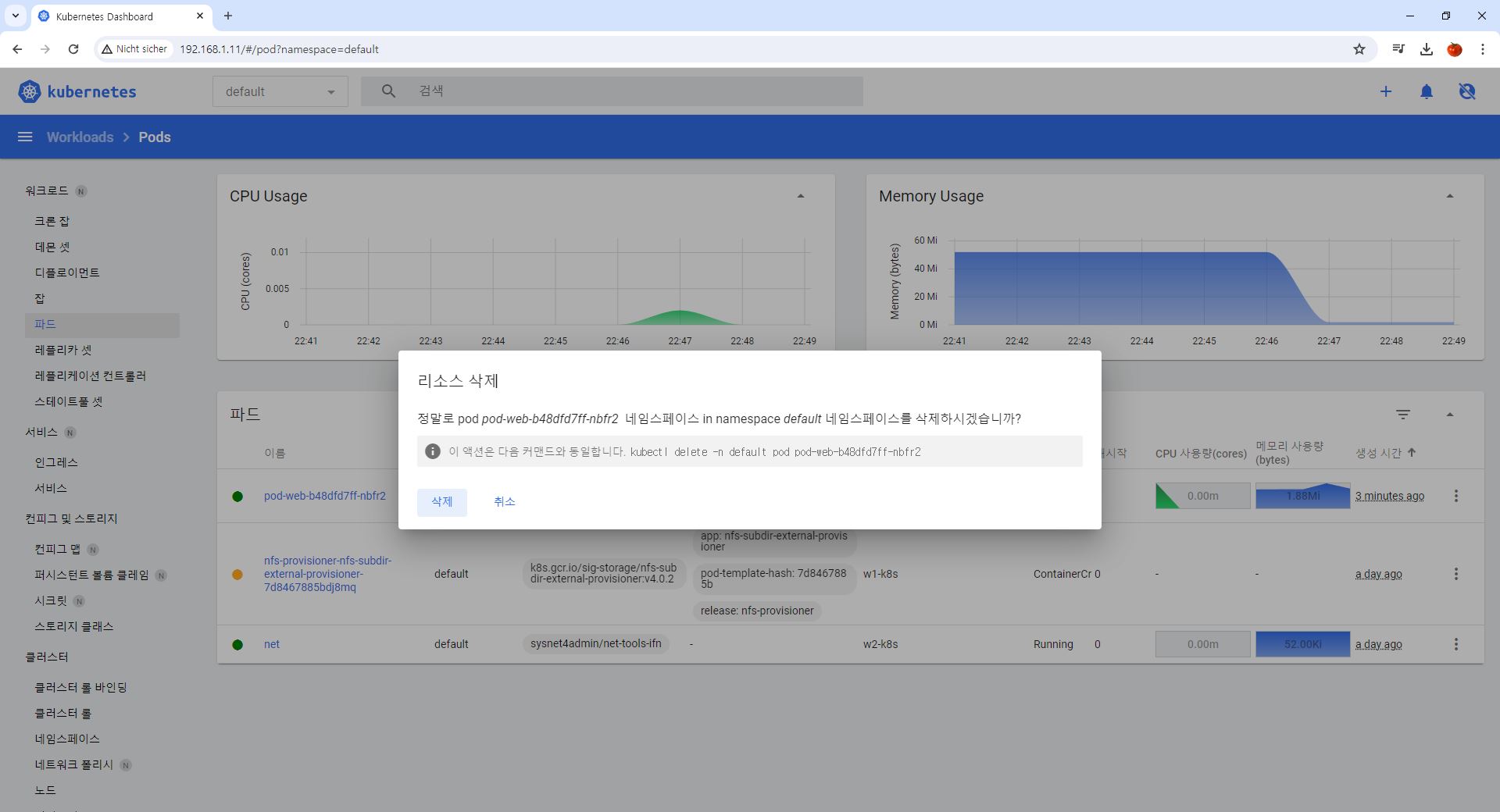
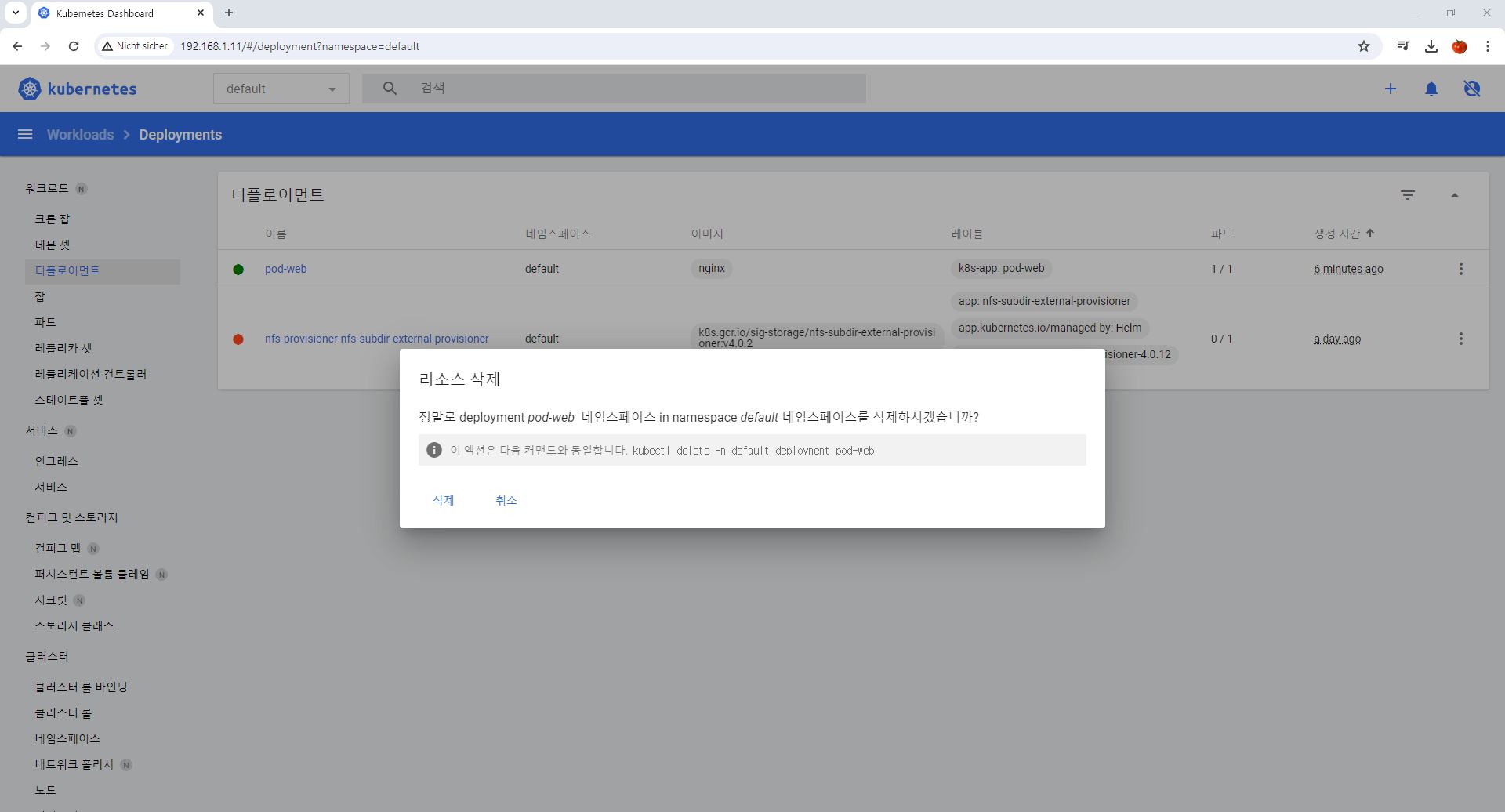
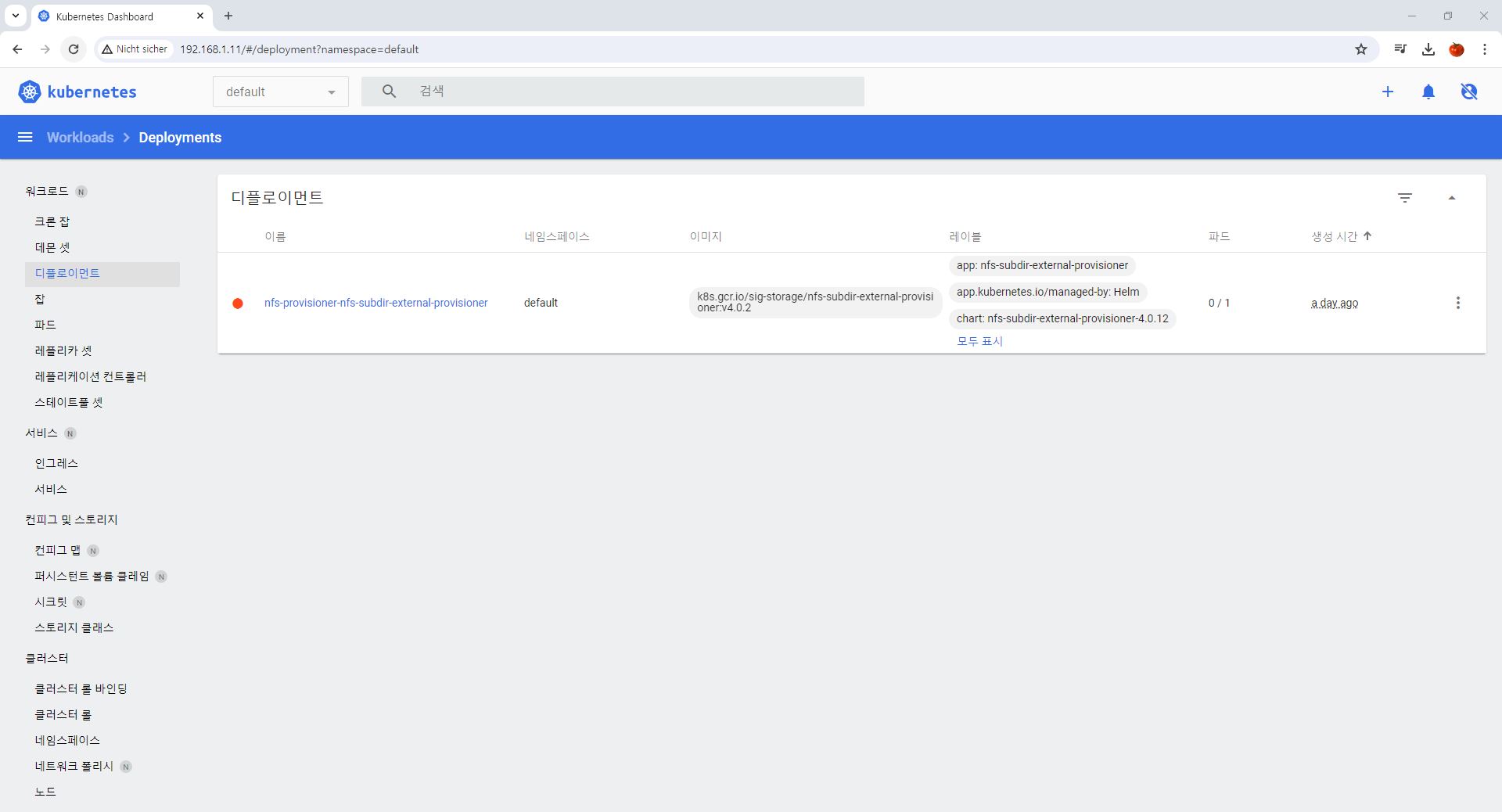
Code Review
- Download Kubernetes Learning Kit
- Unzip on your
HashiCorpfolder. - Use
~\HashiCorp\_Lecture_k8s_learning.kit-main\ch1\1.5\k8s-min-5GiB-wo-add-nodesand~\HashiCorp\_Lecture_k8s_learning.kit-main\ch1\1.6to see all settings files.
Vagrantfile
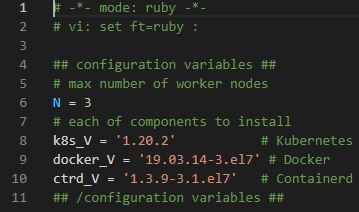
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :- Vagrantfile is made by Ruby.
## configuration variables ##
# max number of worker nodes
N = 3 - Worker Nodes are three.
# each of components to install
k8s_V = '1.20.2' # Kubernetes
docker_V = '19.03.14-3.el7' # Docker
ctrd_V = '1.3.9-3.1.el7' # Containerd
## /configuration variables ##- Versions for Kubernetes, Docker and ContainerD
Master Node
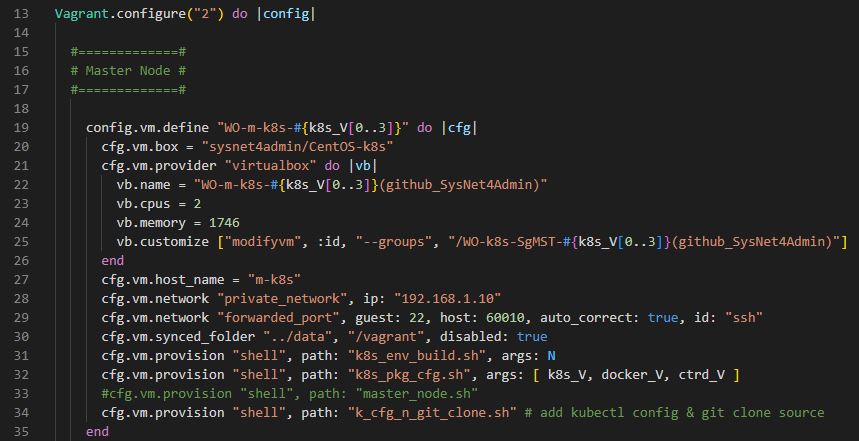
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|- Current Vagrantfile Api Version is 2.
do-endstatement will run line 19~35.
config.vm.define "WO-m-k8s-#{k8s_V[0..3]}" do |cfg|k8s_Vis a variable for kubernetes version and0..3means the index to read.- For example,
k8s_Vis 1.20.0 andk8s_V[0..3]will get1.20.
cfg.vm.box = "sysnet4admin/CentOS-k8s"- VM image is CentOS private image.
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "WO-m-k8s-#{k8s_V[0..3]}(github_SysNet4Admin)"
vb.cpus = 2
vb.memory = 1746
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--groups", "/WO-k8s-SgMST-#{k8s_V[0..3]}(github_SysNet4Admin)"]
end- Our virtual machine software is virtual box.
- Master Node has 2 cpus.
- Master Node has 1746 MB.
- We made a group to set on/off easy.
- If you want to see your customized groups, enter
kubectl get cm kubelet-config-1.22 -n kube-system -o yaml | grep cgroup.
cfg.vm.host_name = "m-k8s"
cfg.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.1.10"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: 60010, auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true - Host name is
m-k8s. private_networkmakes connection network with your pc.forwarded_portset local host to60010.- When there is something wrong in our port, it will fix automatically.
- Port ID is
ssh. synced_folderwill sync your pc folders with virtual machine folders, ifdisabledis false.
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "k8s_env_build.sh", args: N
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "k8s_pkg_cfg.sh", args: [ k8s_V, docker_V, ctrd_V ]
#cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "master_node.sh"
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "k_cfg_n_git_clone.sh" # add kubectl config & git clone source- Run
xxx.shfile in shell with arguments. - We seperated cluster part for practice.
Worker Node
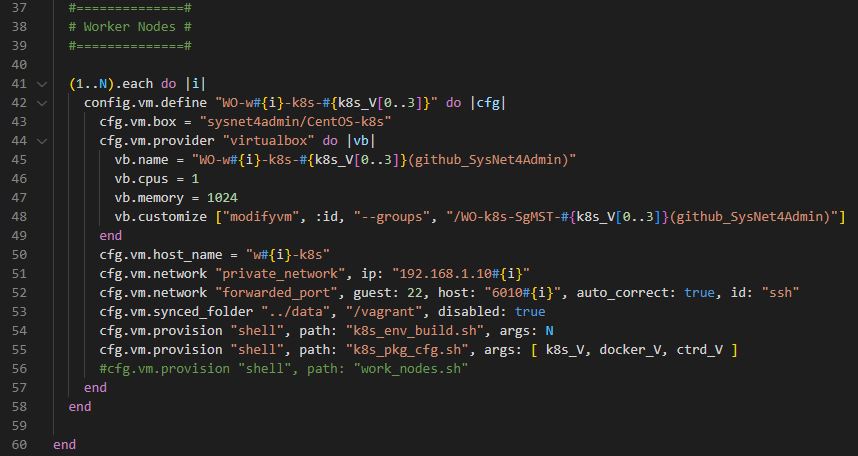
(1..N).each do |i|- Loop statement 1 to 3.
config.vm.define "WO-w#{i}-k8s-#{k8s_V[0..3]}" do |cfg|
cfg.vm.box = "sysnet4admin/CentOS-k8s"
cfg.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.name = "WO-w#{i}-k8s-#{k8s_V[0..3]}(github_SysNet4Admin)"
vb.cpus = 1
vb.memory = 1024
vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--groups", "/WO-k8s-SgMST-#{k8s_V[0..3]}(github_SysNet4Admin)"]
end
cfg.vm.host_name = "w#{i}-k8s"
cfg.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.1.10#{i}"
cfg.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 22, host: "6010#{i}", auto_correct: true, id: "ssh"
cfg.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant", disabled: true
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "k8s_env_build.sh", args: N
cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "k8s_pkg_cfg.sh", args: [ k8s_V, docker_V, ctrd_V ]
#cfg.vm.provision "shell", path: "work_nodes.sh"- Worker Node has 1 cpu.
k8s_env_build.sh
- This file will set kubernetes environment.
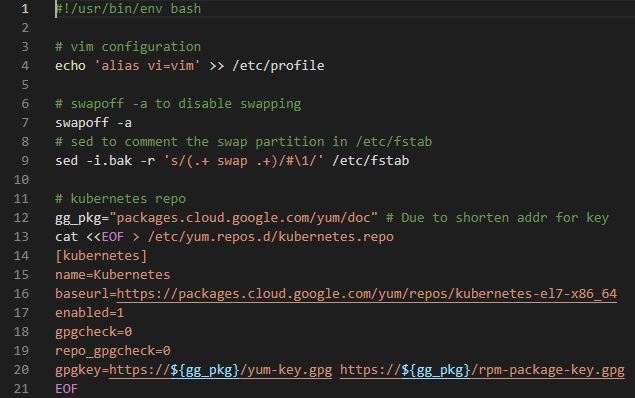
#!/usr/bin/env bash- This script will use bash shell script.
# vim configuration
echo 'alias vi=vim' >> /etc/profilevicommand is same withvim
# swapoff -a to disable swapping
swapoff -a- Swap should be off to install kubernetes.
# sed to comment the swap partition in /etc/fstab
sed -i.bak -r 's/(.+ swap .+)/#\1/' /etc/fstab- Swap is always off when you reboot the machine.
# kubernetes repo
gg_pkg="packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc" # Due to shorten addr for key
cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
gpgkey=https://${gg_pkg}/yum-key.gpg https://${gg_pkg}/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOFgpgcheckis off.repo_gpgcheckis off.- If you need security, you can set those to 1.
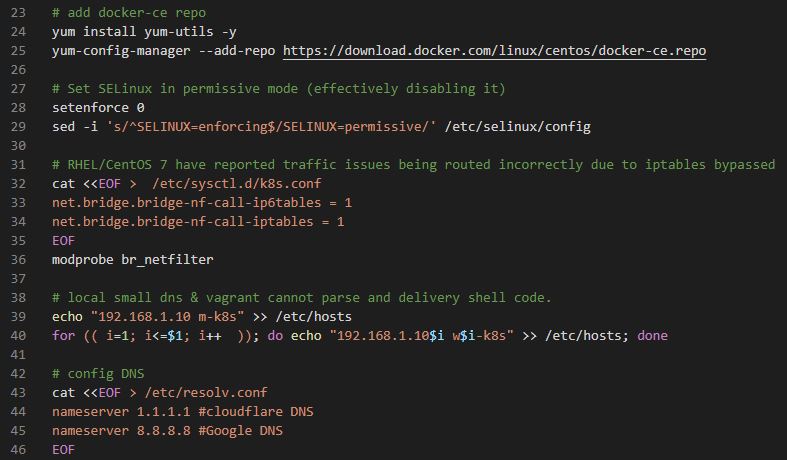
# add docker-ce repo
yum install yum-utils -y
yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo- Use
yumto download docker community repository.
# Set SELinux in permissive mode (effectively disabling it)
setenforce 0
sed -i 's/^SELINUX=enforcing$/SELINUX=permissive/' /etc/selinux/config- SELinux if off.
- If you need security, you can set this to on.
# RHEL/CentOS 7 have reported traffic issues being routed incorrectly due to iptables bypassed
cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
EOF
modprobe br_netfilterbr_netfilteris bridge netfileter.br_netfilterwill connect your machines to one network.
# local small dns & vagrant cannot parse and delivery shell code.
echo "192.168.1.10 m-k8s" >> /etc/hosts
for (( i=1; i<=$1; i++ )); do echo "192.168.1.10$i w$i-k8s" >> /etc/hosts; done- Deploy node name automatically, for example, m-k8s or w1-k8s.
$1isk8s_v.
# config DNS
cat <<EOF > /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 1.1.1.1 #cloudflare DNS
nameserver 8.8.8.8 #Google DNS
EOF- DNS settings.
k8s_env_build.sh
- This script is for installing kubernetes.
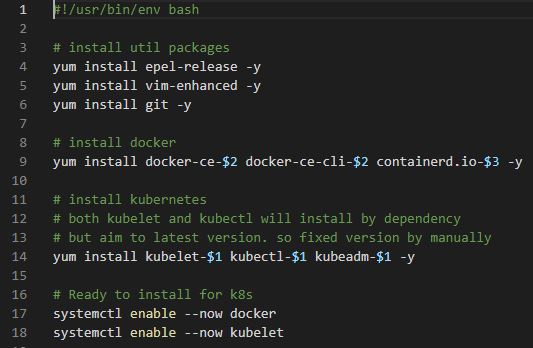
# install util packages
yum install epel-release -y
yum install vim-enhanced -y
yum install git -yepel-releasemakes extended package for CentOs from Red Hat, examples, extended storage.vim-enhancedwill install vim.- You don’t need to intall
gitbut for practice.
# install docker
yum install docker-ce-$2 docker-ce-cli-$2 containerd.io-$3 -y$2isdocker_Vand$3isctrd_V.
# install kubernetes
# both kubelet and kubectl will install by dependency
# but aim to latest version. so fixed version by manually
yum install kubelet-$1 kubectl-$1 kubeadm-$1 -y $1isk8s_V.
# Ready to install for k8s
systemctl enable --now docker
systemctl enable --now kubelet- Ready to system.
k_cfg_n_git_clone.sh
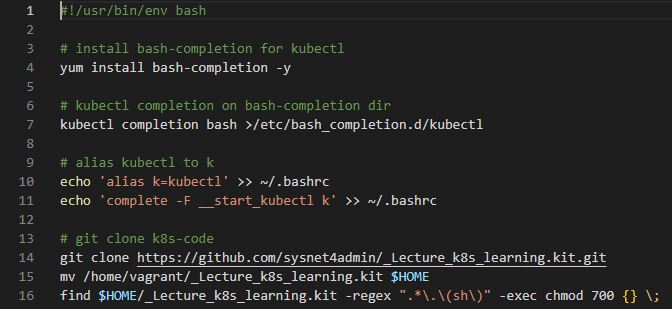
# install bash-completion for kubectl
yum install bash-completion -y
# kubectl completion on bash-completion dir
kubectl completion bash >/etc/bash_completion.d/kubectlbash-completionallow us to use auto kubectl commands.
# alias kubectl to k
echo 'alias k=kubectl' >> ~/.bashrc
echo 'complete -F __start_kubectl k' >> ~/.bashrcaliasmakes short cut of commands.complete -F __start_kubectl kallowkto usebash-completion
# git clone k8s-code
git clone https://github.com/sysnet4admin/_Lecture_k8s_learning.kit.git
mv /home/vagrant/_Lecture_k8s_learning.kit $HOME
find $HOME/_Lecture_k8s_learning.kit -regex ".*\.\(sh\)" -exec chmod 700 {} \;- Download practice codes from git.
WO_master_node.sh
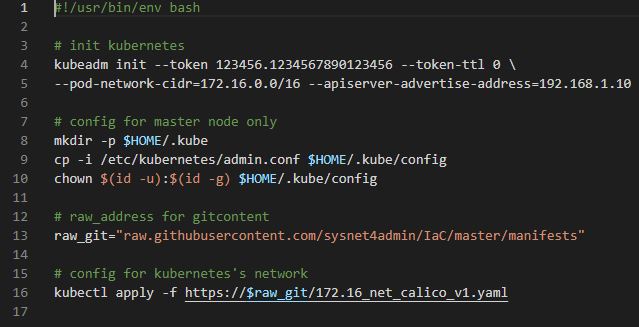
# init kubernetes
kubeadm init --token 123456.1234567890123456 --token-ttl 0 \
--pod-network-cidr=172.16.0.0/16 --apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.1.10- We need
tokento join Master Node and Worker Node. token-ttlexpires the token in 24 hours.pod-network-cidrassigns pod’s network.apiserver-advertise-addressis fixed with Master Node IP address to avoid join problems.
# config for master node only
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config- To skip verification when we use kubectl.
# raw_address for gitcontent
raw_git="raw.githubusercontent.com/sysnet4admin/IaC/master/manifests"
# config for kubernetes's network
kubectl apply -f https://$raw_git/172.16_net_calico_v1.yaml- Apply Calico for kubernetes network.
WO_work_nodes.sh
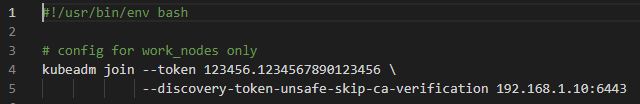
# config for work_nodes only
kubeadm join --token 123456.1234567890123456 \
--discovery-token-unsafe-skip-ca-verification 192.168.1.10:6443- Join with Master Node.
IDE
Deploy Kubernetes VM
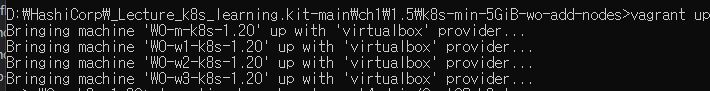
- Open your
~HashiCorp\_Lecture_k8s_learning.kit-main\ch1\1.5\k8s-min-5GiB-wo-add-nodesfolder in command and usevagrant up.
- Open your SuperPutty and click [File]-[Import Sessions]-[From File] to import
~HashiCorp\_Lecture_k8s_learning.kit-main\ch1\1.5\Sessions(k8s_learning).XML.
Install Kubernetes with kubeadm
- Use
~/_Lecture_k8s_learning.kit/ch1/1.6/WO_master_node.shto install kubernetes in master node. - Open to worker node #1, #2 and #3 and use script of
~/_Lecture_k8s_learning.kit/ch1/1.6/WO_worker_node.sh.
