 0)
break;
}
Console.WriteLine($"{count} times executed!");
}
}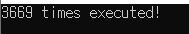
- this mean,
r1=xis ordered first theny=1andr2=yis ordered first thenx=1
Memory Barrier
-
To avoid Hardware optimization
- Memory Barrier
- avoid relocating code
- Visibility
- Full memory Barrier(ASM MFENCE, C# Thread.MemoryBarrier)
- ban Store and Load
- Store Memory Barrier (ASM SFENCE)
- ban only Store
- Load Memory Barrier(ASM LFENCE)
- ban only Load
Memory Barrier timing
- Store
- after store
- Load
- before load
Test
- ServerCore\Program.cs
class Program
{
static int x = 0;
static int y = 0;
static int r1 = 0;
static int r2 = 0;
static void Thread_1()
{
y = 1; //store y
Thread.MemoryBarrier();
r1 = x; // Load x
}
static void Thread_2()
{
x = 1; // Storex
Thread.MemoryBarrier();
r2 = y; // Load y
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int count = 0;
while (true)
{
count++;
x = y = r1 = r2 = 0;
Task t1 = new Task(Thread_1);
Task t2 = new Task(Thread_2);
t1.Start();
t2.Start();
Task.WaitAll(t1, t2);
if (r1 == 0 && r2 == 0)
break;
}
Console.WriteLine($"{count} times executed!");
}
}Interlocked
Race Condition
- Tasks excute withour order
Test
- ServerCore\Program.cs
class Program
{
static int number = 0;
static void Thread_1()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
number++;
}
static void Thread_2()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
number--;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Task t1 = new Task(Thread_1);
Task t2 = new Task(Thread_2);
t1.Start();
t2.Start();
Task.WaitAll(t1, t2);
Console.WriteLine(number);
}
}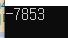
- this happened because
number++andnumber--is not atomic
Interlocked
- make method to atomic
Test
- ServerCore\Program.cs
class Program
{
...
static void Thread_1()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
Interlocked.Increment(ref number);
}
static void Thread_2()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
Interlocked.Decrement(ref number);
}
...
}
- result is changed because
Interlocked.IncrementandInterlocked.Decrementis atomic
Lock
Mutual Exclusive
- Monitor
- if code is too long to make interlocked, we can use
Monitor Entermeans lock the task andExitmeans release the task- after
Exit, other tasks are running
- if code is too long to make interlocked, we can use
Test
- ServerCore\Program.cs
class Program
{
static int number = 0;
static object _obj = new object();
static void Thread_1()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
Monitor.Enter(_obj); // Lock
number++;
Monitor.Exit(_obj); // Release
}
}
static void Thread_2()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
Monitor.Enter(_obj);
number--;
Monitor.Exit(_obj);
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Task t1 = new Task(Thread_1);
Task t2 = new Task(Thread_2);
t1.Start();
t2.Start();
Task.WaitAll(t1, t2);
Console.WriteLine(number);
}
}
Lock
- Lock
Lockis same function with try-catch-finally- object is used like a Lock
Test
- ServerCore\Program.cs
class Program
{
static int number = 0;
static object _obj = new object();
static void Thread_1()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
lock (_obj)
{
number++;
}
}
}
static void Thread_2()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
lock (_obj)
{
number--;
}
}
}
...