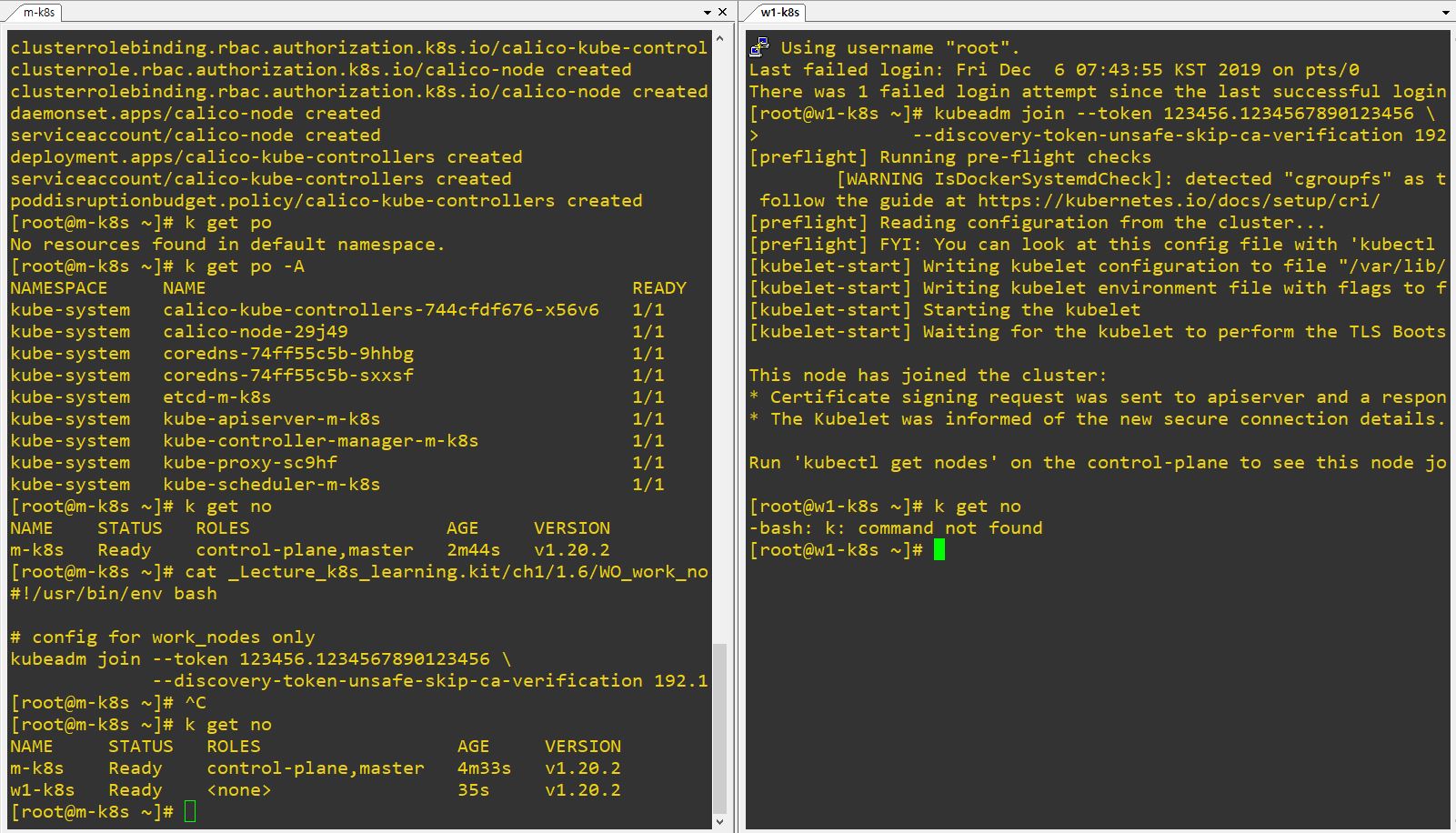
- Open your
~HashiCorp\_Lecture_k8s_learning.kit-main\ch1\1.5\k8s-min-5GiB-wo-add-nodes>folder and usevagrant destroy -fto delete all VM. - We need to delete all VM to upgrade our VM.
IDE 2
- Update Kubernetes, Docker and ContainerD.
- Upgrade memory in master and worker nodes.
Deploy Kubernetes VM
- Open your
~HashiCorp\_Lecture_k8s_learning.kit-main\ch2\2.1\k8s-UpTo-10GiBfolder in command and usevagrant up.
Definitions
Object
- Container
-
Container has one software or system.
- Pod
- Pod has one or union of containers.
- Pod has a volume to save eternal data.
apiVersion: v1 # pod version
kind: Pod # Object type
metadata: # information of pod
labels:
run: po-nginx
name: po-nginx
spec: # spec of pod
containers: # information of container
- image: nginx
name: nginx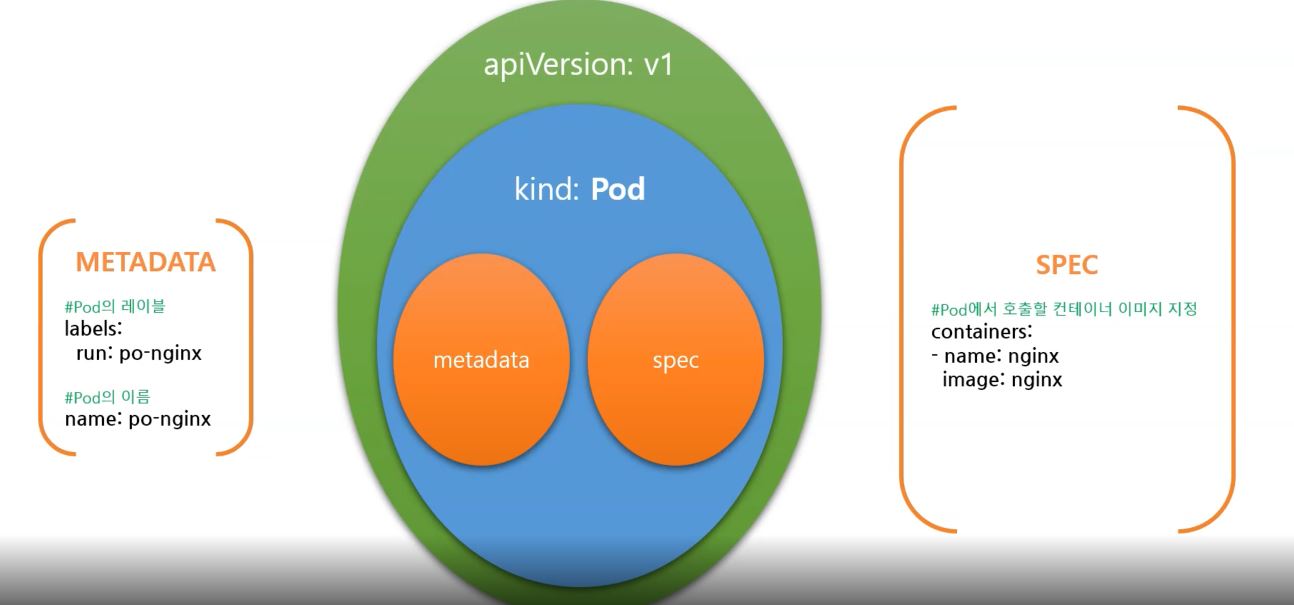
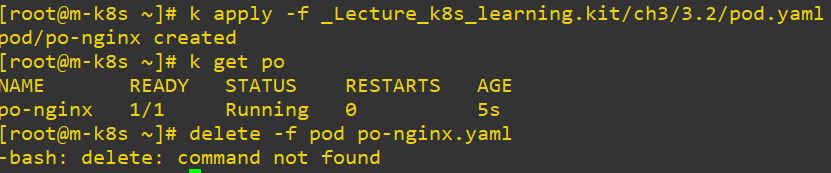
- Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1 # deployment version
kind: Deployment # object type
metadata: # information of deployment
labels:
app: deploy-nginx
name: deploy-nginx
spec: # spec of deployment
replicas: 3 # replica set
selector: # choose templete
matchLabels:
app: po-nginx
template: # templete to make pod
metadata:
labels:
app: po-nginx
spec:
containers: # information of container
- name: nginx
image: nginx # container image
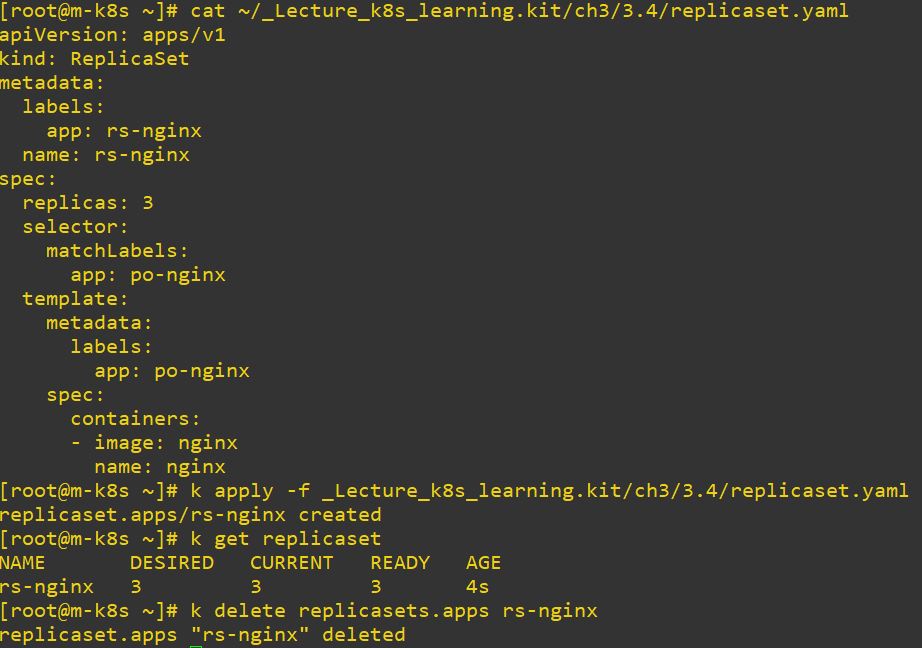
- ReplicaSet
- Deployment needs ReplicaSet to manage count of pods
apiVersion: apps/v1 # replicaset version
kind: ReplicaSet # object type
metadata: # information of replicaset
labels:
app: rs-nginx
name: rs-nginx
spec: # spec of replicaset
replicas: 3
selector: # choose templete
matchLabels:
app: po-nginx
template: # templete to make pod
metadata:
labels:
app: po-nginx
spec:
containers: # information of container
- image: nginx # container image
name: nginx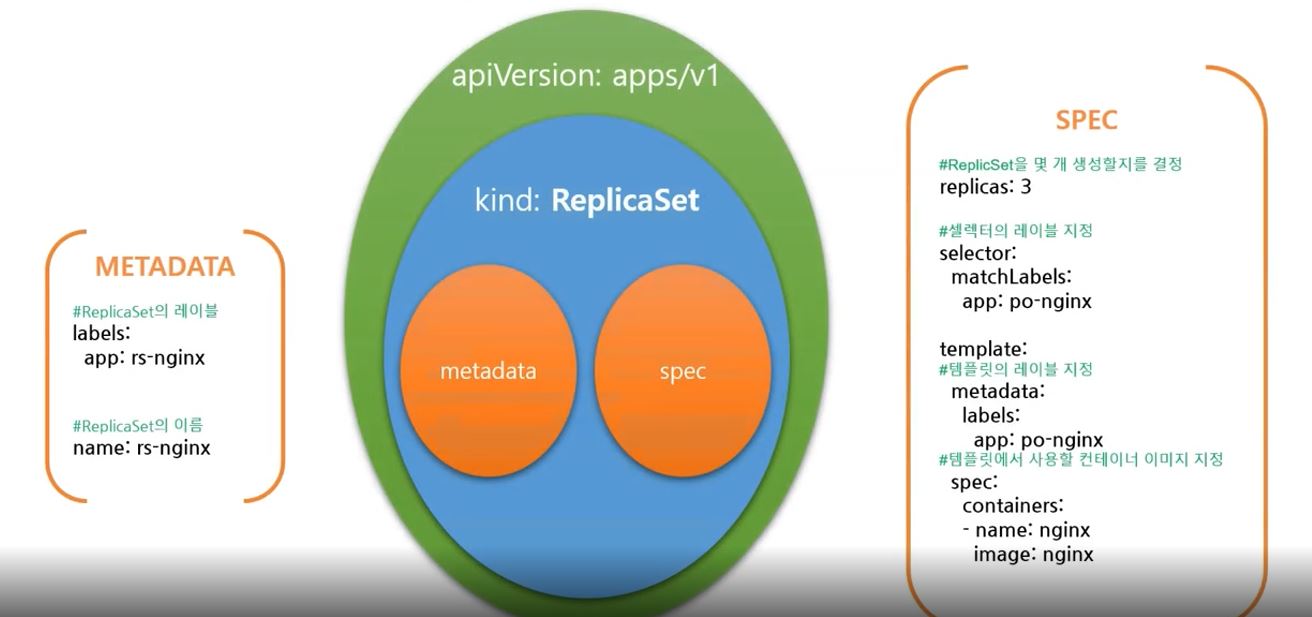
- Honestly, the code is really similler with deployment, but we need ReplicaSet for rolling.
- For example, when you upgrade a pod, Deployment will create ReplicaSet, and ReplilcaSet will duplicate itself.
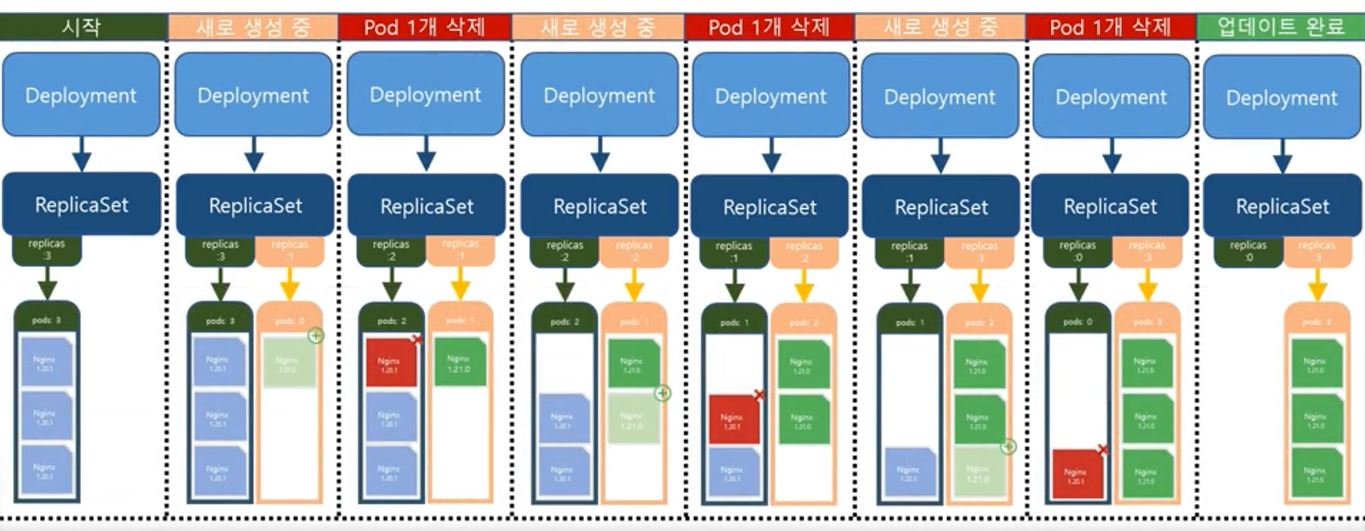
- Job
- You can use job to decrese using memory.
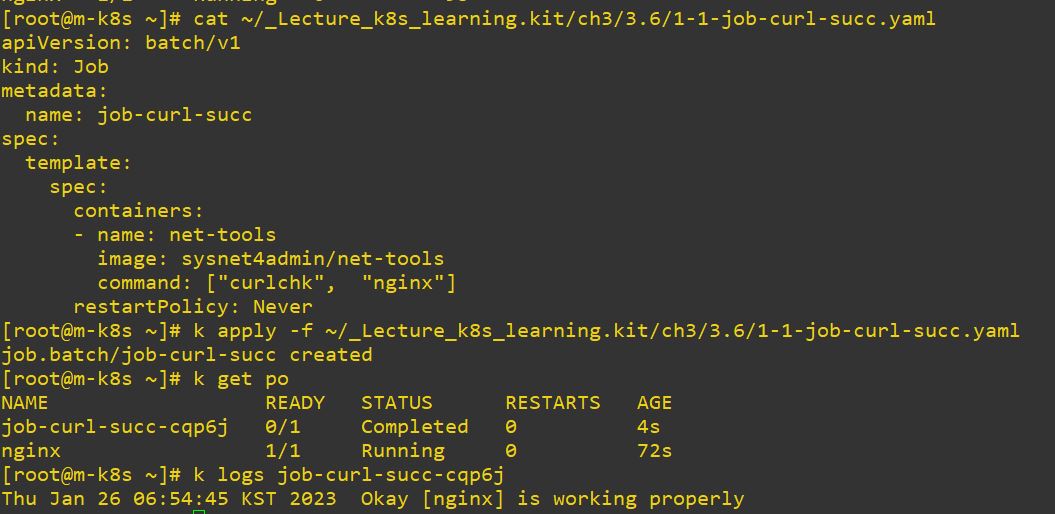
apiVersion: batch/v1 # job version
kind: Job # object type
metadata: # information of job
name: job-curl-succ
spec: # spec of job
template: # templete to make job
spec:
containers: # information of container
- name: net-tools
image: sysnet4admin/net-tools # container image
command: ["curlchk", "nginx"]
restartPolicy: Never # restart optionrestartPolicydefault value in other object isAlwaysand it will restart the object forever.restartPolicyshould be in job and this value should beOnFailureorNever.
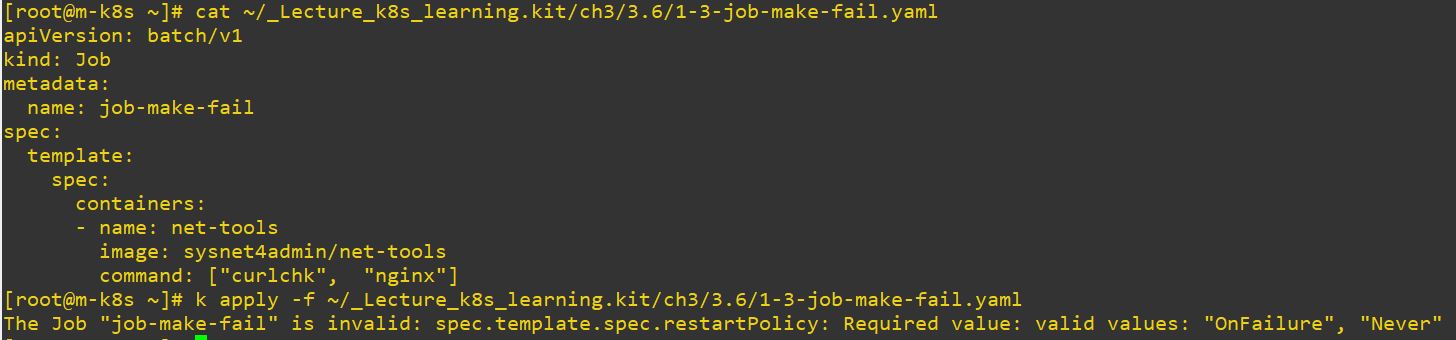
apiVersion: batch/v1 # job version
kind: Job # object type
metadata: # information of job
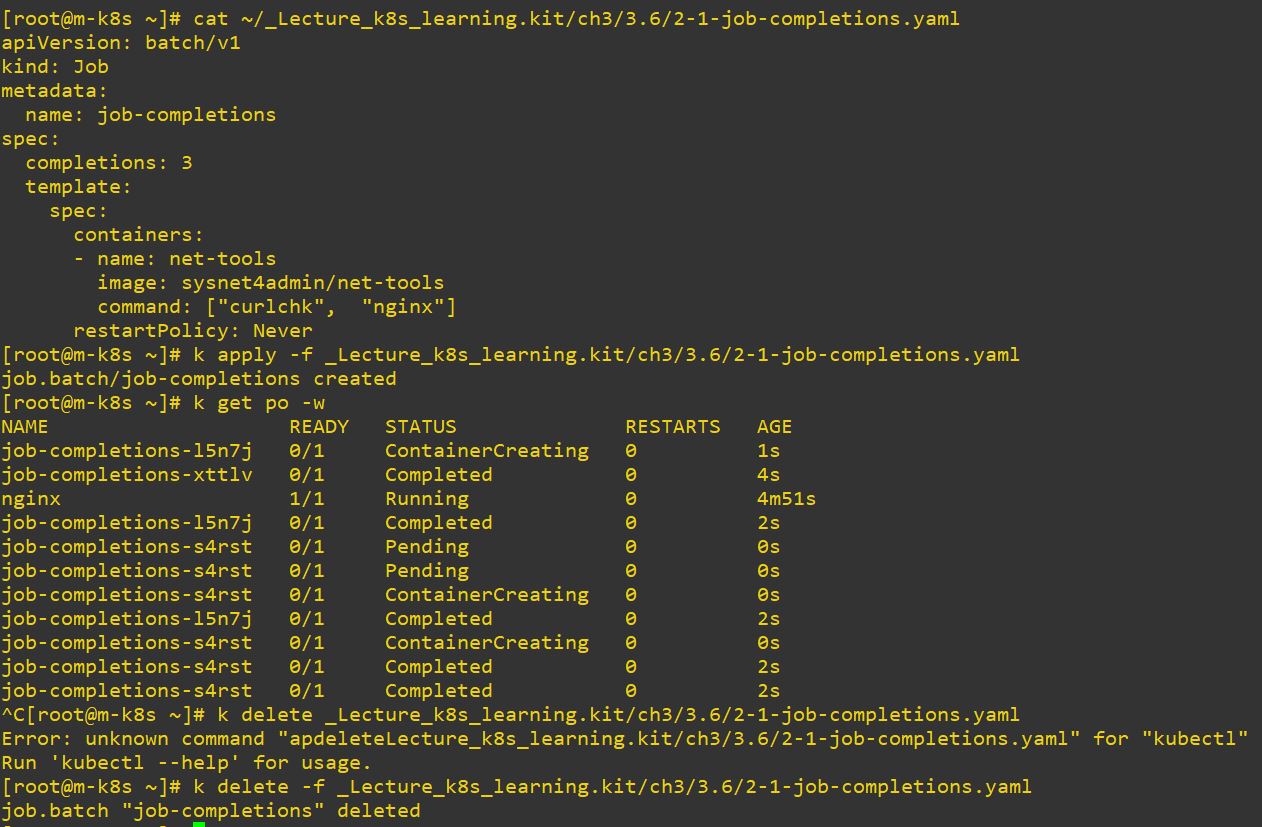
name: job-completions
spec: # spec of job
completions: 3 # run sequentially 3 times
template: # templete to make job
spec:
containers:
- name: net-tools
image: sysnet4admin/net-tools # container image
command: ["curlchk", "nginx"]
restartPolicy: Never # restart option- Use
completionsto run to sequentially.
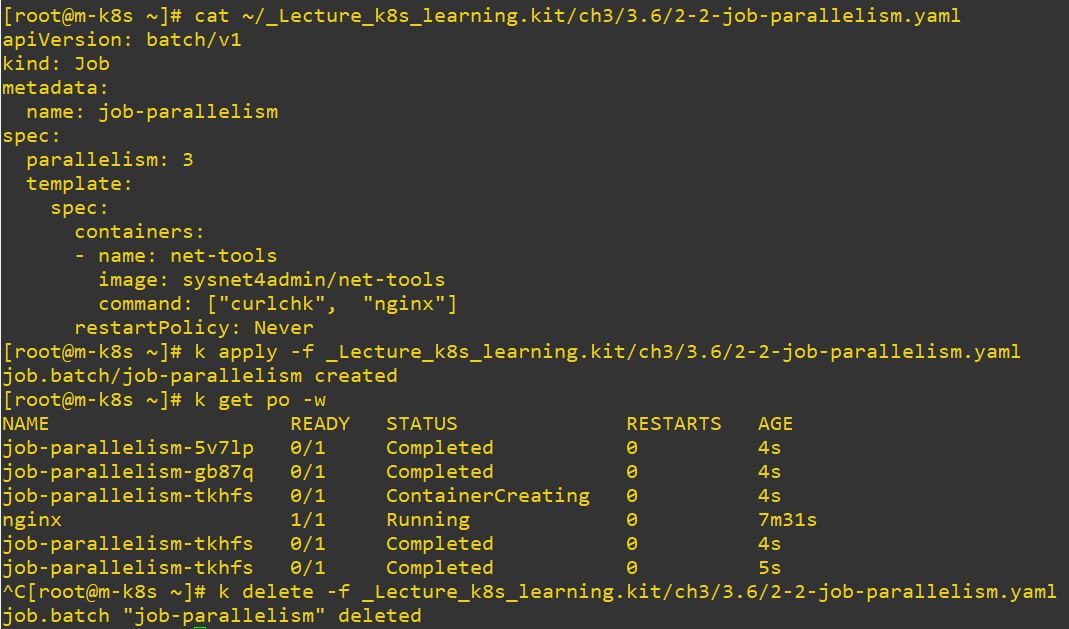
apiVersion: batch/v1 # job version
kind: Job # object type
metadata: # information of job
name: job-parallelism
spec: # spec of job
parallelism: 3 # run parallely 3 times
template: # templete to make job
spec:
containers:
- name: net-tools
image: sysnet4admin/net-tools # container image
command: ["curlchk", "nginx"]
restartPolicy: Never # restart option- Use
parallelismto run to parallely.
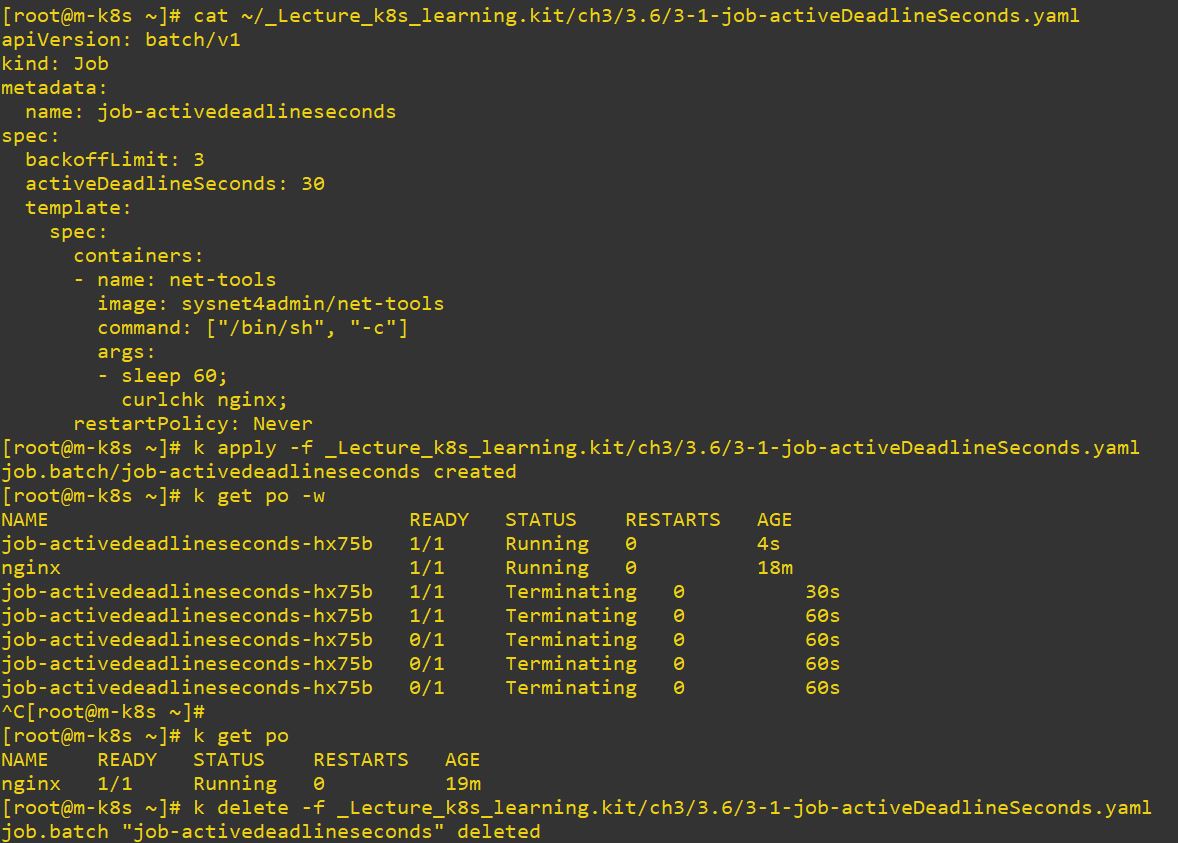
apiVersion: batch/v1 # job version
kind: Job # object type
metadata: # information of job
name: job-activedeadlineseconds
spec: # spec of job
backoffLimit: 3
activeDeadlineSeconds: 30 # dead time after run command
template: # templete to make job
spec:
containers:
- name: net-tools
image: sysnet4admin/net-tools # container image
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- sleep 60;
curlchk nginx;
restartPolicy: Never # restart option- Use
activeDeadlineSecondsto delete on specific time after your command
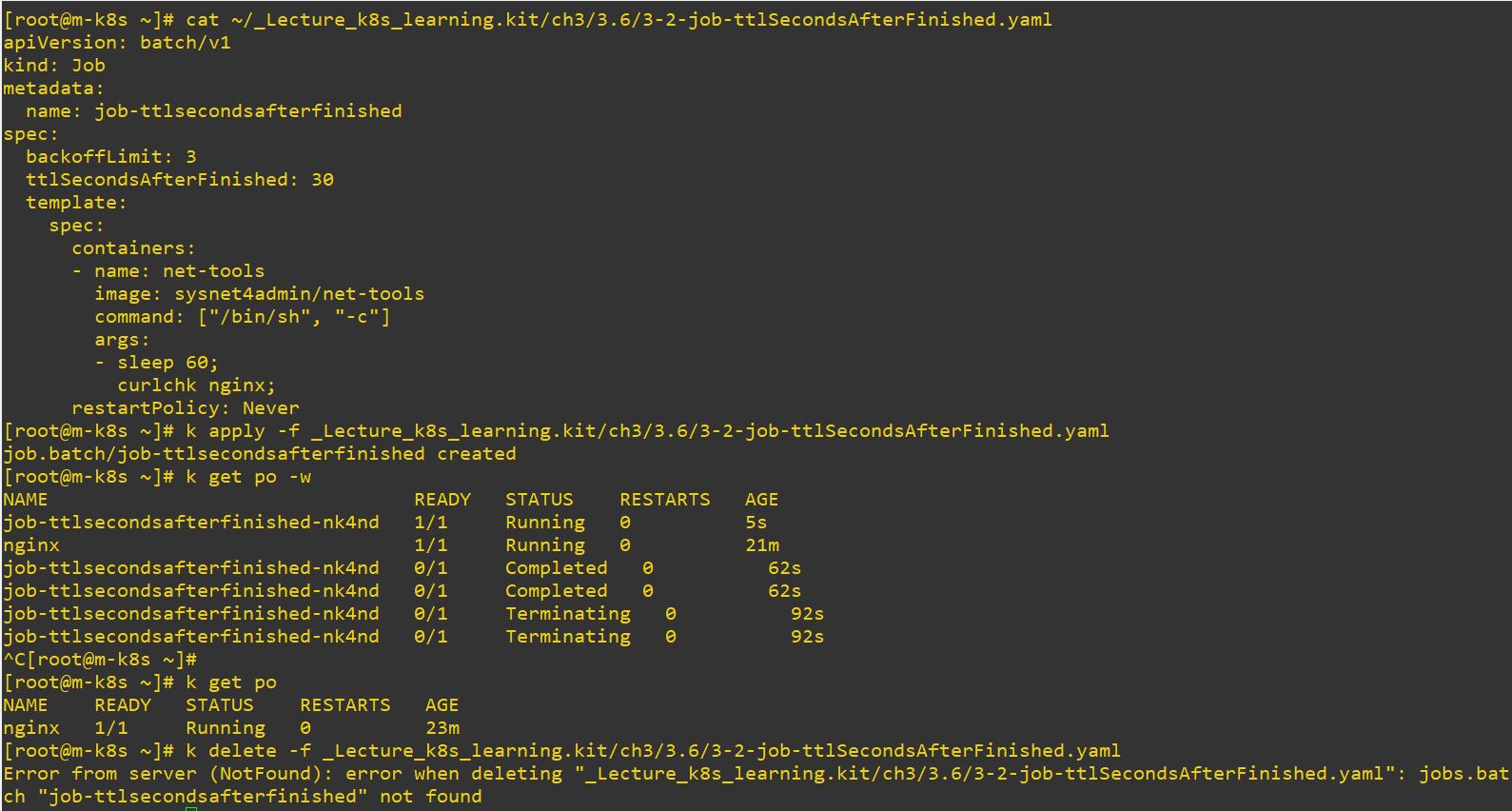
apiVersion: batch/v1 # job version
kind: Job # object type
metadata: # information of job
name: job-ttlsecondsafterfinished
spec: # spec of job
backoffLimit: 3
ttlSecondsAfterFinished: 30 # dead time after completed
template: # templete to make job
spec:
containers:
- name: net-tools
image: sysnet4admin/net-tools # container image
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- sleep 60;
curlchk nginx;
restartPolicy: Never # restart option- Use
ttlSecondsAfterFinishedto delete on specific time after completed
- CronJob
- Use
CronJobto run Job with schedule.
apiVersion: batch/v1 # cron job version
kind: CronJob # object type
metadata: # information of cron job
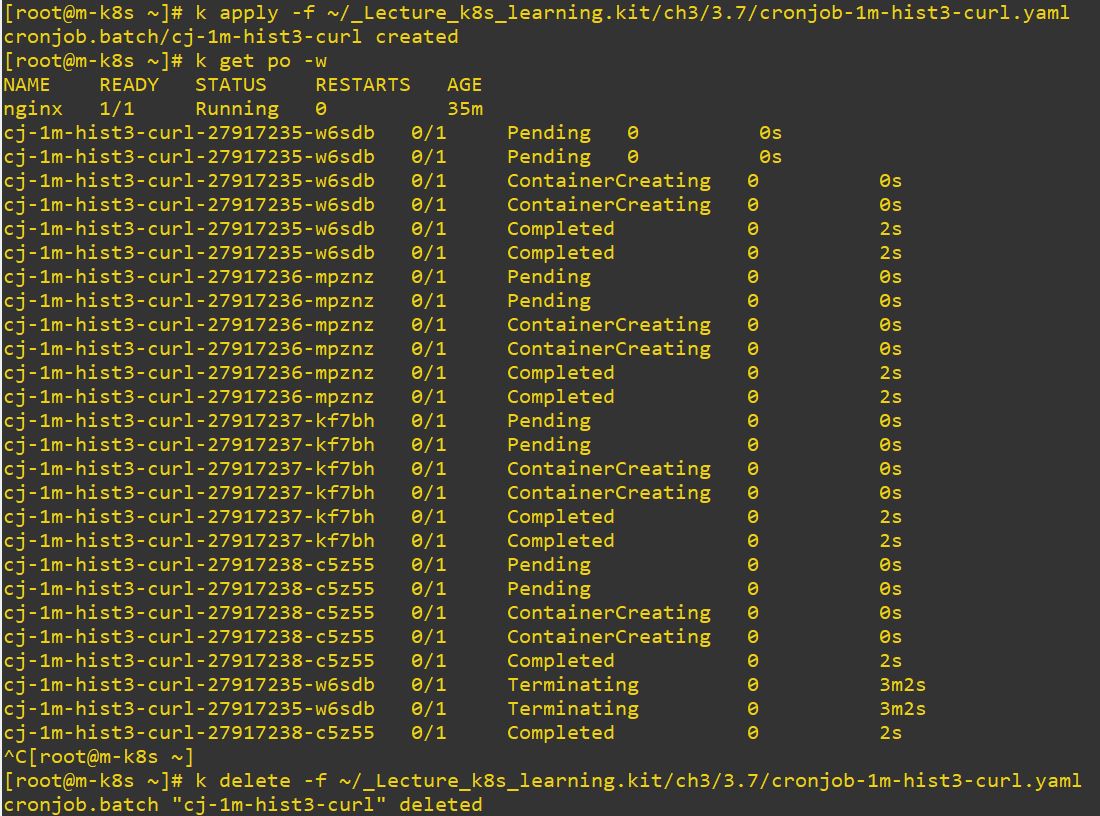
name: cj-1m-hist3-curl
spec: # spec of cron job
schedule: "*/1 * * * *" # cron rule
jobTemplate: # Template for job
spec: # same as before
template: # templete to make job
spec:
containers:
- name: net-tools
image: sysnet4admin/net-tools # container image
command: ["curlchk", "nginx"]
restartPolicy: Never # restart option- cron rule :
*/#repeats the job # periods, and just#repeats the job at #.
apiVersion: batch/v1 # cron job version
kind: CronJob # object type
metadata: # information of cron job
name: cj-1m-hist10-curl
spec: # spec of cron job
schedule: "*/1 * * * *" # cron rule
successfulJobsHistoryLimit: 10
jobTemplate: # Template for job
spec: # same as before
template: # templete to make job
spec:
containers:
- name: net-tools
image: sysnet4admin/net-tools # container image
command: ["curlchk", "nginx"]
restartPolicy: Never # restart optionsuccessfulJobsHistoryLimithold the job until specific number. After the limited number, it will delete first job automatically. Default value is 3.
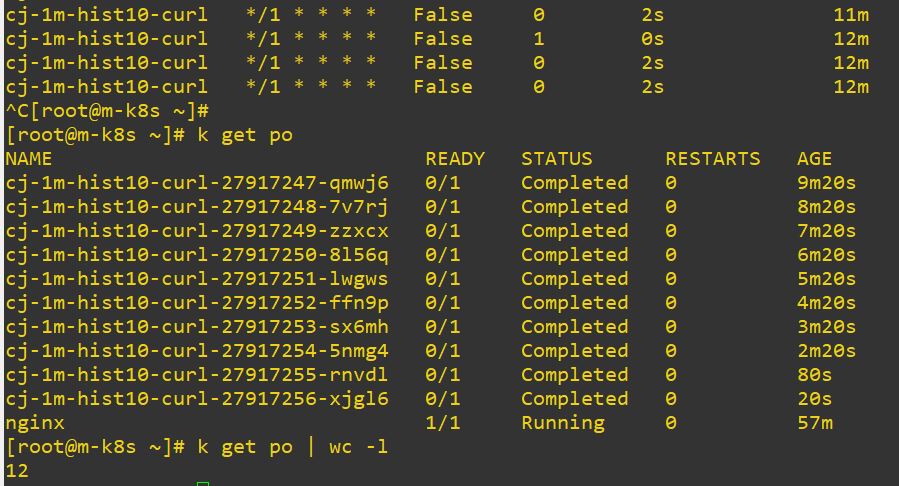
-
Use
k get po | wc -lto get total pods count. - DaemonSet
- DaemonSet makes one pod on each nodes.
apiVersion: apps/v1 # daemon set version
kind: DaemonSet # object type
metadata: # information of daemon set
labels:
app: ds-nginx
name: ds-nginx
spec: # spec of daemon set
selector:
matchLabels:
app: po-nginx
template: # Template for job
metadata:
labels:
app: po-nginx
spec: # same as before
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx # container image- DaemonSet is quit simillar with deployment, but it has no replicas, because one pod can include only one DaemonSet.
- Use
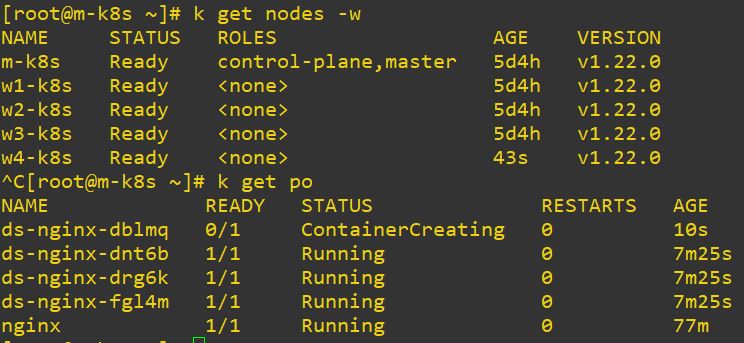
vagrant up w4-k8s-1.22to make fourth worker node.
- Use
vagrant destroy -f w4-k8s-1.22to destroy fourth worker node.
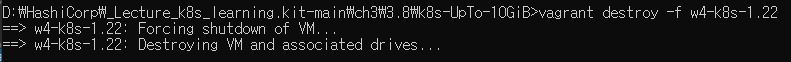
-
When you add node, DamonSet will be created automatically from code.
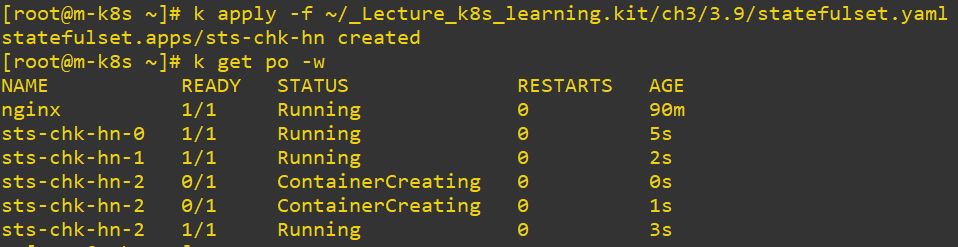
- StatefulSet
- StatefulSet saves state of pod.
apiVersion: apps/v1 # StatefulSet version
kind: StatefulSet # object type
metadata: # information of StatefulSet
name: sts-chk-hn
spec: # spec of StatefulSet
replicas: 3
serviceName: sts-svc-domain #statefulset need it
selector:
matchLabels:
app: sts
template: # Template for StatefulSet
metadata:
labels:
app: sts
spec:
containers:
- name: chk-hn
image: sysnet4admin/chk-hn # container image- You should use
serviceName, because StatefulSet has specific name, not hash value.
- Application
- Pod(s) containing container(s) and volume for specific work is(are) an application.
- For example, NGINX, MySQL, etc.
- Even when you add something on the application, that is also an application.
Commands
- get
-
Read object
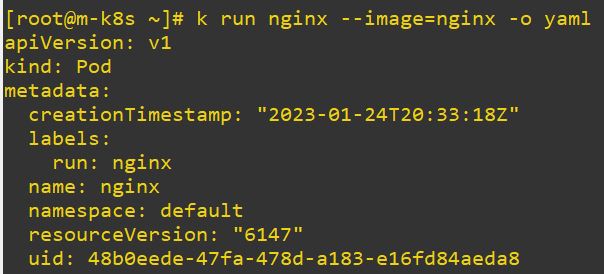
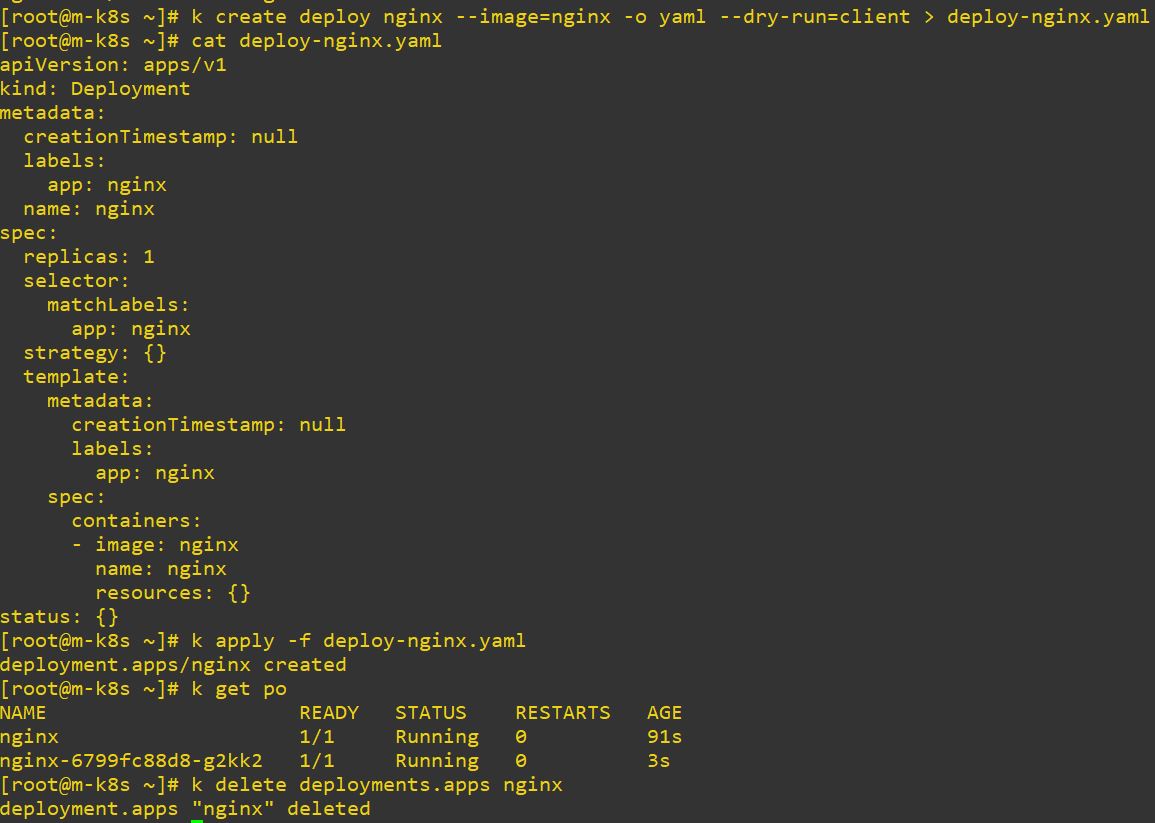
- run, create, apply
- Create object
- delete
-
Delet object
- exec
- Access to container in pod.
- scale
- Add or sub count of pods.
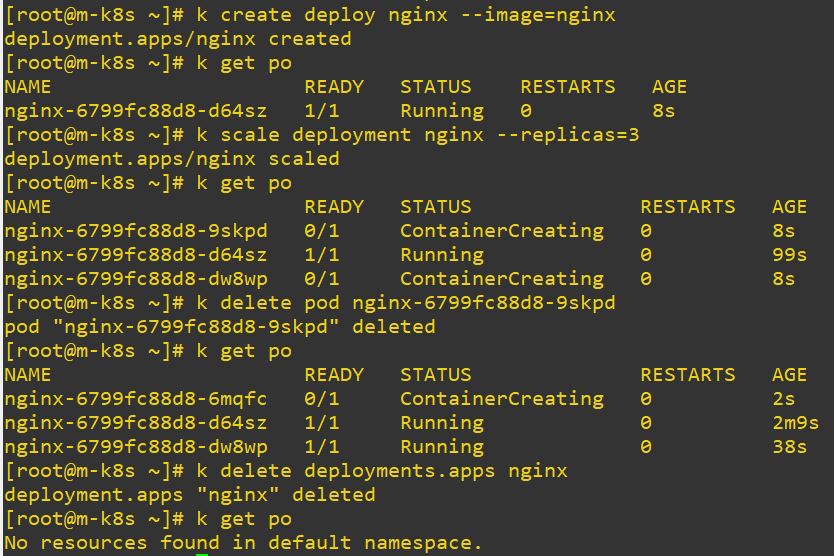
- edit
- Change deployed object.
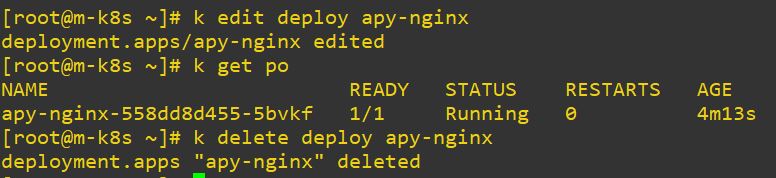
- events
- Check events with namespace.
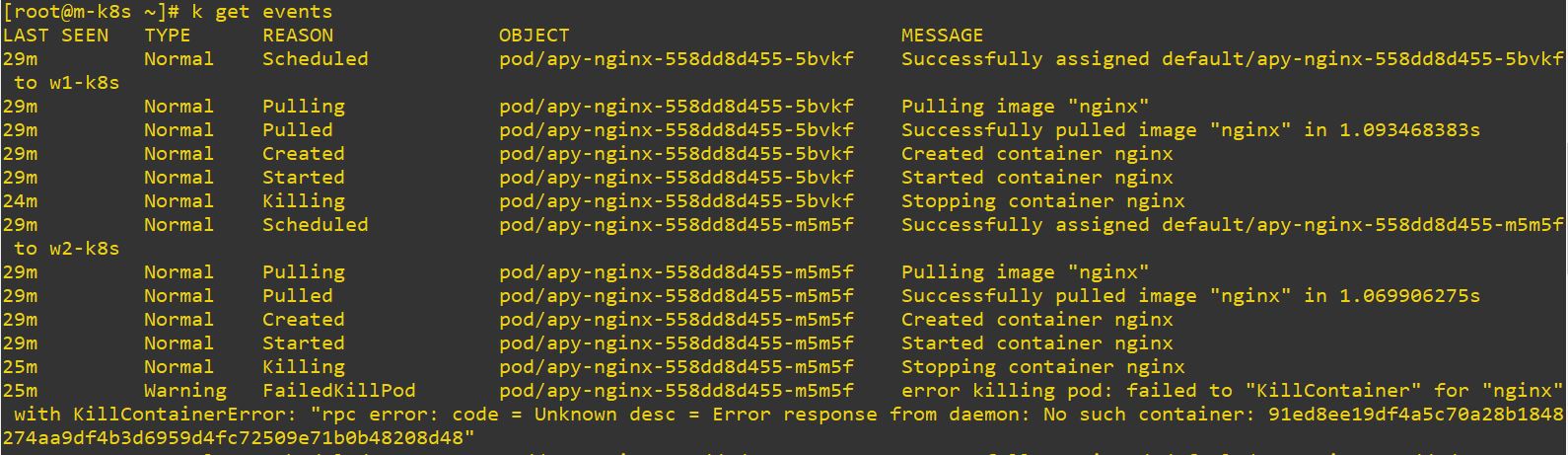
- describe
- Check status of object.
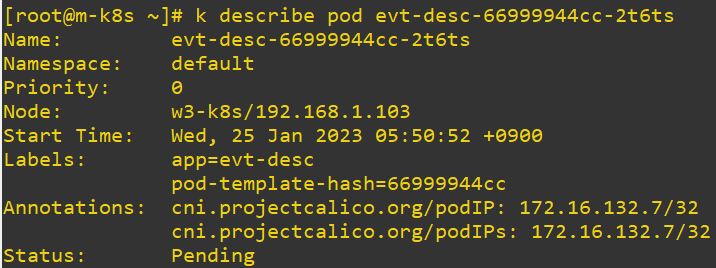
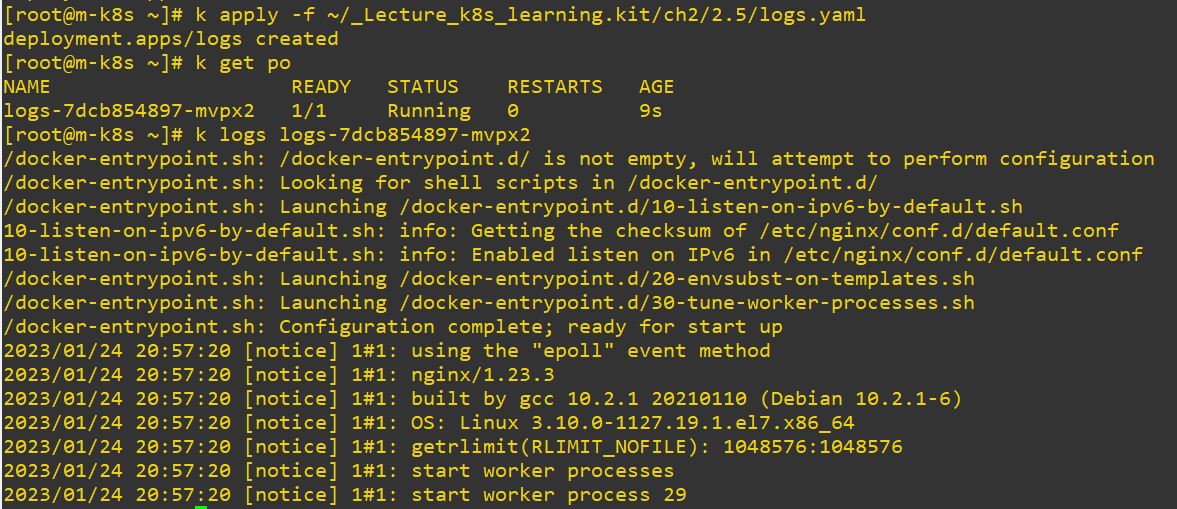
- logs
- Check log.
- Log is worten when deploy is successed.
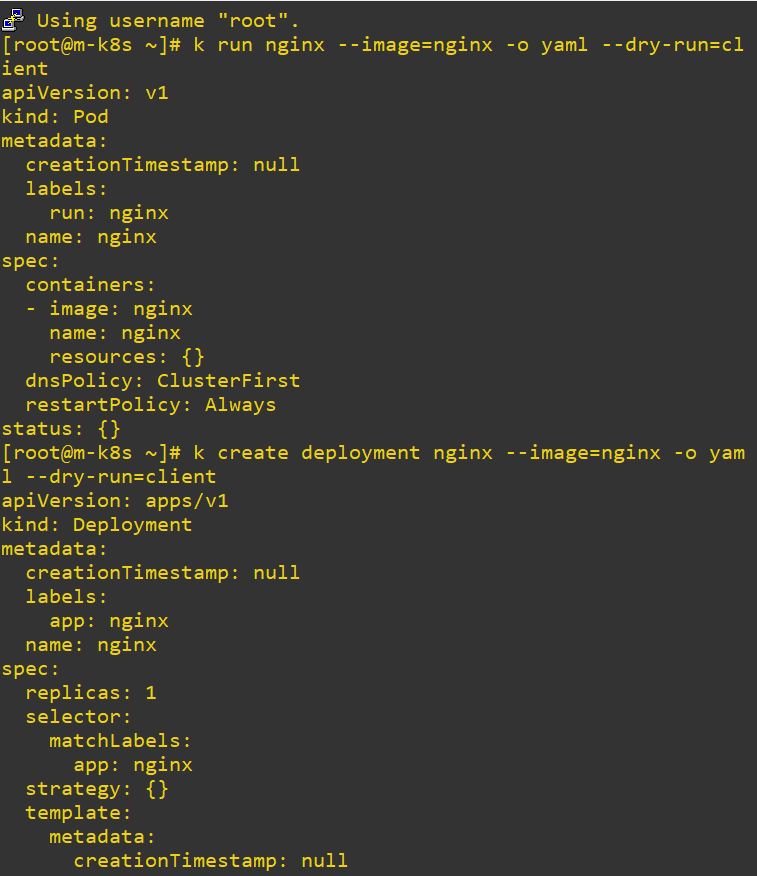
yaml
- -o yaml
- Read yaml code.
- –dry-run=client
- Run yaml code to read.
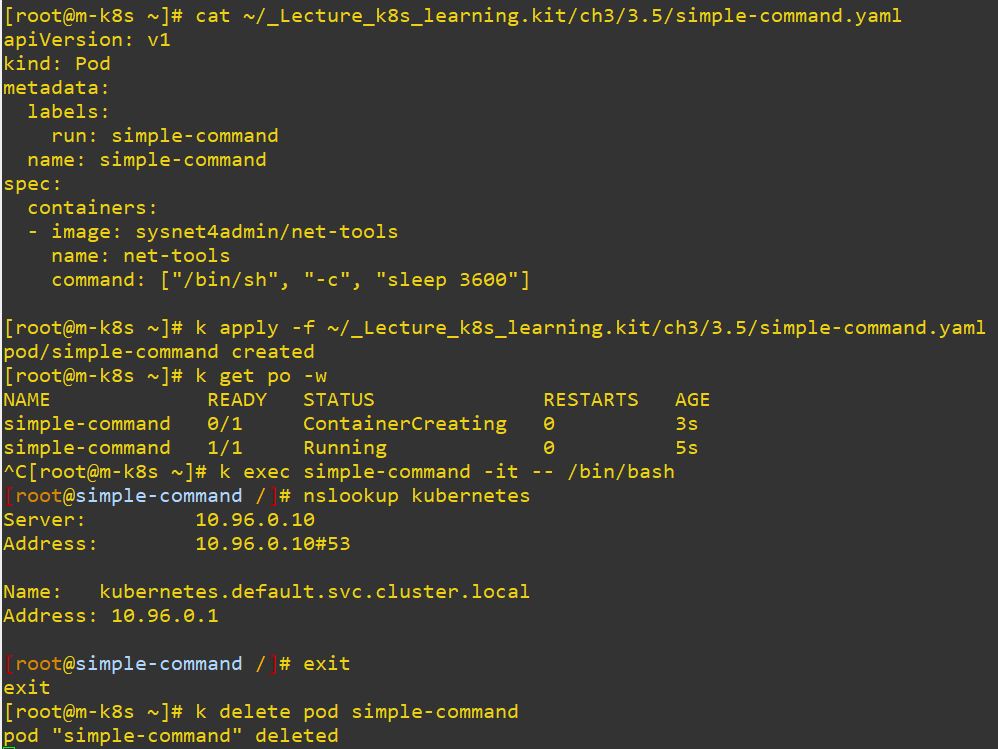
- command
- Use command in yaml file to run specific command.