}
DeadLock
- if there are two keys and two process and each process got one key, then this program never gonna finish
Test
- ServerCore\Program.cs
class SessionManager
{
static object _lock = new object();
public static void TestSession()
{
lock (_lock) { }
}
public static void Test()
{
lock (_lock)
{
UserManager.TestUser();
}
}
}
class UserManager
{
static object _lock = new object();
public static void Test()
{
lock (_lock)
{
SessionManager.TestSession();
}
}
public static void TestUser()
{
lock (_lock) { }
}
}
class Program
{
static int number = 0;
static void Thread_1()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
SessionManager.Test();
}
}
static void Thread_2()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
UserManager.Test();
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Task t1 = new Task(Thread_1);
Task t2 = new Task(Thread_2);
t1.Start();
t2.Start();
Task.WaitAll(t1, t2);
Console.WriteLine(number);
}
}- Sleep
- you can stop one of thread untill other thread gonna be finished
Test
- ServerCore\Program.cs
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Task t1 = new Task(Thread_1);
Task t2 = new Task(Thread_2);
t1.Start();
Thread.Sleep(1000);
t2.Start();
Task.WaitAll(t1, t2);
Console.WriteLine(number);
}
SpinLock
- one thread waits other thread untill this thread gonna be finished
Test
- ServerCore\Program.cs
class SpinLock
{
volatile bool _locked = false;
public void Acquire()
{
while (_locked)
{
//wait for lock to release
}
_locked = true;
}
public void Release()
{
_locked = false;
}
}
class Program
{
static int _num = 0;
static SpinLock _lock = new SpinLock();
static void Thread_1()
{
for(int i=0; i<100000; i++)
{
_lock.Acquire();
_num++;
_lock.Release();
}
}
static void Thread_2()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
_lock.Acquire();
_num--;
_lock.Release();
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Task t1 = new Task(Thread_1);
Task t2 = new Task(Thread_2);
t1.Start();
t2.Start();
Task.WaitAll(t1, t2);
Console.WriteLine(_num);
}
}
-
this happened because this process is not atomic
-
Interlocked.Exchange
Test
- ServerCore\Program.cs
class SpinLock
{
volatile int _locked = 0;
public void Acquire()
{
while(true)
{
int original = Interlocked.Exchange(ref _locked, 1);
if (original == 0)
break;
}
}
public void Release()
{
_locked = 0;
}
}
- Interlocked.CompareExchange
Test
- ServerCore\Program.cs
class SpinLock
{
volatile int _locked = 0;
public void Acquire()
{
while(true)
{
int expected = 0;
int desired = 1;
if (Interlocked.CompareExchange(ref _locked, desired, expected) == expected)
break;
}
}
public void Release()
{
_locked = 0;
}
}
Context Switching
- Thread.Sleep(1);
- an unconditional rest
- Monitor and lock
- Thread.Sleep(0);
- an unconditial yield
- but thread cannot yield to lower priority
- if there is only same or lower priority with current thread, then current thread is excuted
- SpinLock
- Thread.Yield();
- a generous concession
- if there is excutable thread, then this thread is excuted
- if threr is not excutable thread, remained time is removed
- Mutex
ResetEvent
- AutoResetEvemt
- speed is really not good, but thread is excuted automatically
Test
- ServerCore\Program.cs
class Lock
{
AutoResetEvent _available = new AutoResetEvent(true);
public void Acquire()
{
_available.WaitOne();
}
public void Release()
{
_available.Set();
}
}
class Program
{
static int _num = 0;
static Lock _lock = new Lock();
...
}
Mutex
- Mutex
- Mutex can count wait and release, and use threadId
Test
- ServerCore\Program.cs
class Program
{
static int _num = 0;
static Mutex _lock = new Mutex();
static void Thread_1()
{
for(int i=0; i<10000; i++)
{
_lock.WaitOne();
_num++;
_lock.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
static void Thread_2()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
_lock.WaitOne();
_num--;
_lock.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Task t1 = new Task(Thread_1);
Task t2 = new Task(Thread_2);
t1.Start();
t2.Start();
Task.WaitAll(t1, t2);
Console.WriteLine(_num);
}
}
ReaderWriterLock
- in normal situation, there is no lock
- but if in specific situation, for example, you want to write, then lock is excuted
Test : Non Recursive Lock
- ServerCore\Lock.cs
- Spin Lock Policy: 5000 times → Yield