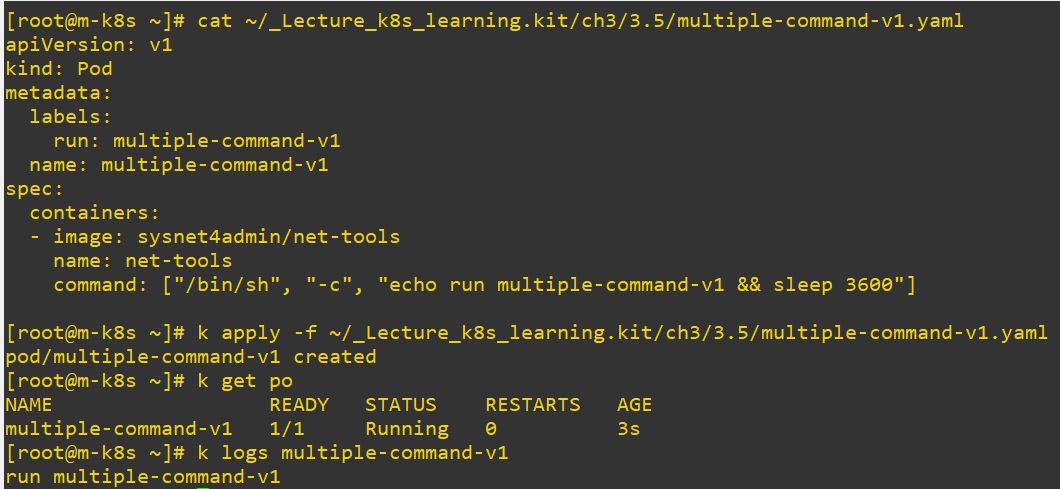
- multiple commands
- Use
&&to run multiple commands at once.
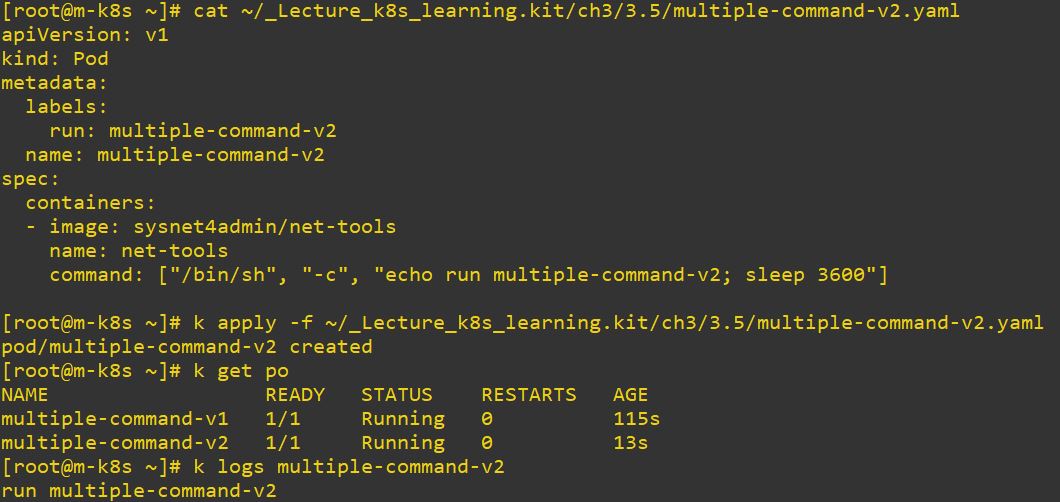
- Use
;to run multiple commans step by step.
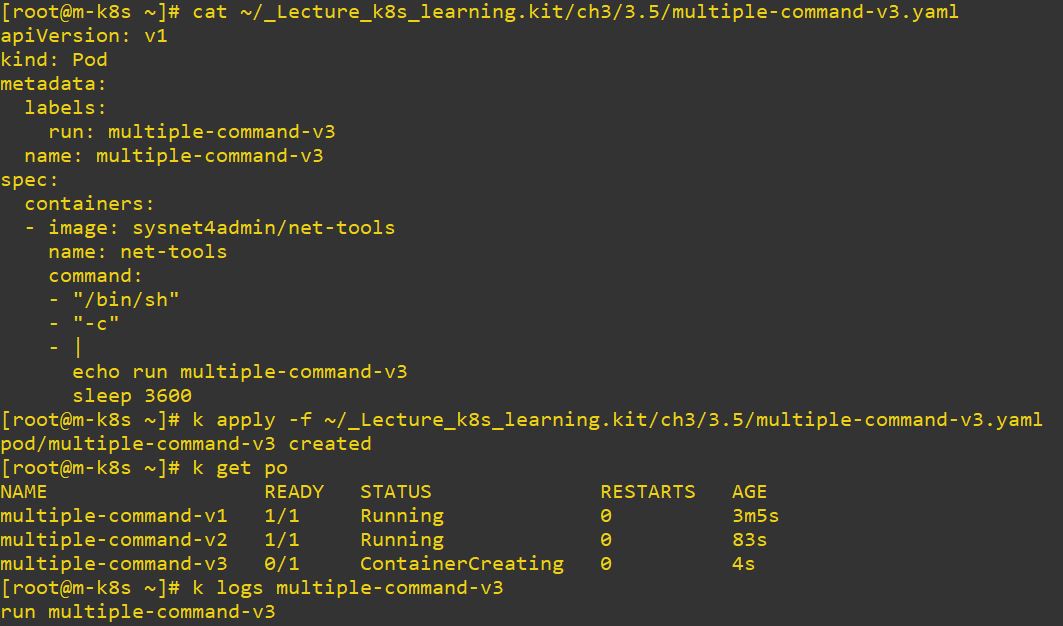
- Use
|to separate command lines.
- Use
argto separate config and commands.
Expose Deployed Application
- We don’t use HostPort and HostNetwork, because we should know where the pods is running.
Port-forward
- We have host port and guest port. When we use host port, then this host port will be changed to guest port.
- For example, our host port is 60010, and when we connect to 60010, then our master node will change 60010 to 22 and connect to 22.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: fwd-chk-hn
spec:
containers:
- name: chk-hn
image: sysnet4admin/chk-hn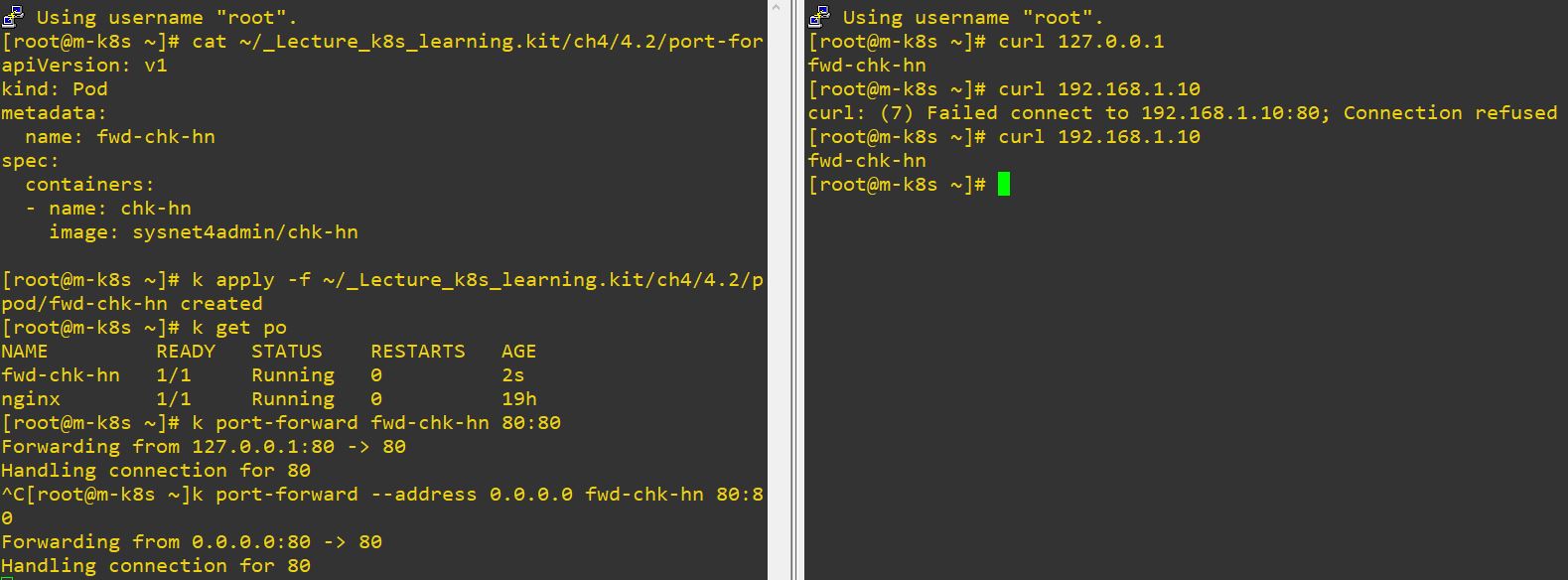
k port-forward fwd-chk-hn 80:80means, we will open 80 with specific address and it will be changed to 80.k port-forward --address 0.0.0.0 fwd-chk-hn 80:80means, we will open 80 with all address and it will be changed to 80.
HostPort
- Outside users should know, which node they will connect.
- For example, 8080 is second worker node host port, and it will change 8080 to 80.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: hp-chk-hn
spec:
containers:
- name: chk-hn
image: sysnet4admin/chk-hn
ports:
- containerPort: 80
hostPort: 8080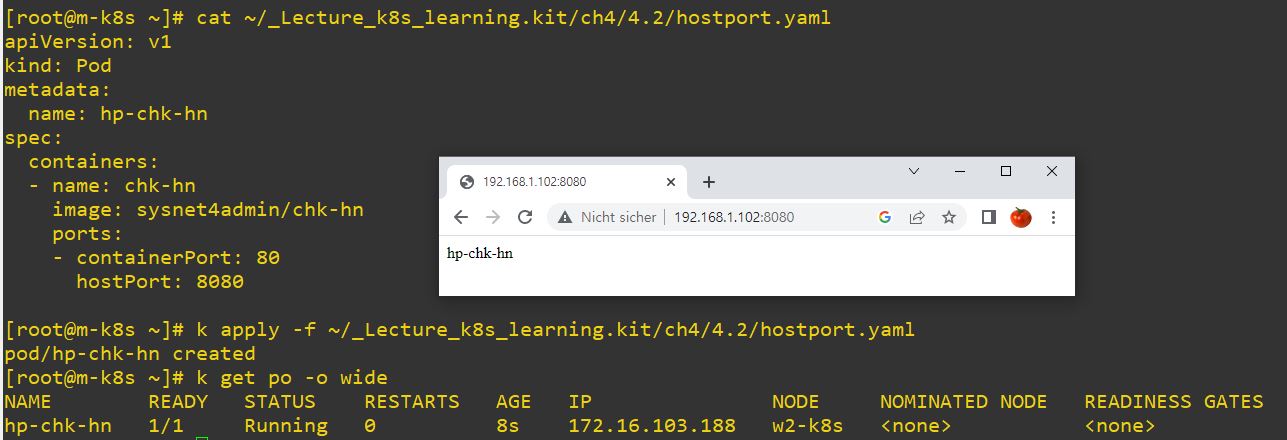
HostNetwork
- Outside users should know, which node they will connect. And they connect directly that port.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: hnet-chk-hn
spec:
hostNetwork: true
containers:
- name: chk-hn
image: sysnet4admin/chk-hn 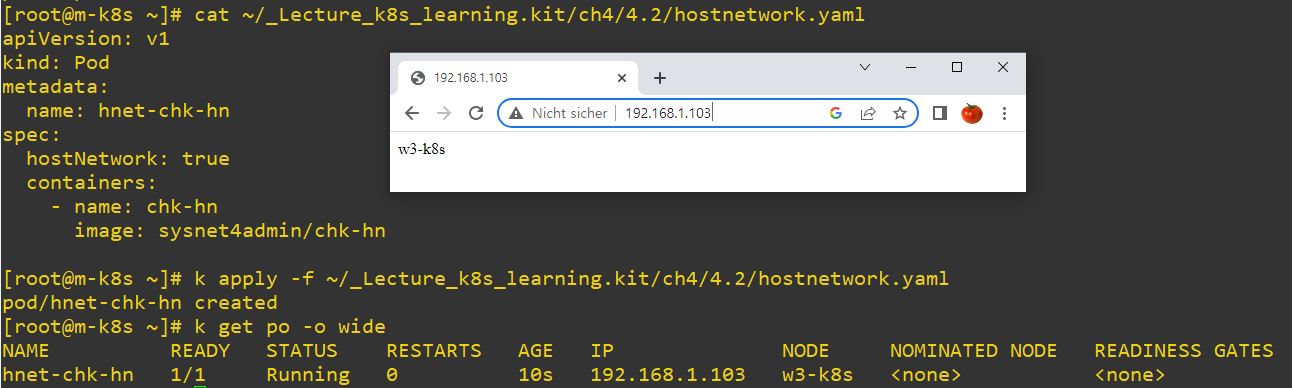
NodePort
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-nginx
labels:
app: deploy-nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
--- # separator for objects
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: np-nginx
spec:
selector:
app: deploy-nginx # deployment to expose
ports:
- name: http
port: 80 # service
targetPort: 80 # pod
nodePort: 30000 #option
type: NodePort # using NodePort- User will connect 30000 node and node will connect to 80 service and service will connect to 80 pod.
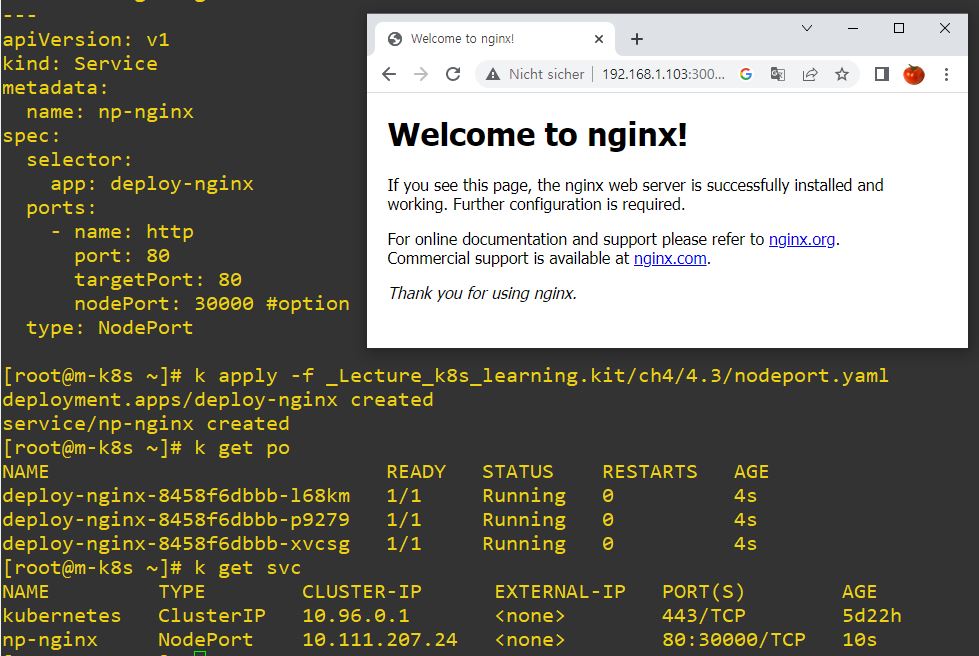
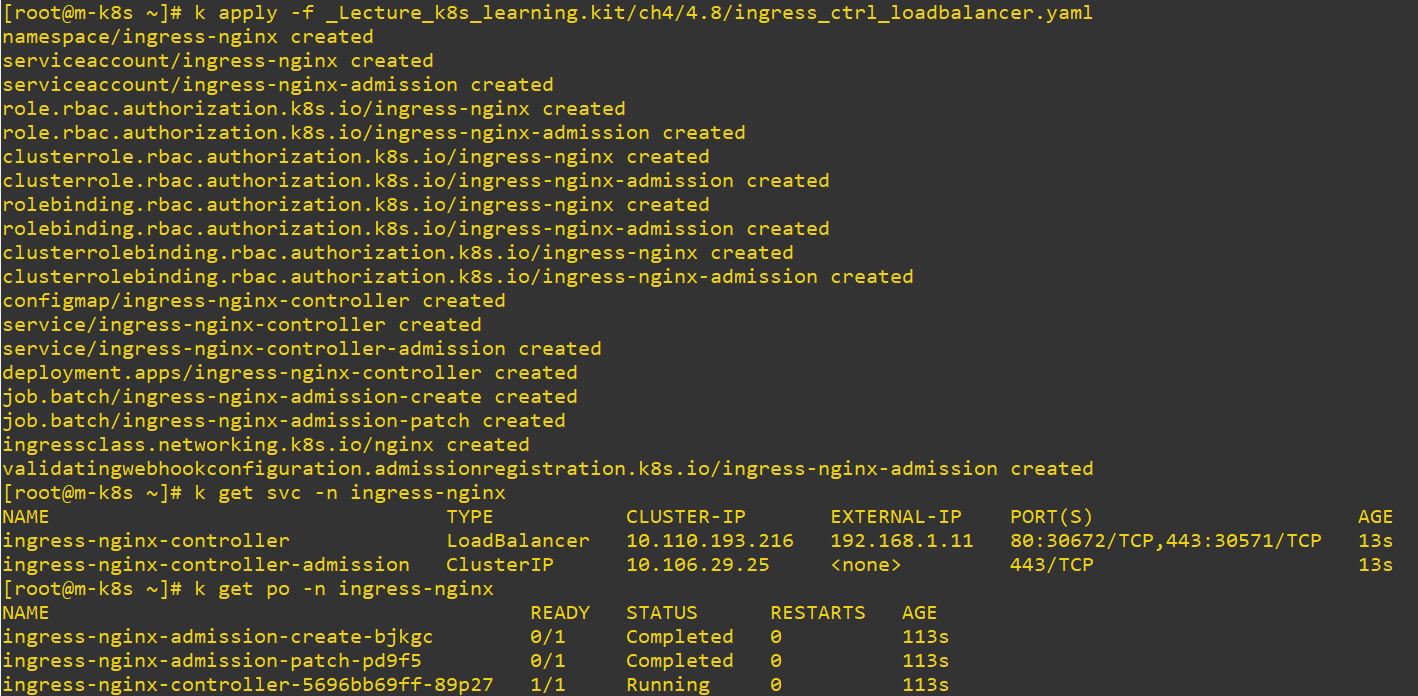
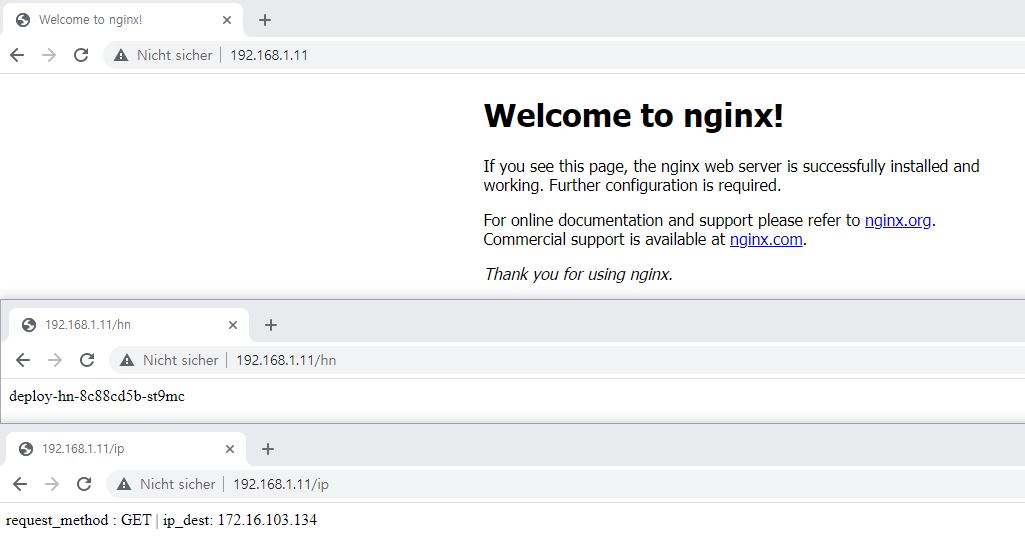
LoadBalancer
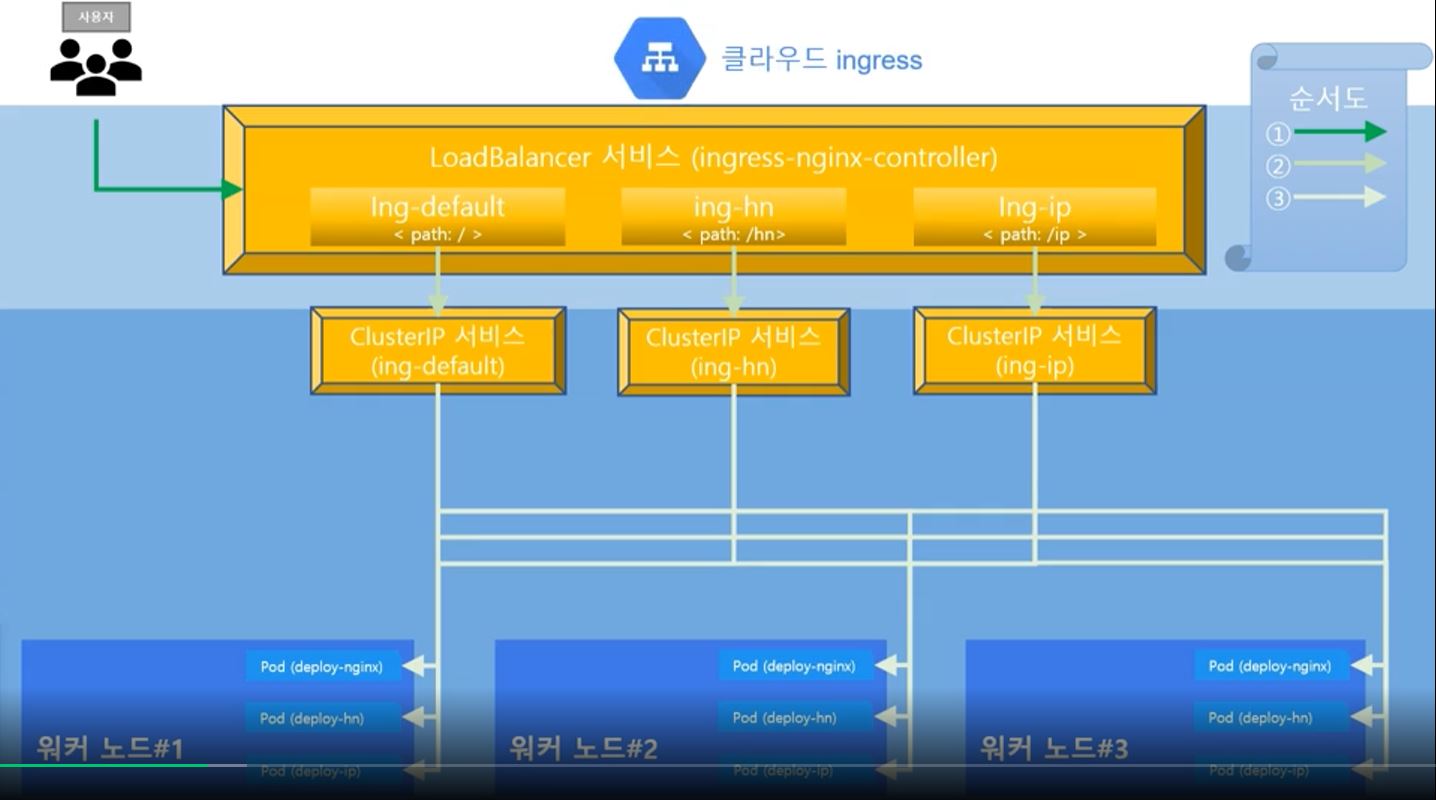
- We will use matalib instead of NodePort.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-nginx
labels:
app: deploy-nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: lb-nginx
spec:
selector:
app: deploy-nginx
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: LoadBalancerapiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-chk-ip
labels:
app: deploy-chk-ip
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-chk-ip
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-chk-ip
spec:
containers:
- name: chk-ip
image: sysnet4admin/chk-ip
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: lb-chk-ip
spec:
selector:
app: deploy-chk-ip
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: LoadBalancer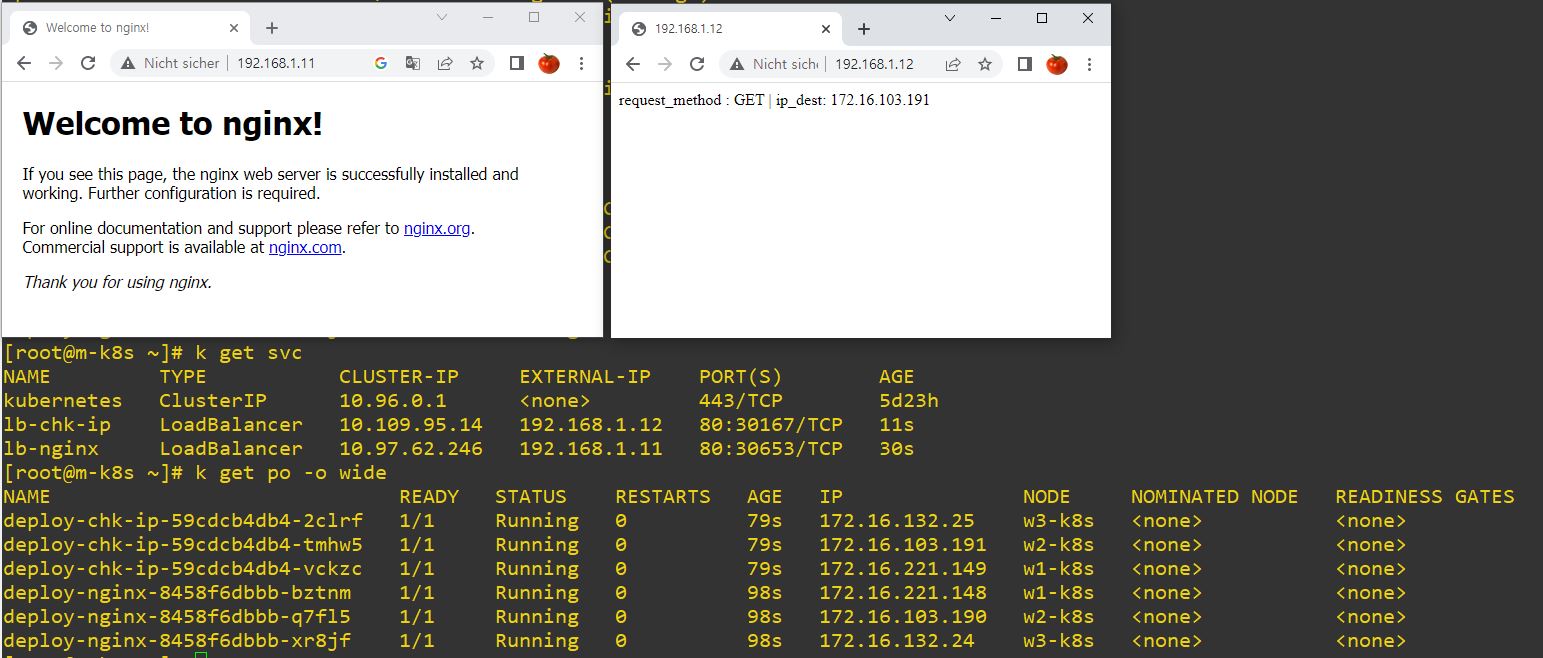
ExternalName
- ExternalName has no Deployment because it uses external name to service.
- ExternalName is matched metadata’s name.
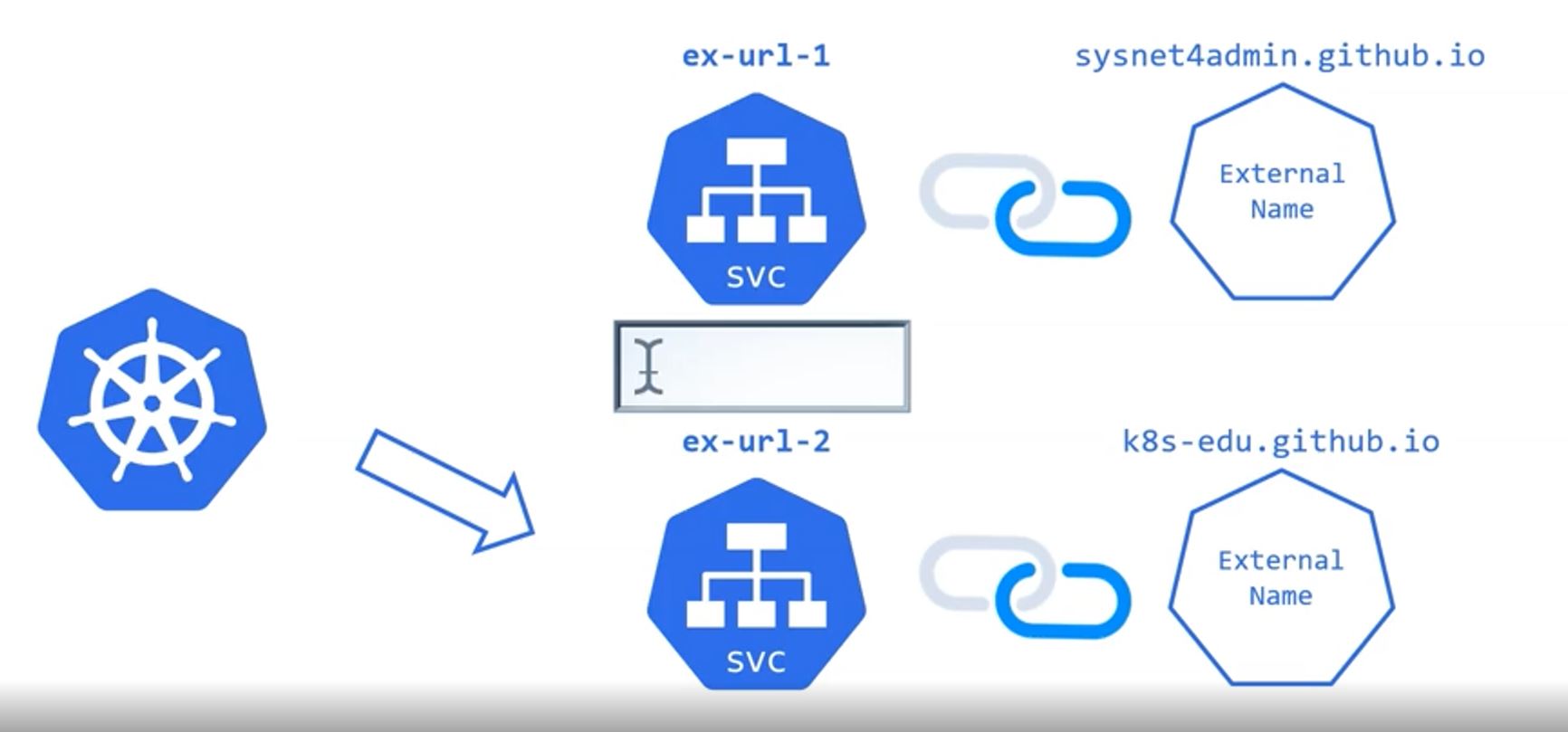
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ex-url-1
namespace: default
spec:
type: ExternalName
externalName: sysnet4admin.github.io # External Domain NameapiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ex-url-2
namespace: default
spec:
type: ExternalName
externalName: k8s-edu.github.io # changable as you want 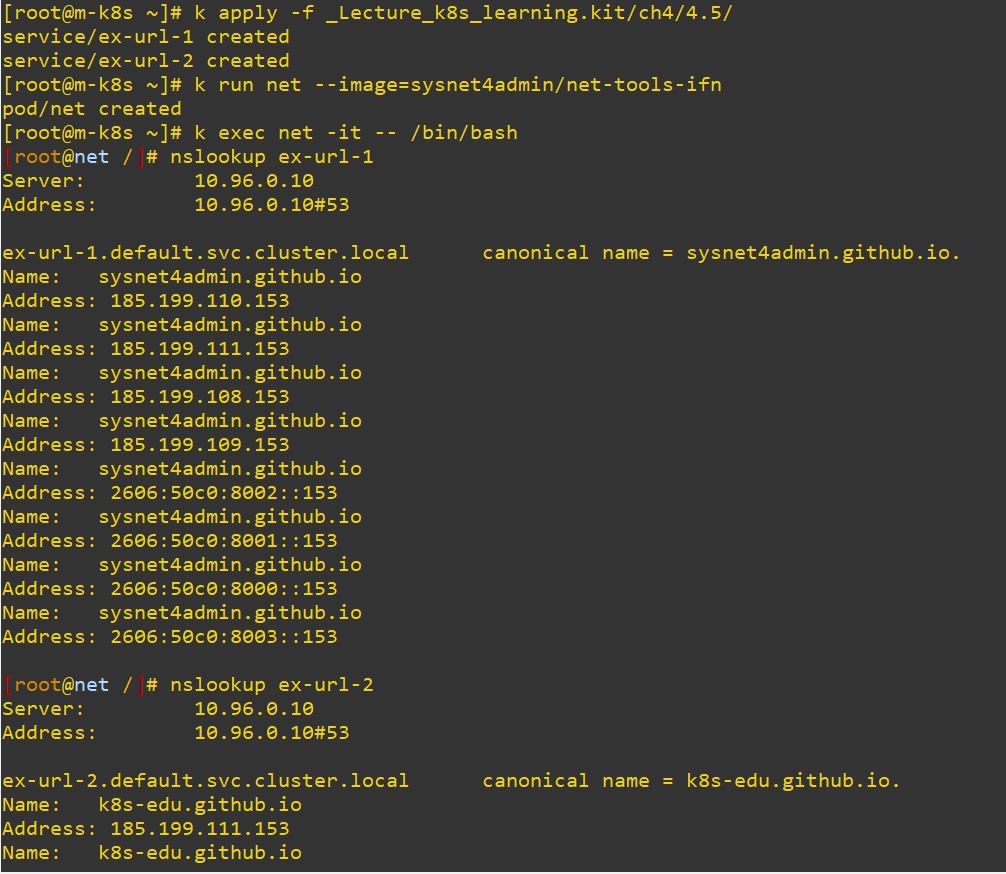
ClusterIP
- ClusterIP exposes Deployment or Pod.
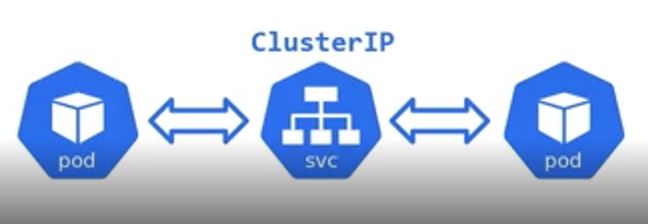
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-nginx
labels:
app: deploy-nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: cl-nginx
spec:
selector:
app: deploy-nginx
ports: # ClusterIP has port and target port to connect each other.
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: ClusterIPHeadless
- Headless exposes Deployment or Pod without IP.
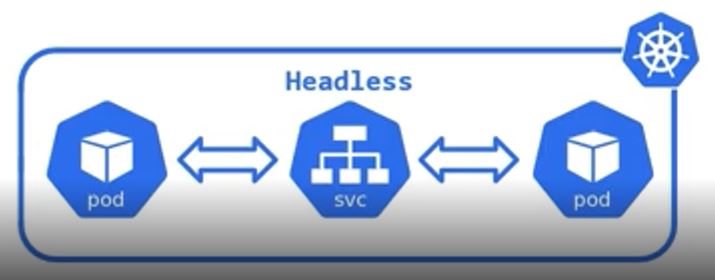
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-nginx
labels:
app: deploy-nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hdl-nginx
spec:
selector:
app: deploy-nginx
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
clusterIP: None # Headless has no type and no IP.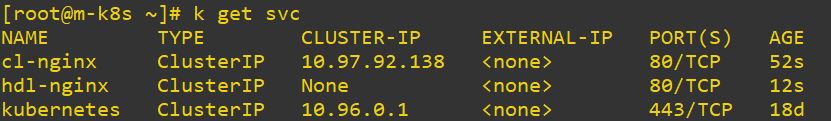
- Headless can communicate with domain name, without IP and connect to StateFulset with domain name.
- StateFulset matches service Name to connect Headless.
- When you use StateFulset with LoadBalancer, each External IP calls can show different pods. Therefore, I recommend, using StateFulset with Headless.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: sts-chk-hn
spec:
replicas: 3
serviceName: sts-svc-domain #statefulset need it
selector:
matchLabels:
app: sts
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: sts
spec:
containers:
- name: chk-hn
image: sysnet4admin/chk-hn
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: sts-svc-domain
spec:
selector:
app: sts
ports:
- port: 80
clusterIP: None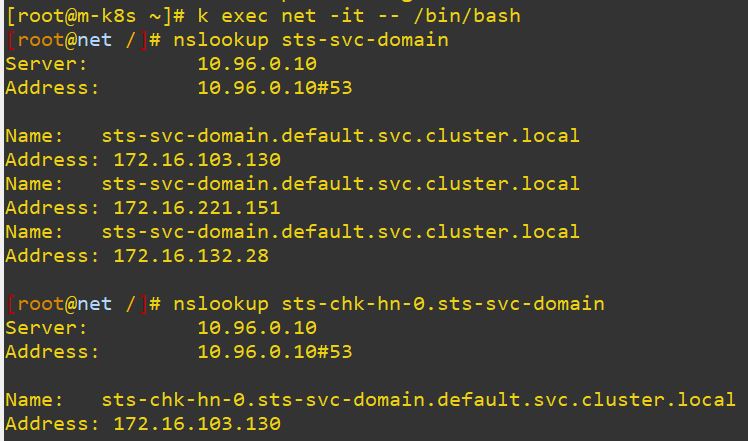
EndPoint
- When you create Deployment and LoadBalancer together, EndPoint is also created.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-chk-ip
labels:
app: deploy-chk-ip
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-chk-ip
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-chk-ip
spec:
containers:
- name: chk-ip
image: sysnet4admin/chk-ip
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: lb-chk-ip
spec:
selector:
app: deploy-chk-ip
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: LoadBalancer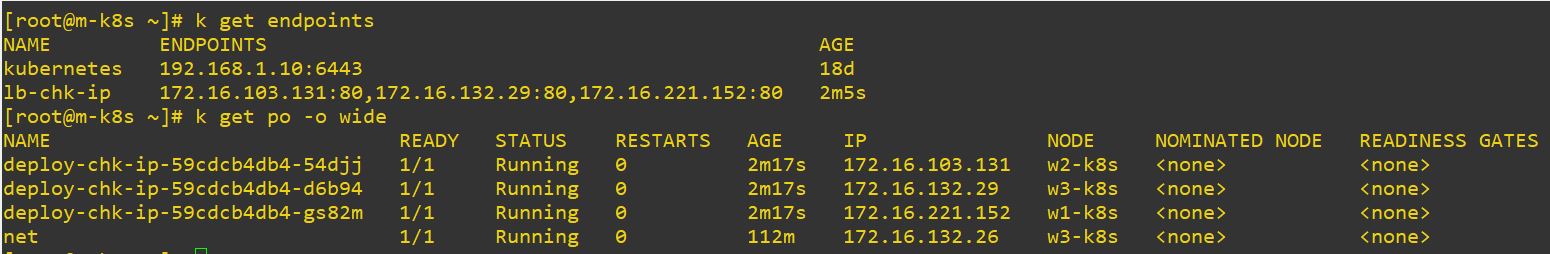
- You can create EndPoint independently.
- Create Service first as ClusterIP and create also EndPoint with service name and LoadBalancer IP. As a result, you can call EndPoint with service name and EndPoint is binded with LoadBalancer IP, like double binding.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: external-data
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Endpoints
metadata:
name: external-data # match name with service.
subsets:
- addresses:
- ip: 192.168.1.11 # LoadBalancer IP
ports:
- name: http
port: 80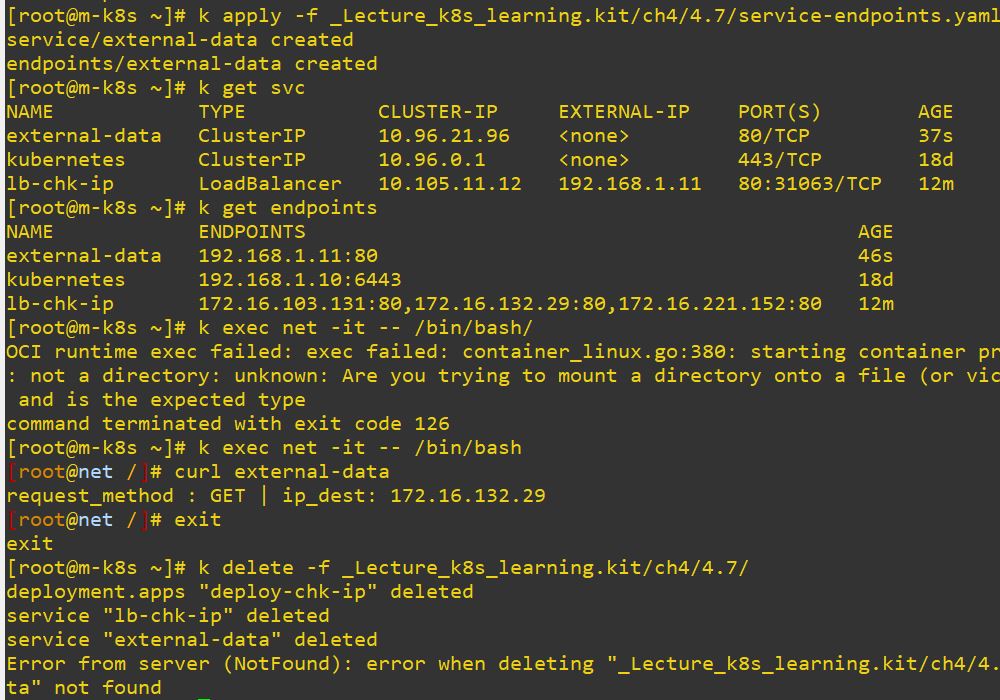
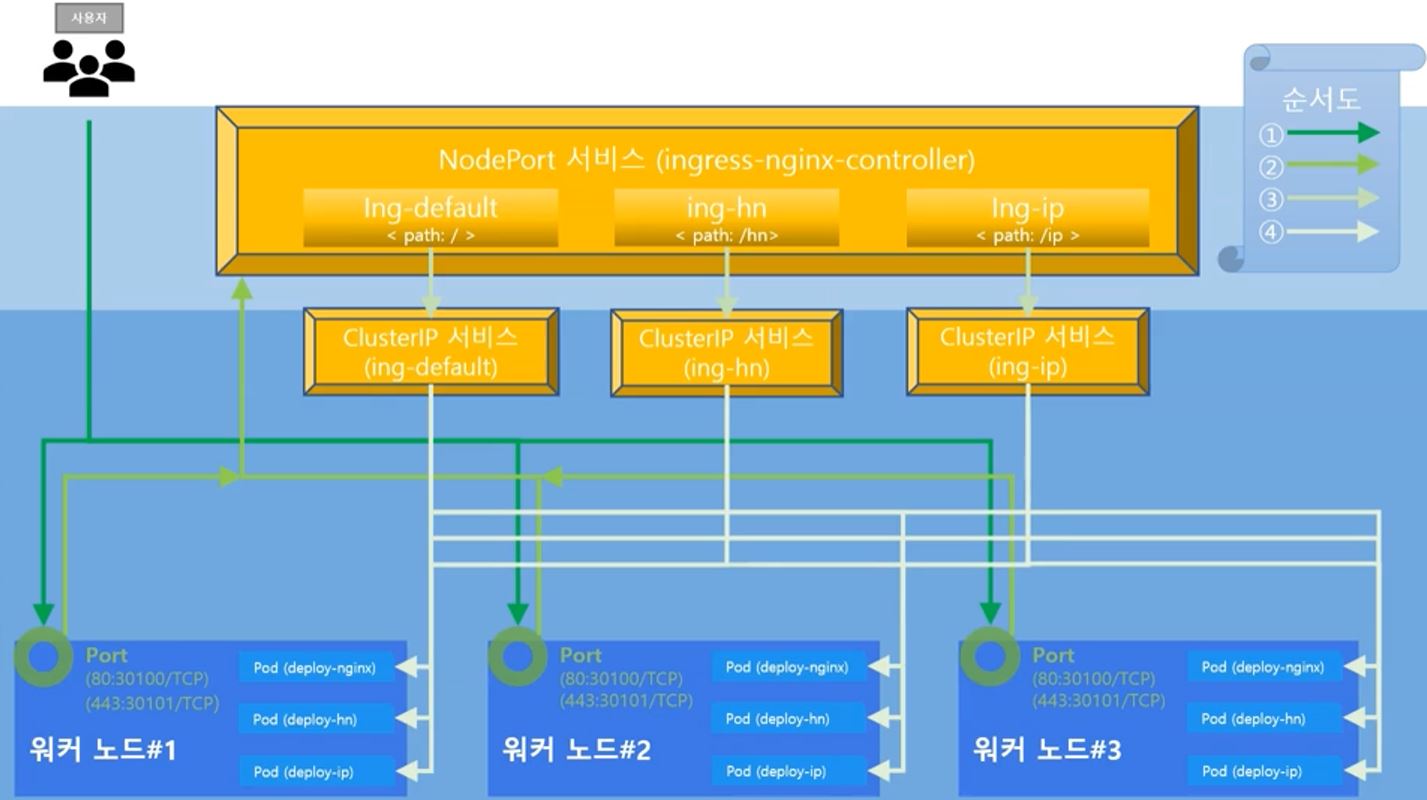
Ingress
- Ingress cannot exist without service.
- Ingress has routing information and service routs the app.
-
Services
-
deploy-nginx
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-nginx
labels:
app: deploy-nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ing-default
spec:
selector:
app: deploy-nginx
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: ClusterIP- deploy-hn
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-hn
labels:
app: deploy-hn
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-hn
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-hn
spec:
containers:
- name: chk-hn
image: sysnet4admin/chk-hn
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ing-hn
spec:
selector:
app: deploy-hn
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: ClusterIP- deploy-ip
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-ip
labels:
app: deploy-ip
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-ip
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-ip
spec:
containers:
- name: chk-ip
image: sysnet4admin/chk-ip
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ing-ip
spec:
selector:
app: deploy-ip
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: ClusterIP- Ingress
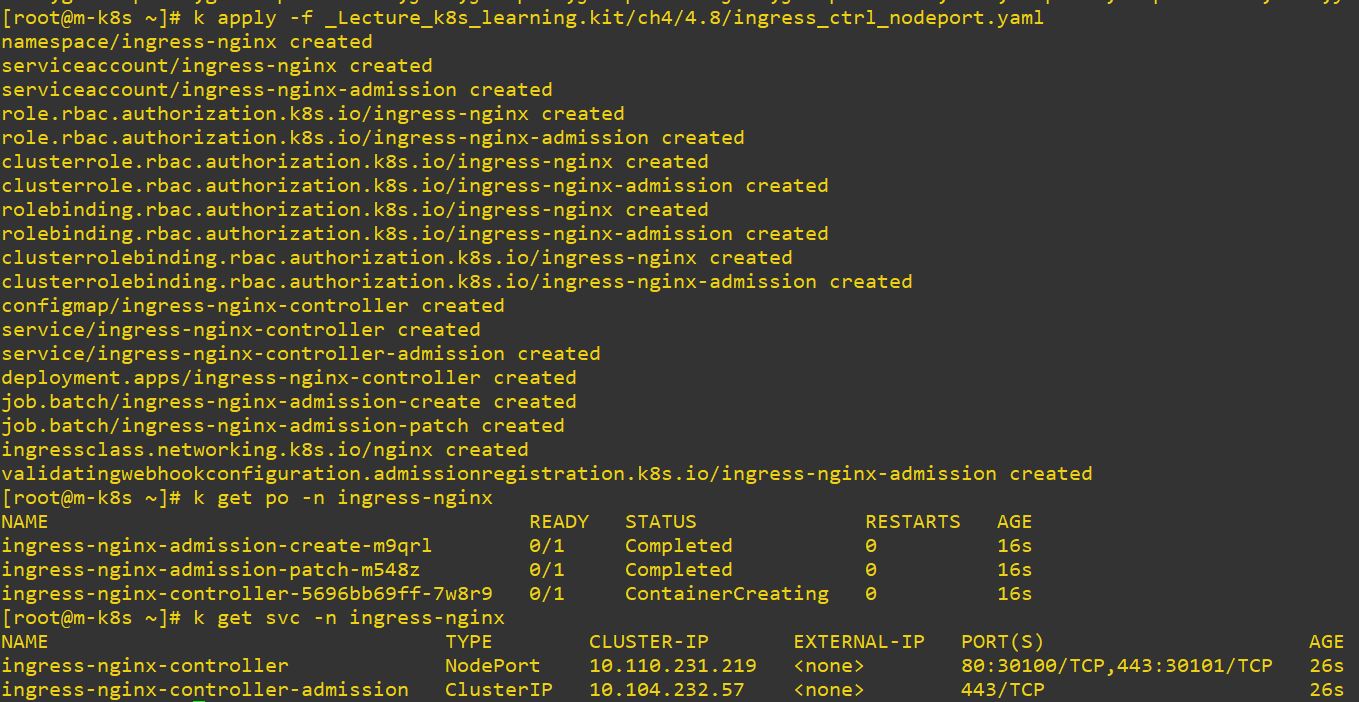
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress
annotations: # set default path
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx"
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: ing-default
port:
number: 80
- path: /hn
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: ing-hn
port:
number: 80
- path: /ip
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: ing-ip
port:
number: 80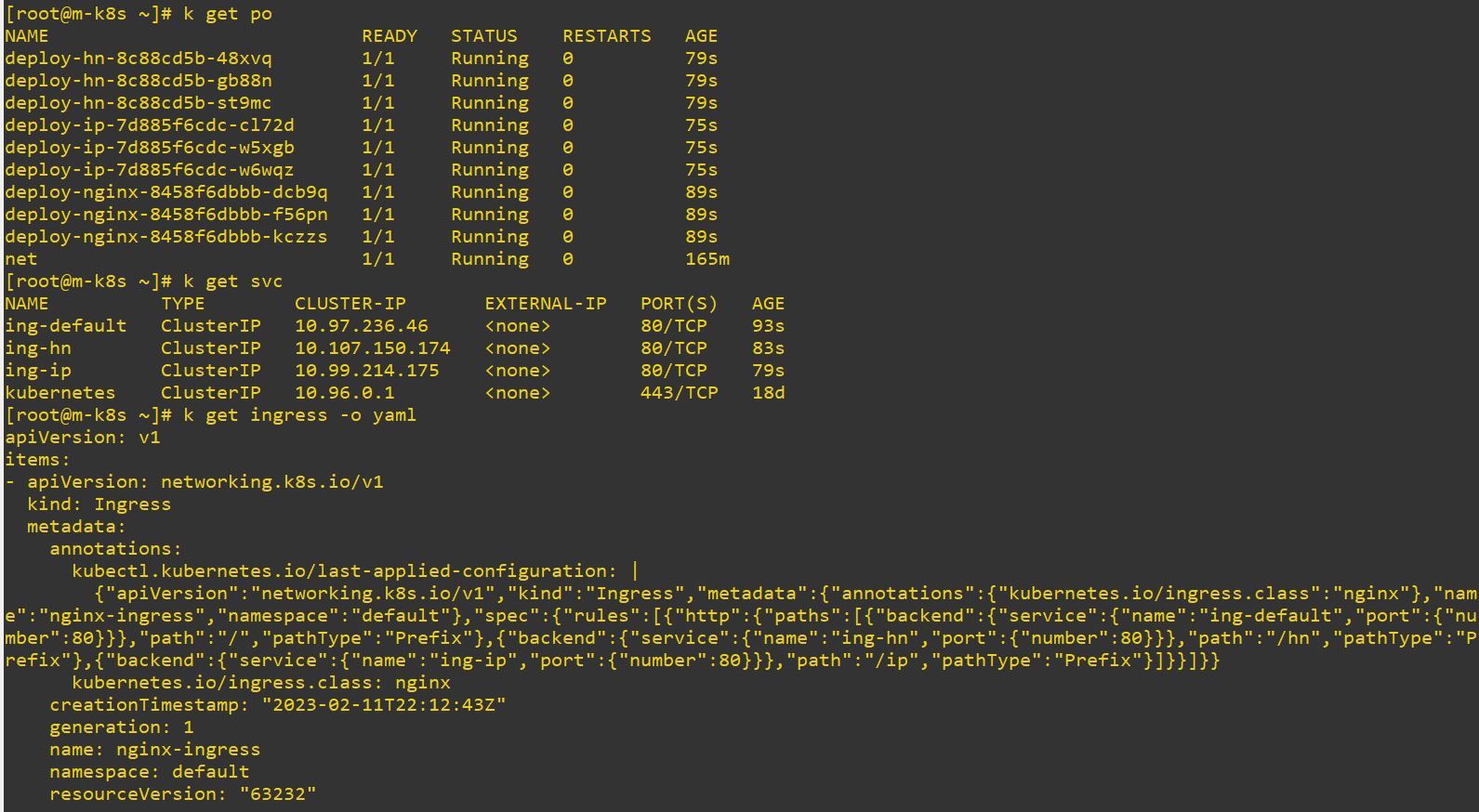
- with NodePort
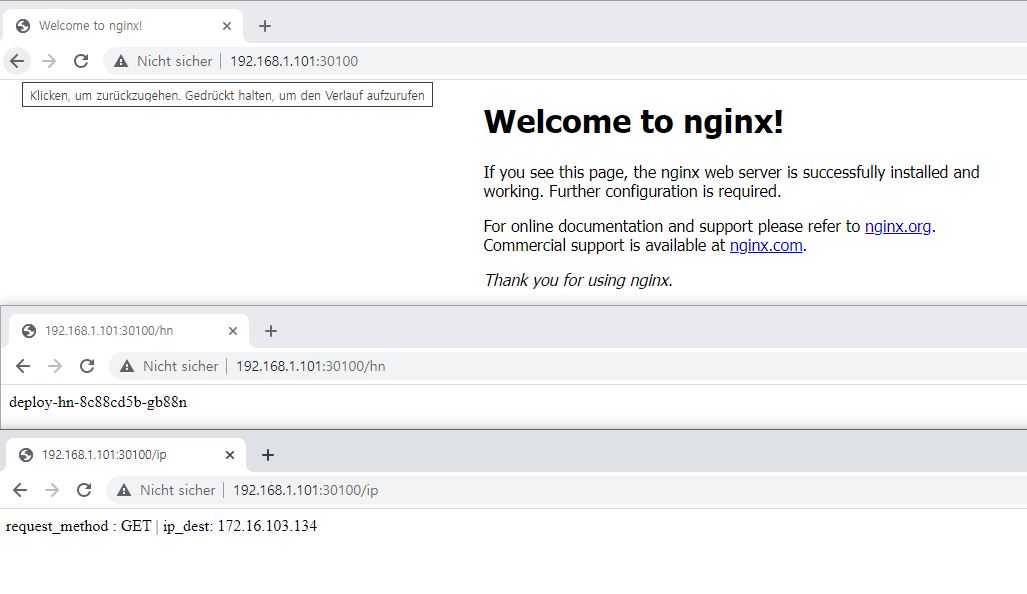
- with LoadBalancer
Label vs Annotation
- Label is for human and annotation is for system.