class Lock
{
// 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
const int EMPTY_FLAG = 0x00000000;
// 0111 1111 1111 1111 0000 0000 0000 0000
const int WRITE_MASK = 0x7FFF0000;
// 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 1111 1111 1111
const int READ_MASK = 0x0000FFFF;
const int MAX_SPIN_COUNT = 5000;
// 32bits = [Unused(1)] [WriteThreadId(15)] [ReadCount(16)]
int _flag = EMPTY_FLAG;
public void WriteLock()
{
// noone has WriteLock or ReadLock, then get ownership by compitition
int desired = (Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId << 16) & WRITE_MASK;
while (true)
{
for(int i=0; i<MAX_SPIN_COUNT; i++)
{
if (Interlocked.CompareExchange(ref _flag, desired, EMPTY_FLAG) == EMPTY_FLAG)
return;
}
Thread.Yield();
}
}
public void WriteUnlock()
{
Interlocked.Exchange(ref _flag, EMPTY_FLAG);
}
public void ReadLock()
{
// noone has WriteLock, then add 1 to ReadCount
while (true)
{
for(int i=0; i<MAX_SPIN_COUNT; i++)
{
int expected = (_flag & READ_MASK);
if (Interlocked.CompareExchange(ref _flag, expected + 1, expected) == expected)
return;
}
Thread.Yield();
}
}
public void ReadUnlock()
{
Interlocked.Decrement(ref _flag);
}
}Test : Recursive Lock
- ServerCore\Lock.cs
- Spin Lock Policy: 5000 times → Yield
- WriteLock → WriteLock OK, WriteLock → ReadLock OK, ReadLock → WriteLock NO
class Lock
{
// 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
const int EMPTY_FLAG = 0x00000000;
// 0111 1111 1111 1111 0000 0000 0000 0000
const int WRITE_MASK = 0x7FFF0000;
// 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 1111 1111 1111
const int READ_MASK = 0x0000FFFF;
const int MAX_SPIN_COUNT = 5000;
int _writeCount = 0;
// 32bits = [Unused(1)] [WriteThreadId(15)] [ReadCount(16)]
int _flag = EMPTY_FLAG;
public void WriteLock()
{
// check that same thread has already WriteLock
int lockThreadId = (_flag & WRITE_MASK) >> 16;
if(Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId == lockThreadId)
{
_writeCount++;
return;
}
// noone has WriteLock or ReadLock, then get ownership by compitition
int desired = (Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId << 16) & WRITE_MASK;
while (true)
{
for(int i=0; i<MAX_SPIN_COUNT; i++)
{
if (Interlocked.CompareExchange(ref _flag, desired, EMPTY_FLAG) == EMPTY_FLAG)
{
_writeCount = 1;
return;
}
}
Thread.Yield();
}
}
public void WriteUnlock()
{
int lockCount = --_writeCount;
if(lockCount == 0)
Interlocked.Exchange(ref _flag, EMPTY_FLAG);
}
public void ReadLock()
{
// check that same thread has already WriteLock
int lockThreadId = (_flag & WRITE_MASK) >> 16;
if (Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId == lockThreadId)
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref _flag);
return;
}
// noone has WriteLock, then add 1 to ReadCount
while (true)
{
for(int i=0; i<MAX_SPIN_COUNT; i++)
{
int expected = (_flag & READ_MASK);
if (Interlocked.CompareExchange(ref _flag, expected + 1, expected) == expected)
return;
}
Thread.Yield();
}
}
public void ReadUnlock()
{
Interlocked.Decrement(ref _flag);
}
}- ServerCore\Program.cs
class Program
{
static volatile int count = 0;
static Lock _lock = new Lock();
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Task t1 = new Task(delegate ()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
_lock.WriteLock();
count++;
_lock.WriteUnlock();
}
});
Task t2 = new Task(delegate ()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++)
{
_lock.WriteLock();
count--;
_lock.WriteUnlock();
}
});
t1.Start();
t2.Start();
Task.WaitAll(t1, t2);
Console.WriteLine(count);
}
}
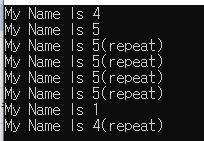
Thread Local Storage
- Global variables that are uniquely accessible
Test
- ServerCore\Program.cs
class Program
{
static ThreadLocal<string> ThreadName = new ThreadLocal<string>(() => { return $"My Name Is {Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"; });
static void WhoAmI()
{
bool repeat = ThreadName.IsValueCreated;
if(repeat)
Console.WriteLine(ThreadName.Value + "(repeat)");
else
Console.WriteLine(ThreadName.Value);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ThreadPool.SetMinThreads(1, 1);
ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(3, 3);
Parallel.Invoke(WhoAmI, WhoAmI, WhoAmI, WhoAmI, WhoAmI, WhoAmI, WhoAmI, WhoAmI);
ThreadName.Dispose();
}
}