Volume
emptyDir
- emptyDir is shared memory in pods.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod # make emptyDir as a pod
metadata:
name: pod-emptydir
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: web-page # make container 1
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html # container 1 first page
name: empty-directory
- name: html-builder # make container 2
image: alpine
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /html-dir # container 2 first page is /html-dir/index.html
name: empty-directory
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- echo "This page created on $(date +%Y-%m-%d)" > /html-dir/index.html;
sleep infinity;
volumes:
- name: empty-directory
emptyDir: {}- In this example, we will create 2 containers.
- After creating each of first page, this first page gonna be empty-directory.
- This created empty-directory will be a volume and this volume connects 2 containers.
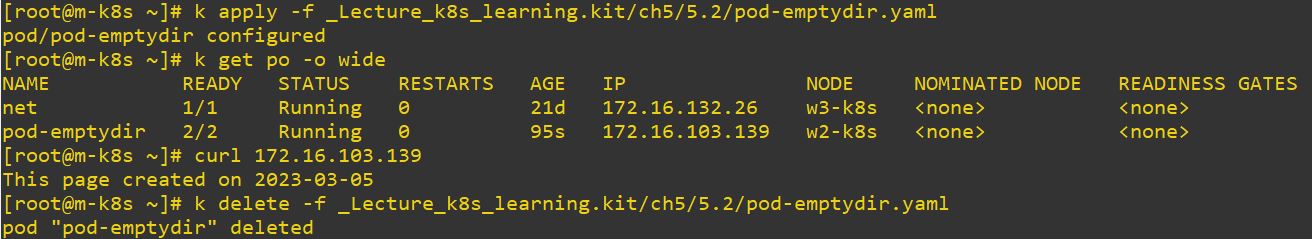
- We called container 2 with IP but actual running pod is container 1.
hostPath
- hostPath can use Node directories.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-hostpath
labels:
app: deploy-hostpath
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-hostpath
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-hostpath
spec:
containers:
- name: host-mon
image: sysnet4admin/sleepy
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /host-log
name: hostpath-directory
volumes:
- name: hostpath-directory
hostPath:
path: /var/log- It connects
/var/logand/host-logwith namehostpath-directory. - When Deployment is released on Node, Node can take diffrent amounts of Deployments.
- So it’s difficult to make a hostPath on one Node.
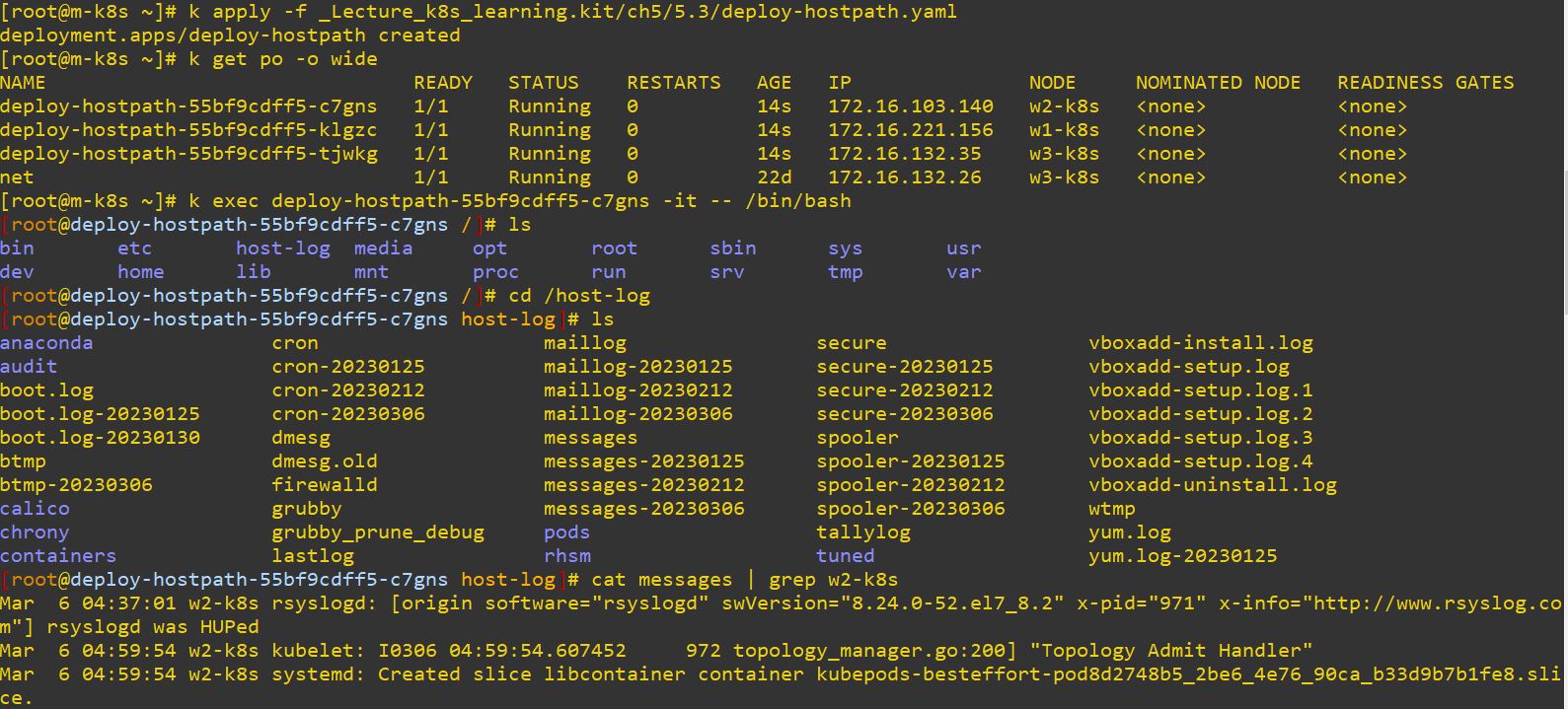
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: ds-hostpath
labels:
app: ds-hostpath
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: ds-hostpath
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: ds-hostpath
spec:
containers:
- name: host-mon
image: sysnet4admin/sleepy
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /host-log
name: hostpath-directory
volumes:
- name: hostpath-directory
hostPath:
path: /var/log- DaemonSet is created on one Node. It means our hostPath is separated fairly on Nodes.
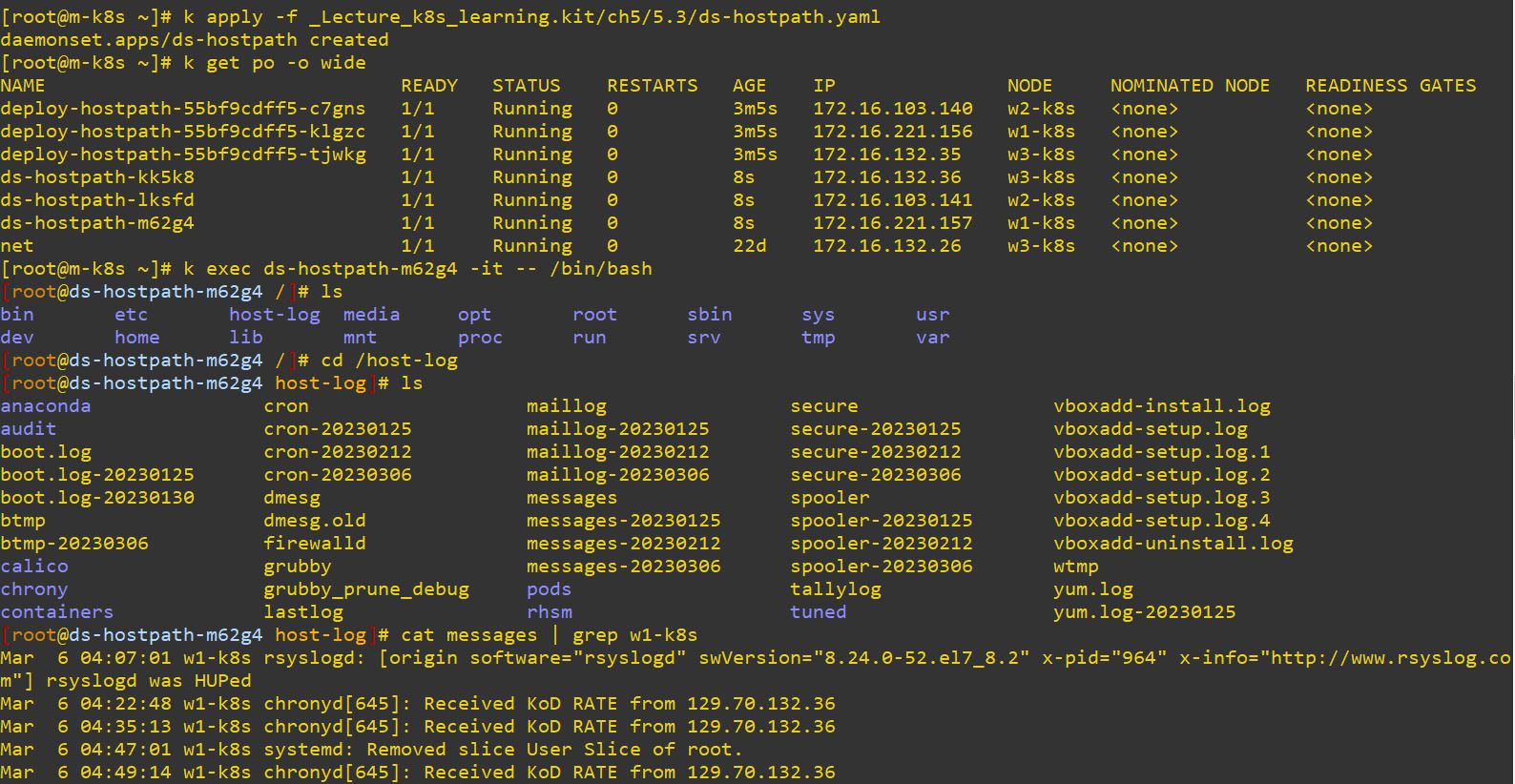
NFS
- Network File System
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-nfs
labels:
app: deploy-nfs
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-nfs
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-nfs
spec:
containers:
- name: chk-log
image: sysnet4admin/chk-log
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-vol
mountPath: /audit
volumes:
- name: nfs-vol
nfs:
server: 192.168.1.10
path: /nfs_shared/nfs-vol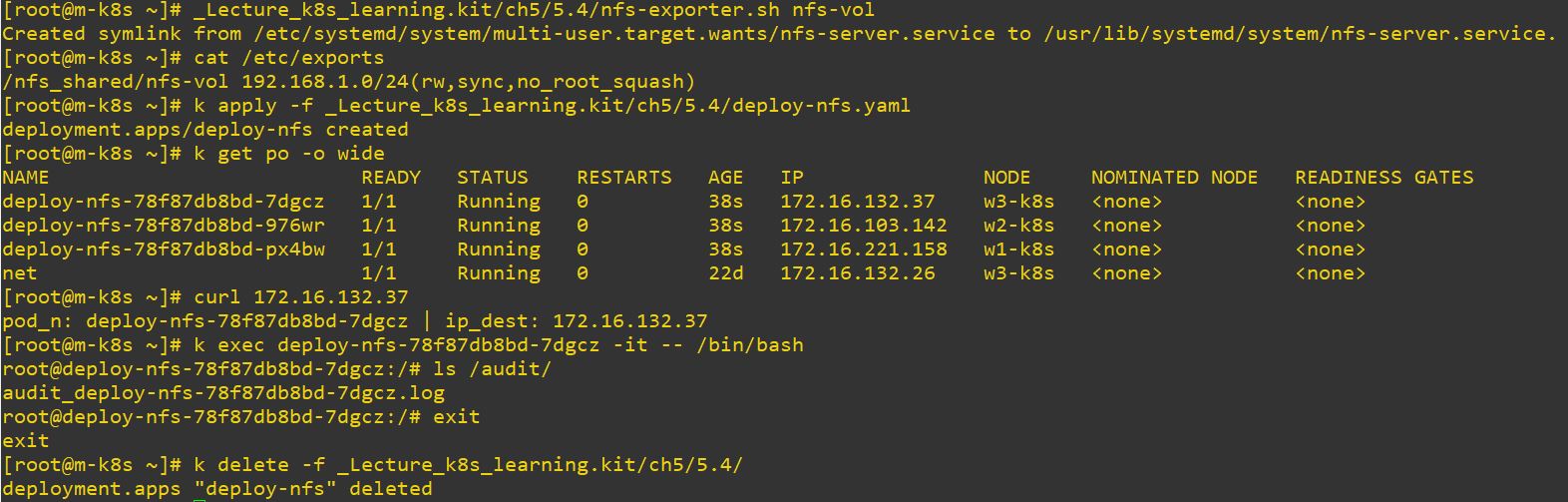
PV & PVC
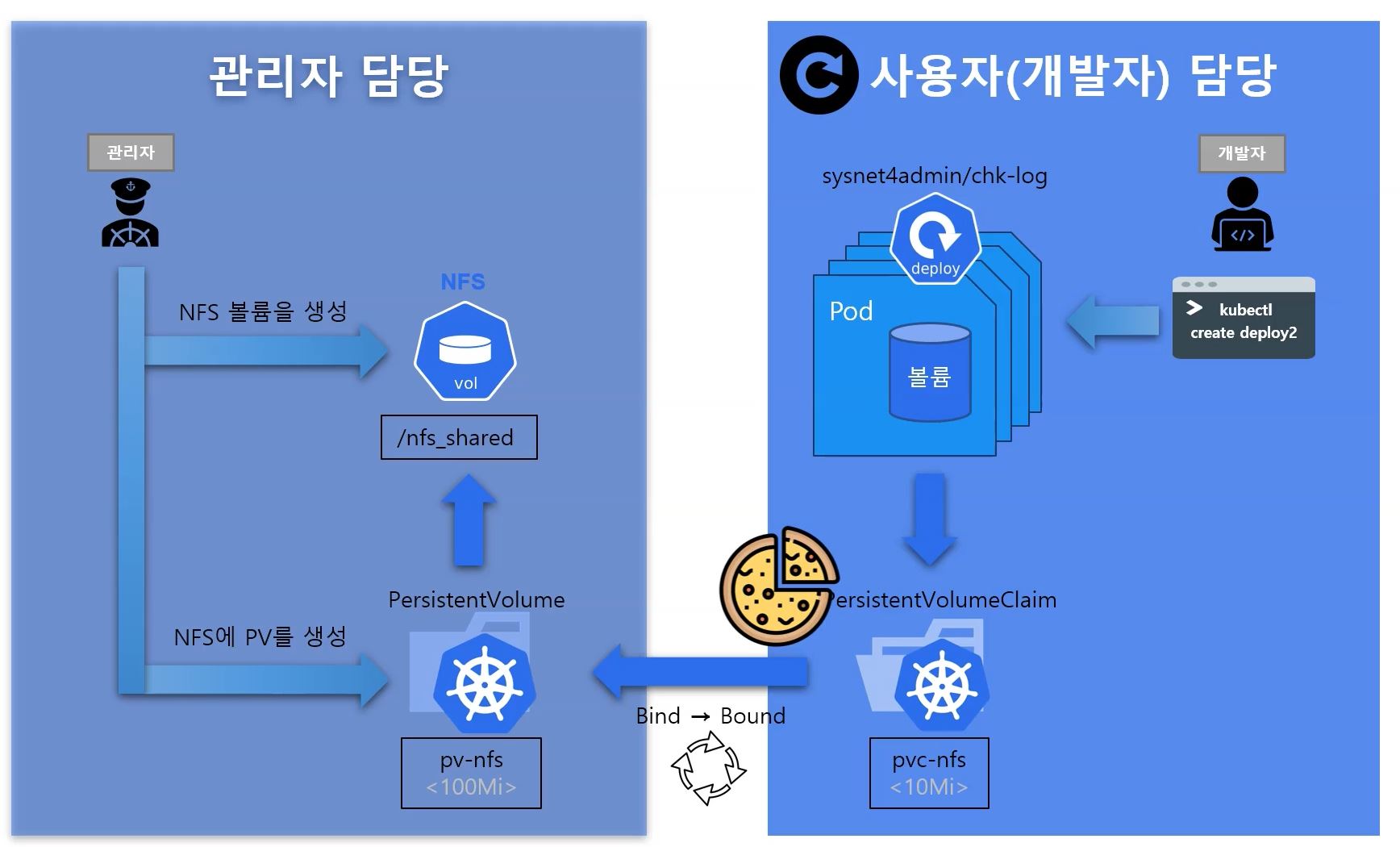
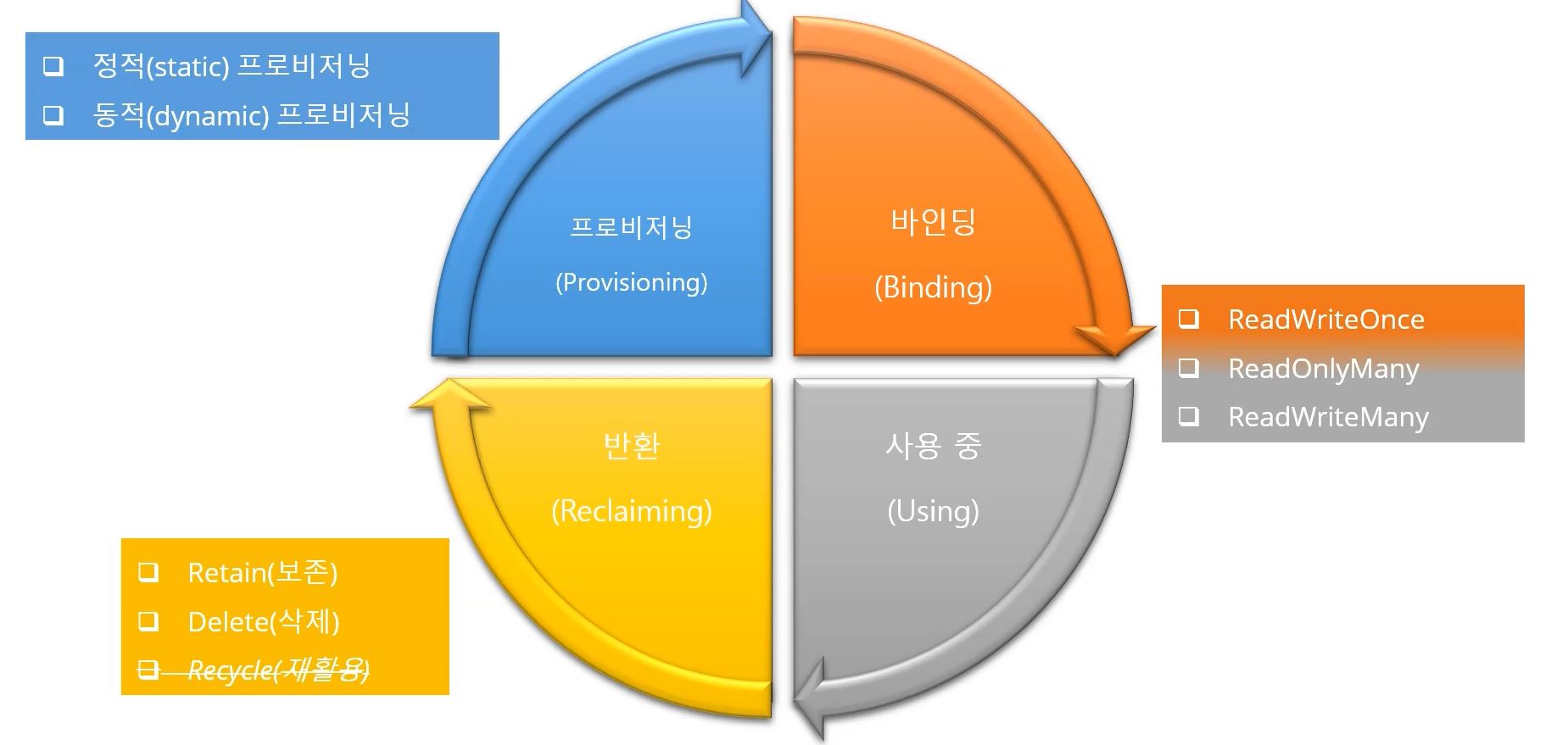
- accessModes
- ReadWriteOnce(RWO) : Read and Write on only one node.
- ReadOnlyMany(ROX) : Read on several nodes.
- ReadWriteMany(RWX) : Read and Write on several nodes.
- Block Storage uses RWO and ROX and Object Storage uses RWX.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-pvc
labels:
app: deploy-pvc
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-pvc
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-pvc
spec:
containers:
- name: chk-log
image: sysnet4admin/chk-log
volumeMounts:
- name: pvc-vol
mountPath: /audit
volumes:
- name: pvc-vol
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: pvc-nfs # created pvc namePV
- Persistent Volume
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: pv-nfs
spec:
capacity:
storage: 100Mi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
nfs:
server: 192.168.1.10
path: /nfs_shared/pvc-vol- persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy
- Retain : retain PV even you delete PVC
- Delete : delete PV when you delete PVC
PVC
- Persistent Volume Claim
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: pvc-nfs
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Mi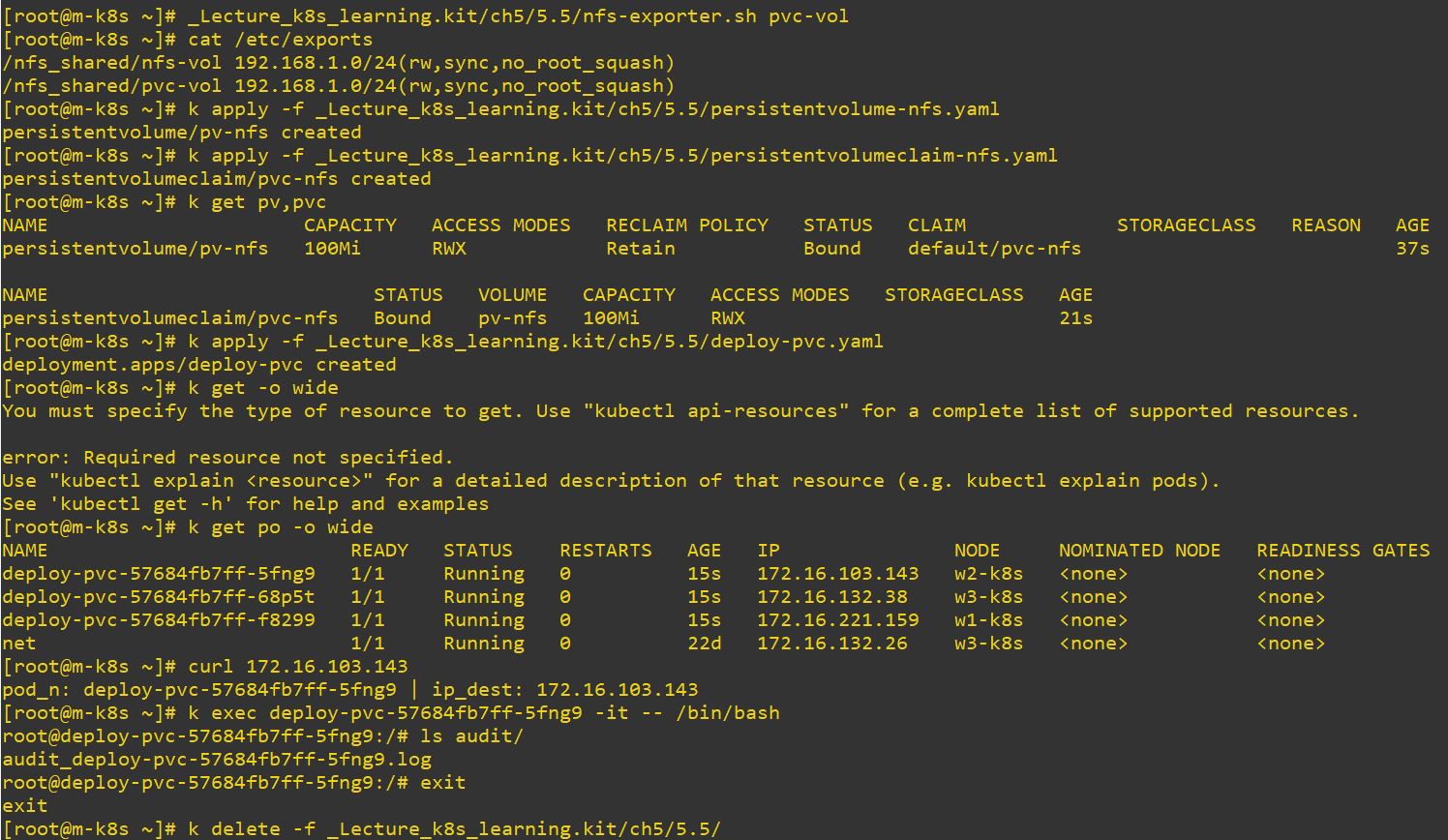
StorageClass
- Persitent Volume Claim make StorageClass first, and then StorageClass make a Persistent Volume.
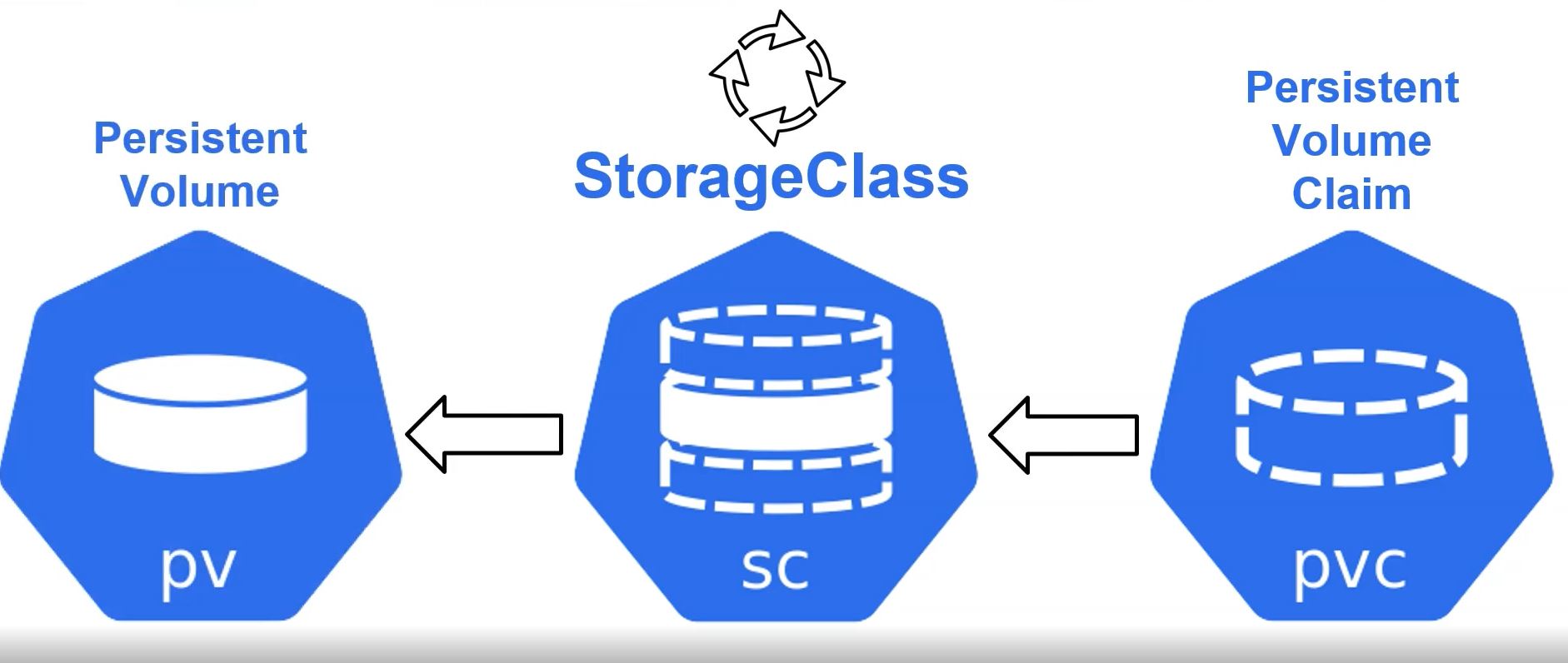
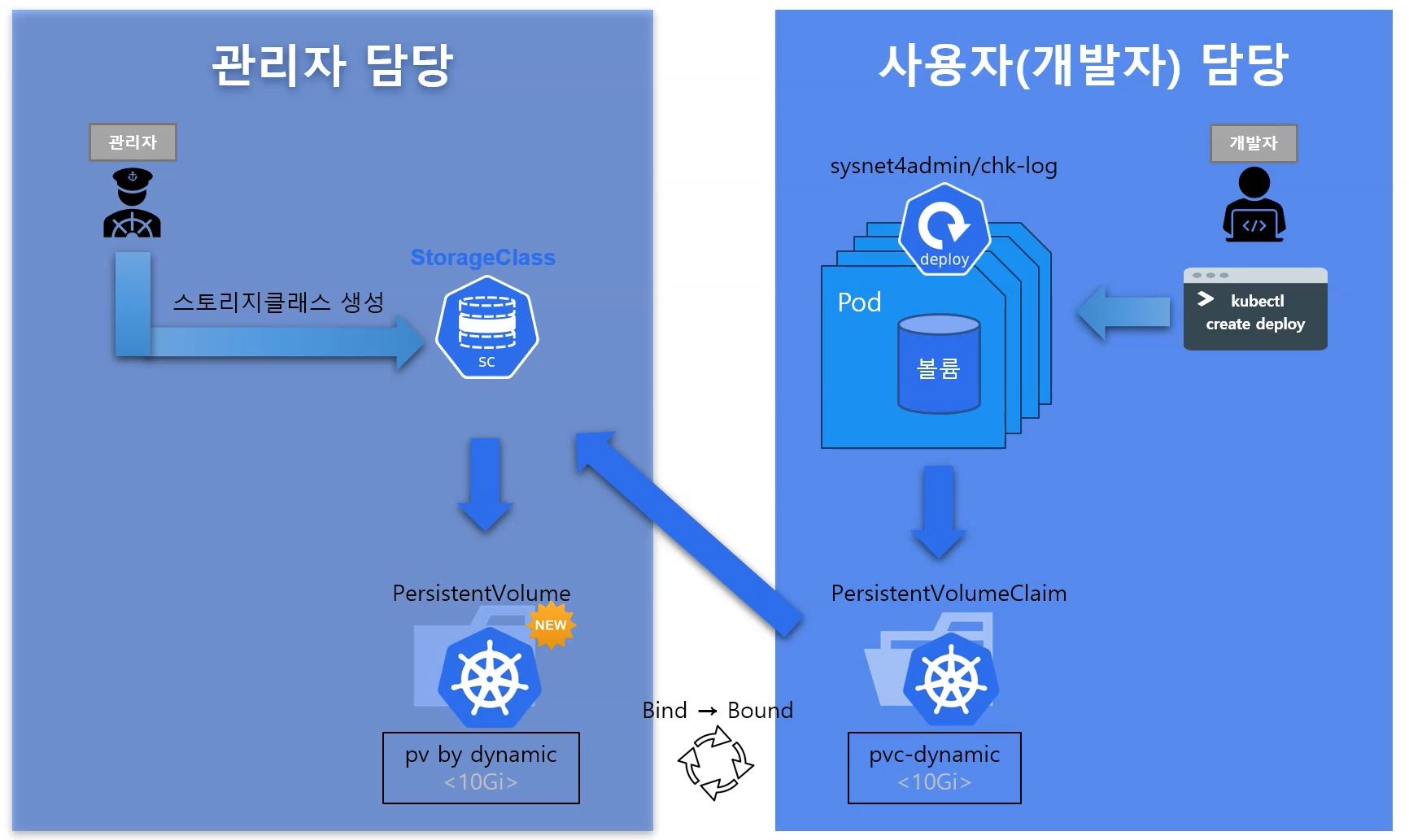

- Provisioning
- Static : nfs, PV & PVC
- Dynamic : StorageClass
- In nfs mode, administrator should create pv everytime when it is requested.
- In PV & PVC mode, administrator should prepare always PV before user uses pvc.
- In StorageClass mode, administrator don’t need to prepare pvc before, because StorageClass will create PVC automatically everytime when it is requested.
- provisioner
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
serviceAccountName: nfs-client-provisioner
containers:
- name: nfs-client-provisioner
image: k8s.gcr.io/sig-storage/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner:v4.0.2
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-client-root
mountPath: /persistentvolumes
env:
- name: PROVISIONER_NAME
value: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
- name: NFS_SERVER # NFS Server
value: 192.168.1.10
- name: NFS_PATH
value: /nfs_shared/dynamic-vol
volumes:
- name: nfs-client-root
nfs:
server: 192.168.1.10 # NFS Client Root
path: /nfs_shared/dynamic-vol-
NFS server and NFS client Root should have same values.
-
StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: managed-nfs-storage
# or choose another name, must match deployment's env PROVISIONER_NAME'
provisioner: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
parameters:
# waits for nfs.io/storage-path annotation, if not specified will accept as empty string.
pathPattern: "${.PVC.namespace}/${.PVC.annotations.nfs.io/storage-path}"
onDelete: delete- PVC
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: pvc-dynamic
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
storageClassName: managed-nfs-storage # name of StorageClass- Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-pvc
labels:
app: deploy-pvc
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-pvc
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-pvc
spec:
containers:
- name: chk-log
image: sysnet4admin/chk-log
volumeMounts:
- name: pvc-vol
mountPath: /audit
volumes:
- name: pvc-vol
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: pvc-dynamic # PVC name 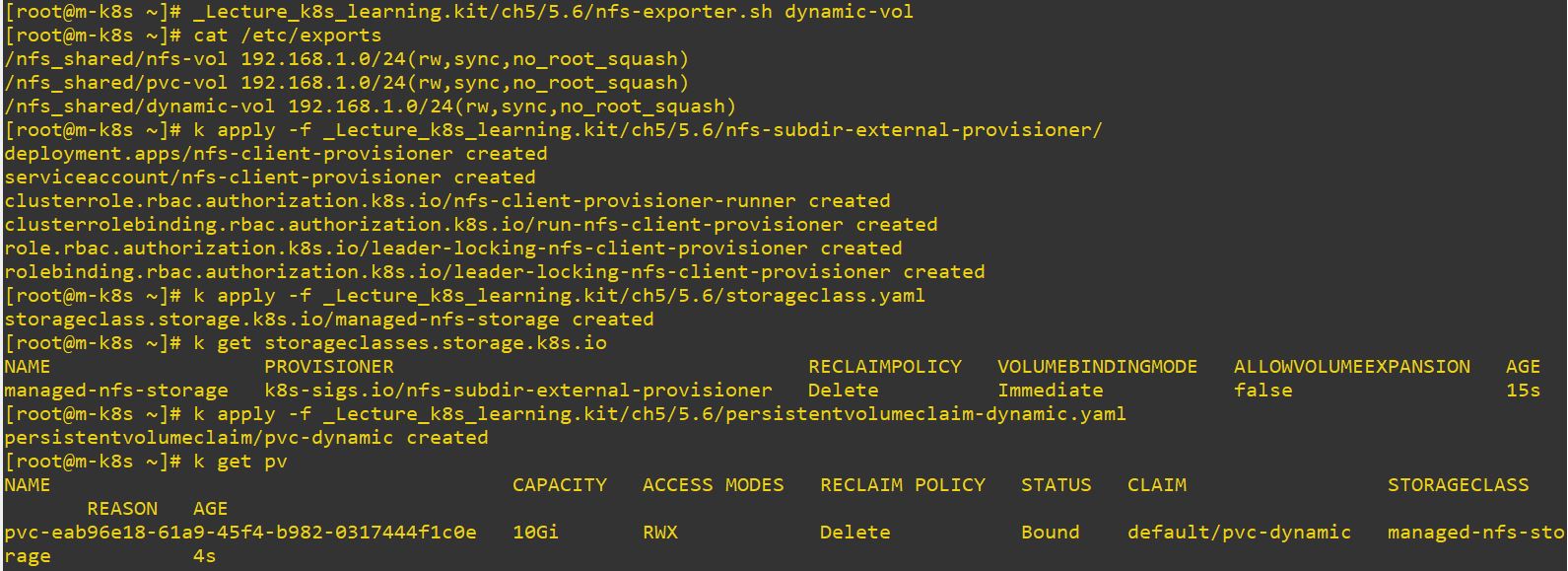
vol
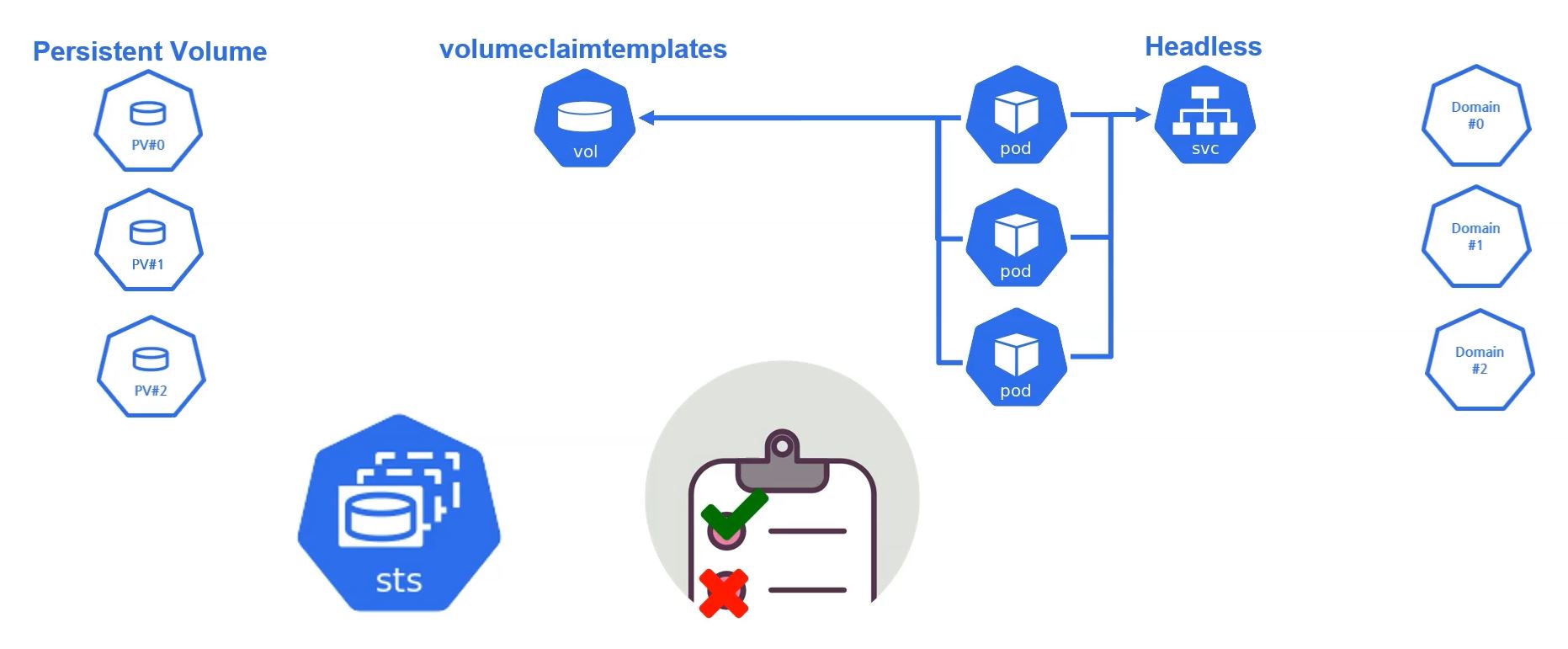
- volumeClaimTemplates
- This is a volume type only for StateFullSet.
- StateFullSet has Status and independent Domain (with Headless). It means, StateFullSet accesses Pod independently.
- Therefore, each pod has unique value and status.
- When this pod claims volumeClaimTemplates, it creates independent PV.
- As a result, When you deploy with StateFullSet, your Pod has independent Domain, volumeClaimTemplates and PV.

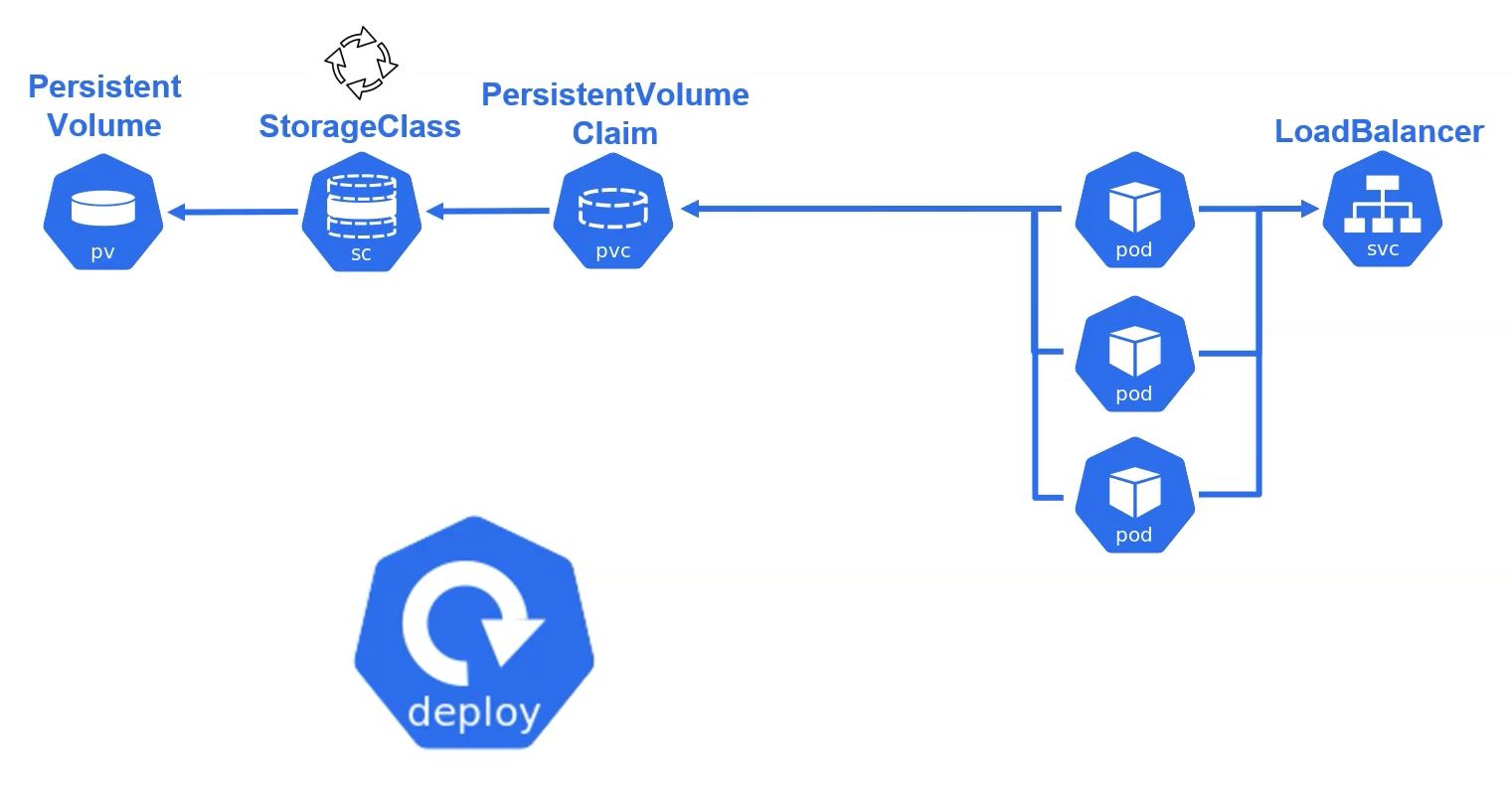
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: sts
spec:
replicas: 3
serviceName: sts-svc-domain #statefulset need it
selector:
matchLabels:
app: sts
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: sts
spec:
containers:
- name: chk-hn
image: sysnet4admin/chk-hn
volumeMounts:
- name: each-sts-backup # should be same with vol
mountPath: /backup_data
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: each-sts-backup
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ] # cause it takes only one Pod
storageClassName: "managed-nfs-storage"
resources:
requests:
storage: 20Gi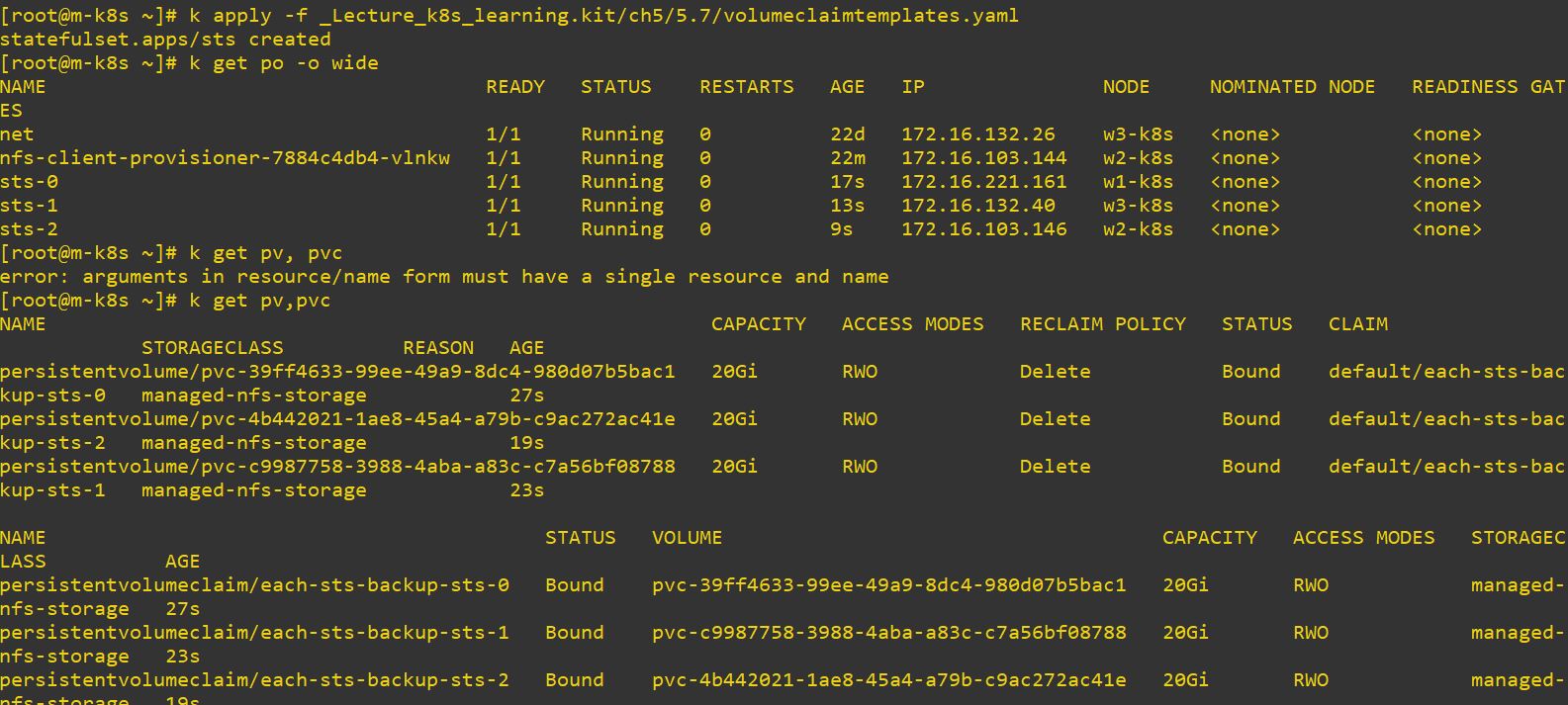
Node Contributions and Management
Cordon
- When you use cordon in specific node, that node is not affected from scheduling.
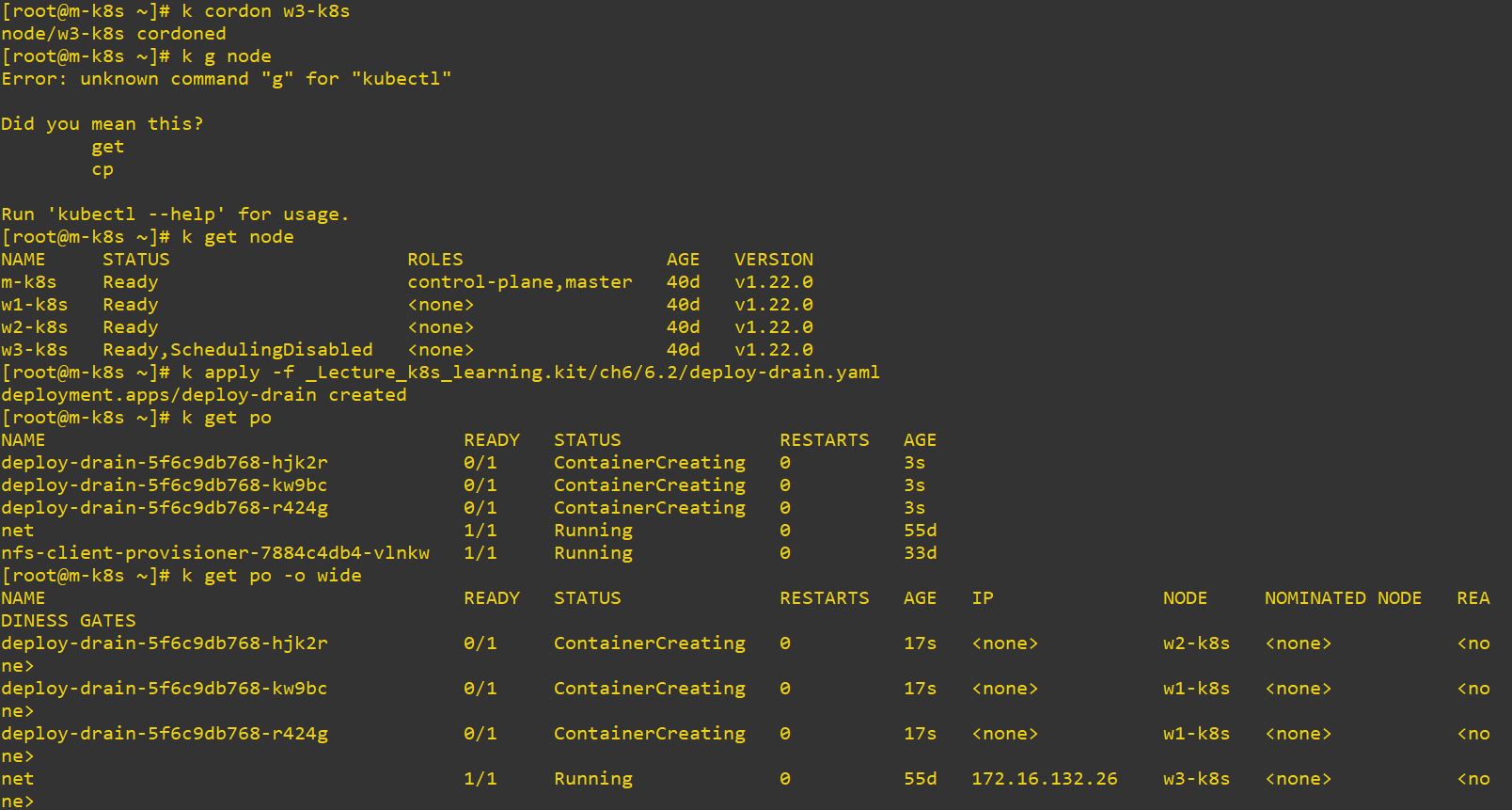
- w3-k8s is not updated, cause we set it with cordon.
Drain
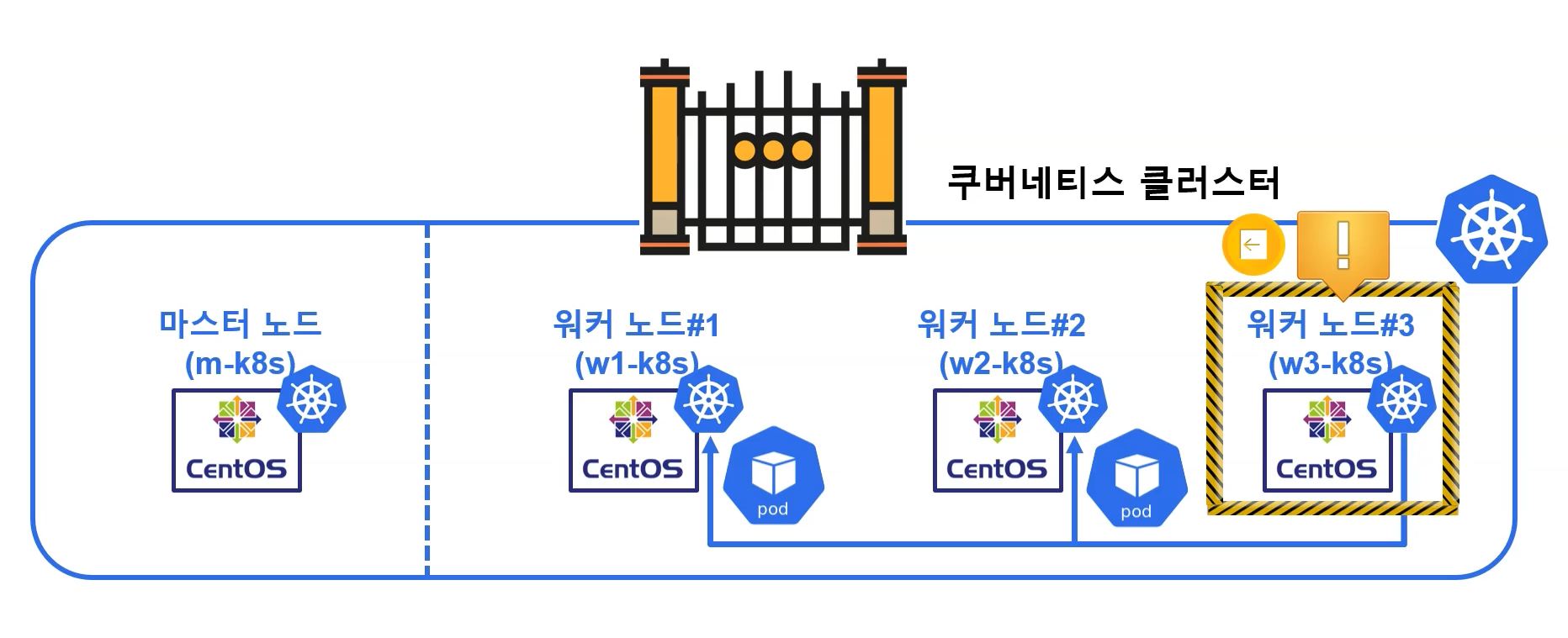
- Drain moves original pod to other nodes and set cordon on the node.
- Set drain on pod to maintanance or when the pod can occur some error.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-drain
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-drain
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-drain
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx 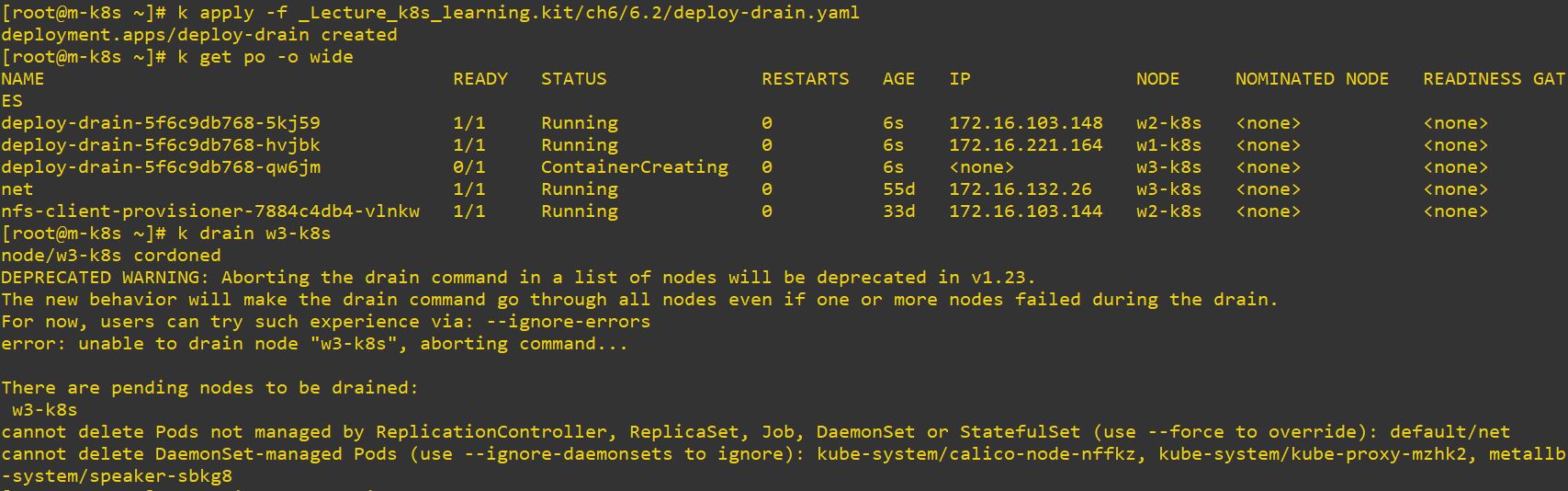
- At first, you will get this error to drain, because daemonset pod cannot be deleted.
- So you should use
--ignore-daemonsets --force
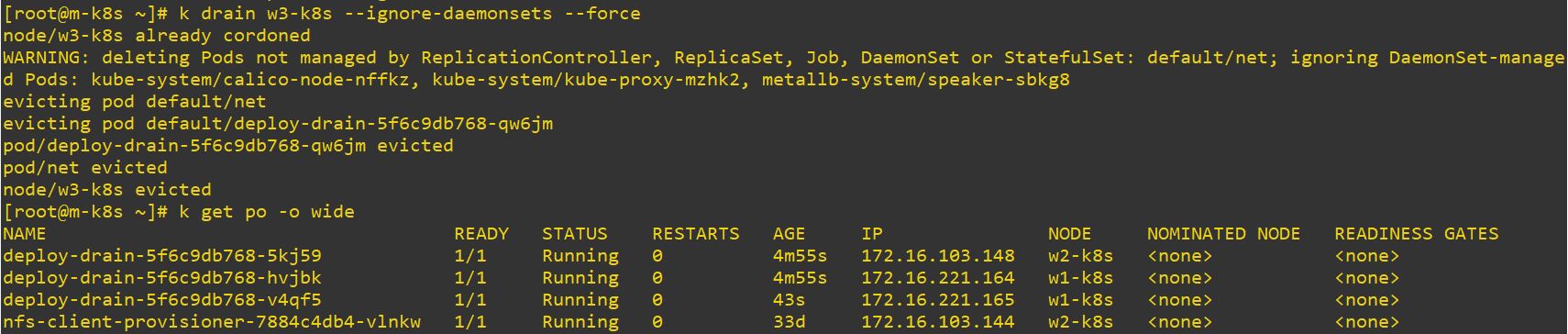
- And now you can see, we missed one pod
net.

nodeName
- Use nodeName to set where your pod should be deployed.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nodename
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
nodeName: w3-k8s # set nodeName where pod be deployed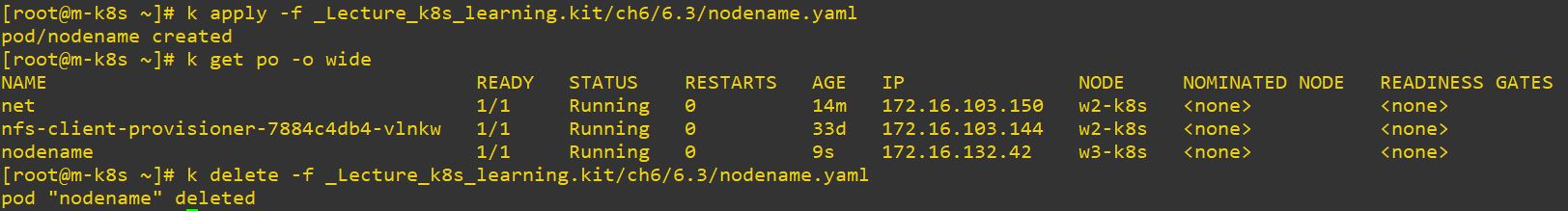
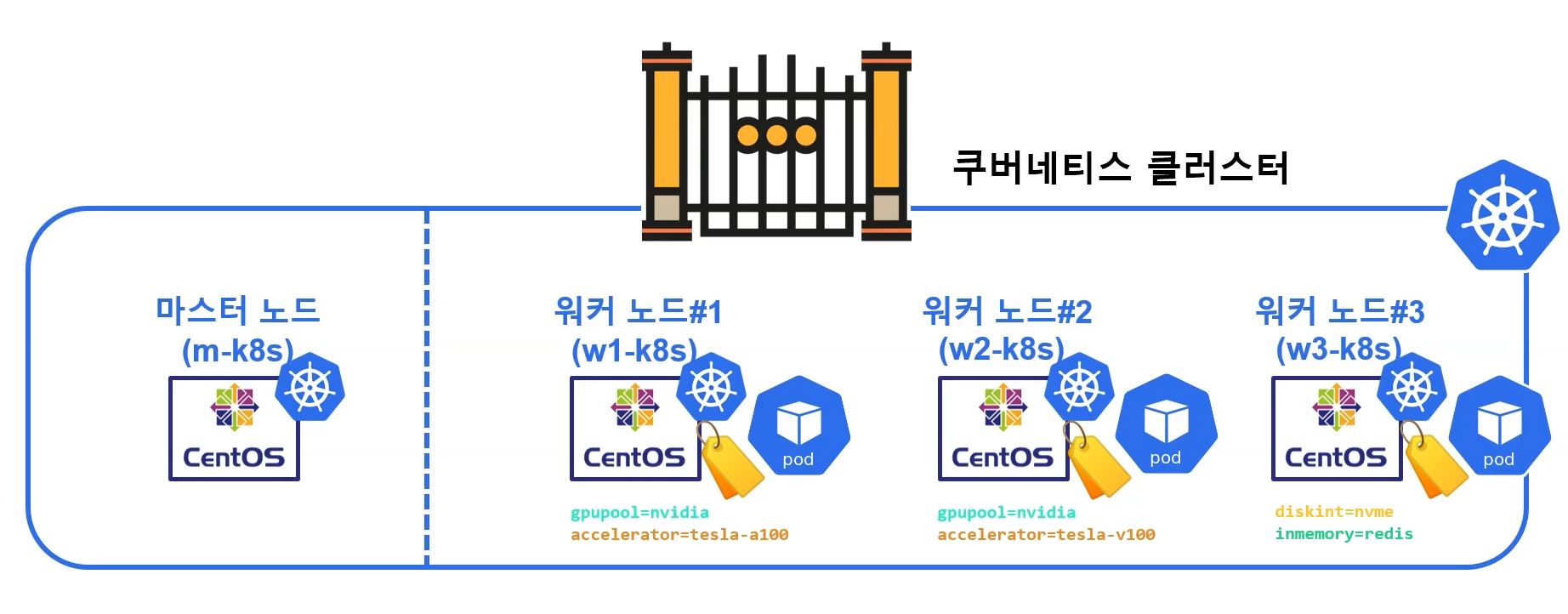
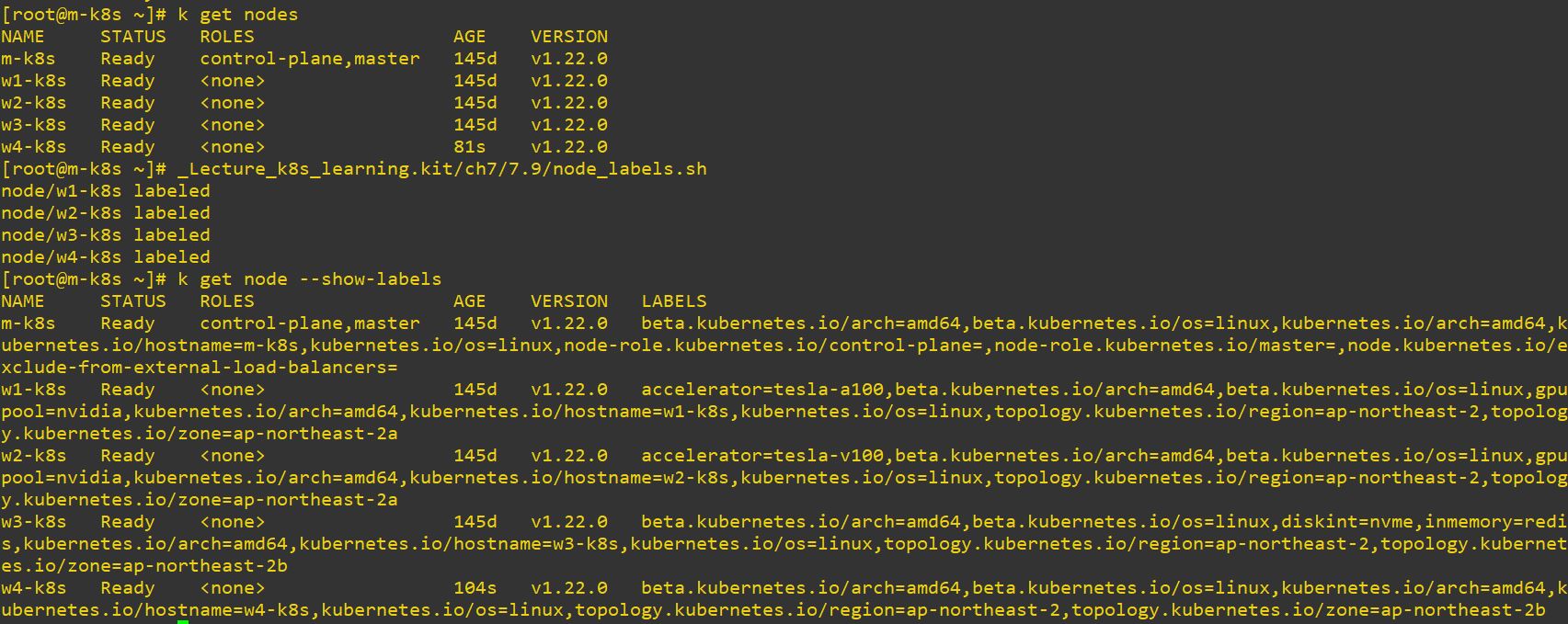
nodeLabel
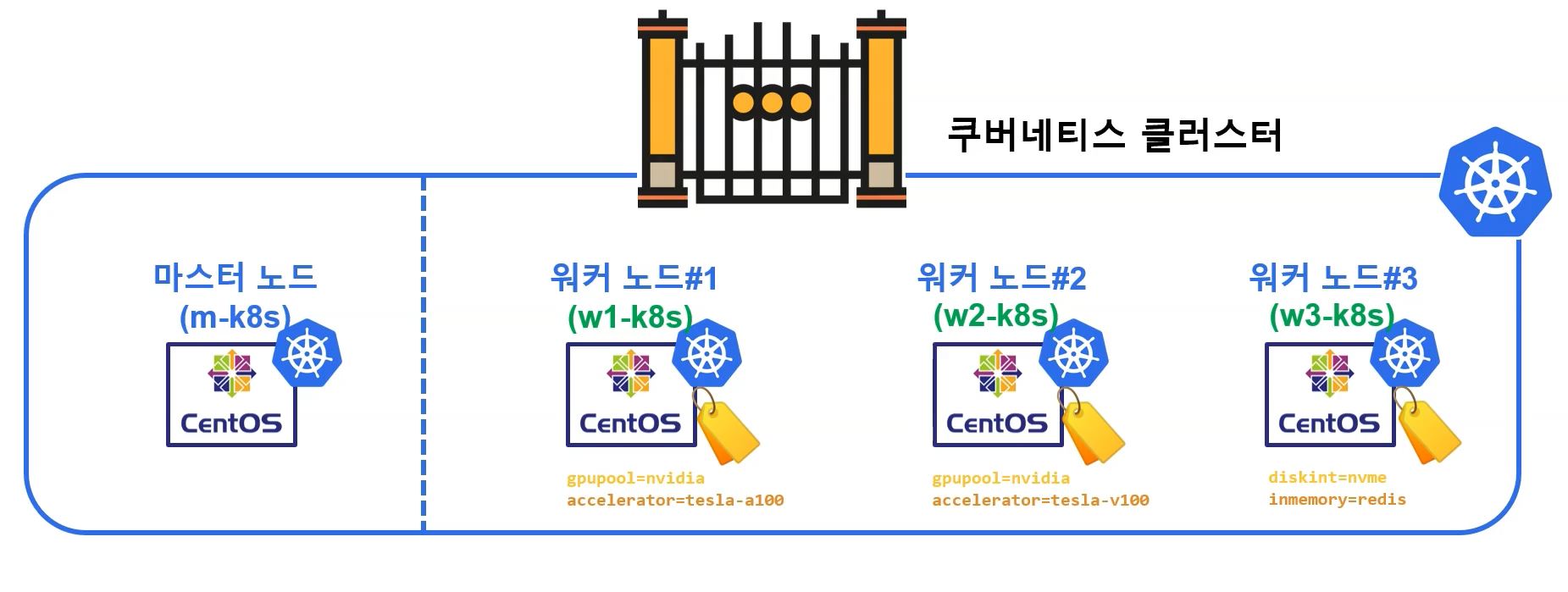
- With nodeLabel and nodeSelector you can release several pods at once.
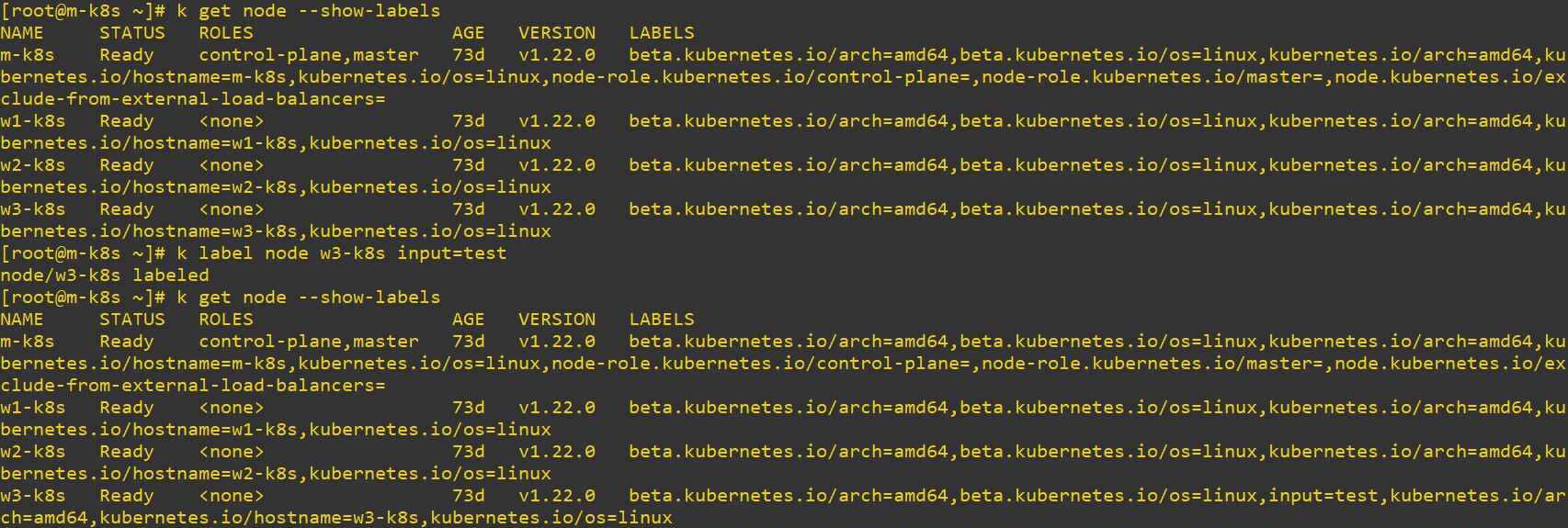
- Use
k get node --show-labelsto see labels of nodes - Use
k label node [node] [label]to add label on specific node
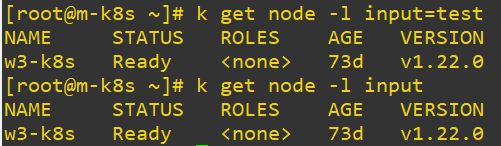
- Use
k get node -l [label]to search nodes with label =symbol on label seperate key(left) value(right) and of course you can use only one when you search.
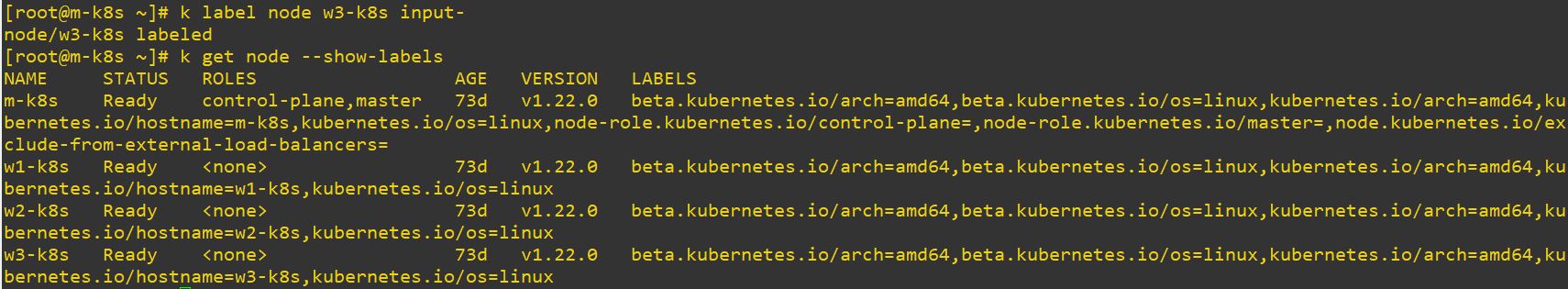
- Use
k label node [node] [label]-to delete label on node
#!/usr/bin/env bash
kubectl label node w1-k8s gpupool=nvidia accelerator=tesla-a100
kubectl label node w2-k8s gpupool=nvidia accelerator=tesla-v100
kubectl label node w3-k8s diskint=nvme inmemory=redis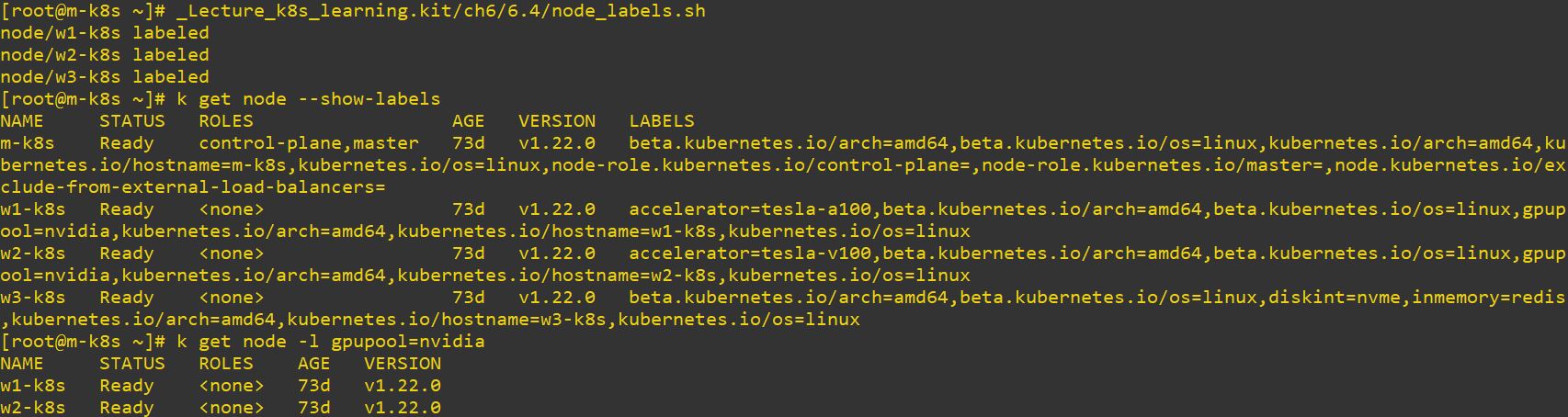
nodeSelector
- Use nodeSelector to set, in which node the pod should be deployed
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nodeselector-inmemory
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
nodeSelector:
inmemory: redis # w3-k8s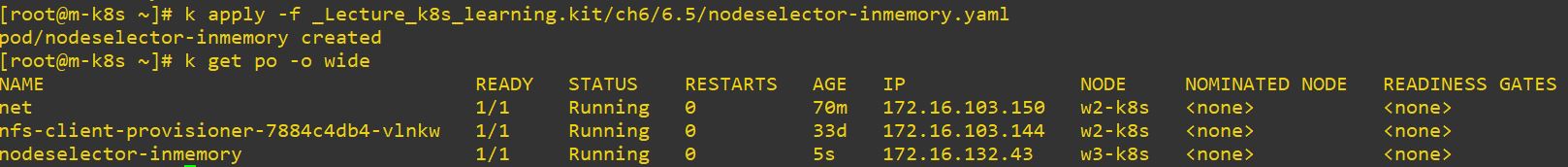
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nodeselector-gpupool
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
nodeSelector:
gpupool: nvidia # w1-k8s, w2-k8s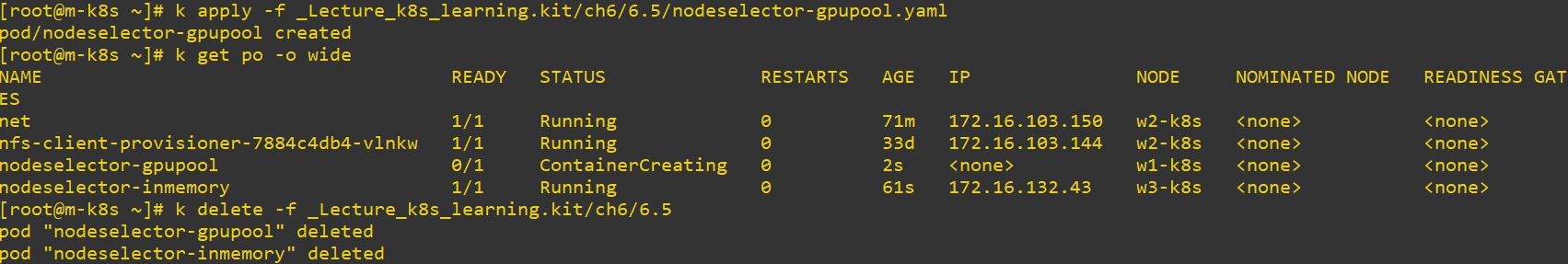
nodeAffinity
- Use nodeAffinity to set more felexible confitions.
- There is two options to set: requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution and preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution
- Operators:
- In vs NotIn
- Exists vs DoesNotExist
- Gt vs Lt
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nodeaffinity
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions: # inmemory-redis
- key: inmemory
operator: In
values:
- redis
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx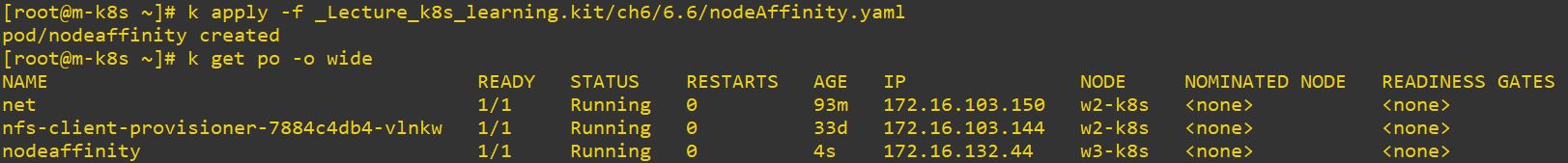
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: nodeaffinity-preferred
name: nodeaffinity-preferred
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nodeaffinity-preferred
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nodeaffinity-preferred
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
affinity:
nodeAffinity: # It will search nodes who has gpupool-nvidia and prefer node who has accelerator-tesla-a100 to release
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions: # gpupool-nvidia
- key: gpupool
operator: In
values:
- nvidia
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- weight: 1 # higher means more affinity
preference:
matchExpressions: # accelerator-tesla-a100
- key: accelerator
operator: In
values:
- tesla-a100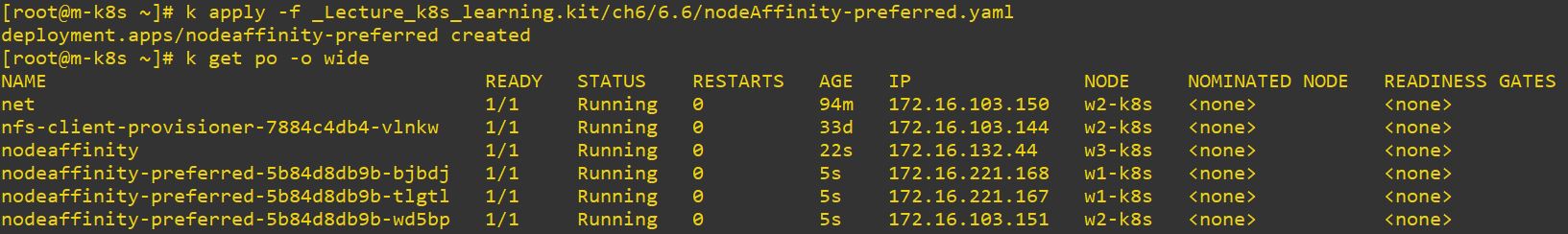
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: anti-nodeaffinity
name: anti-nodeaffinity
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: anti-nodeaffinity
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: anti-nodeaffinity
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
affinity:
nodeAffinity: # It will search nodes who has gpupool-nvidia and unprefer node who has accelerator-tesla-a100 to release
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions: # gpupool-nvidia
- key: gpupool
operator: In
values:
- nvidia
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- weight: 1
preference:
matchExpressions:
- key: accelerator # accelerator-tesla-a100 is unpreferred
operator: NotIn
values:
- tesla-a100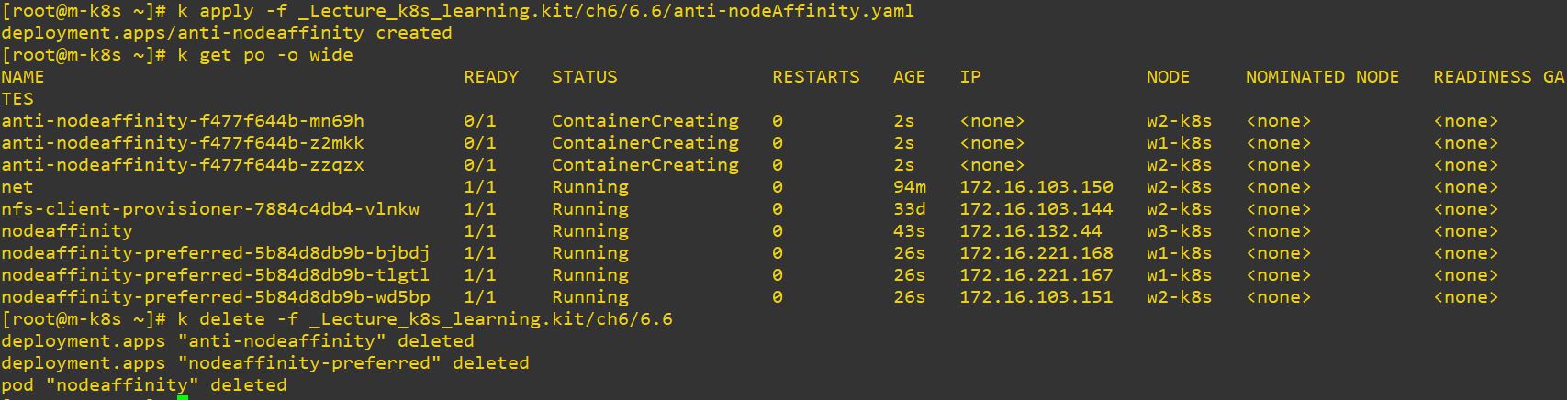
Taints & Tolerations
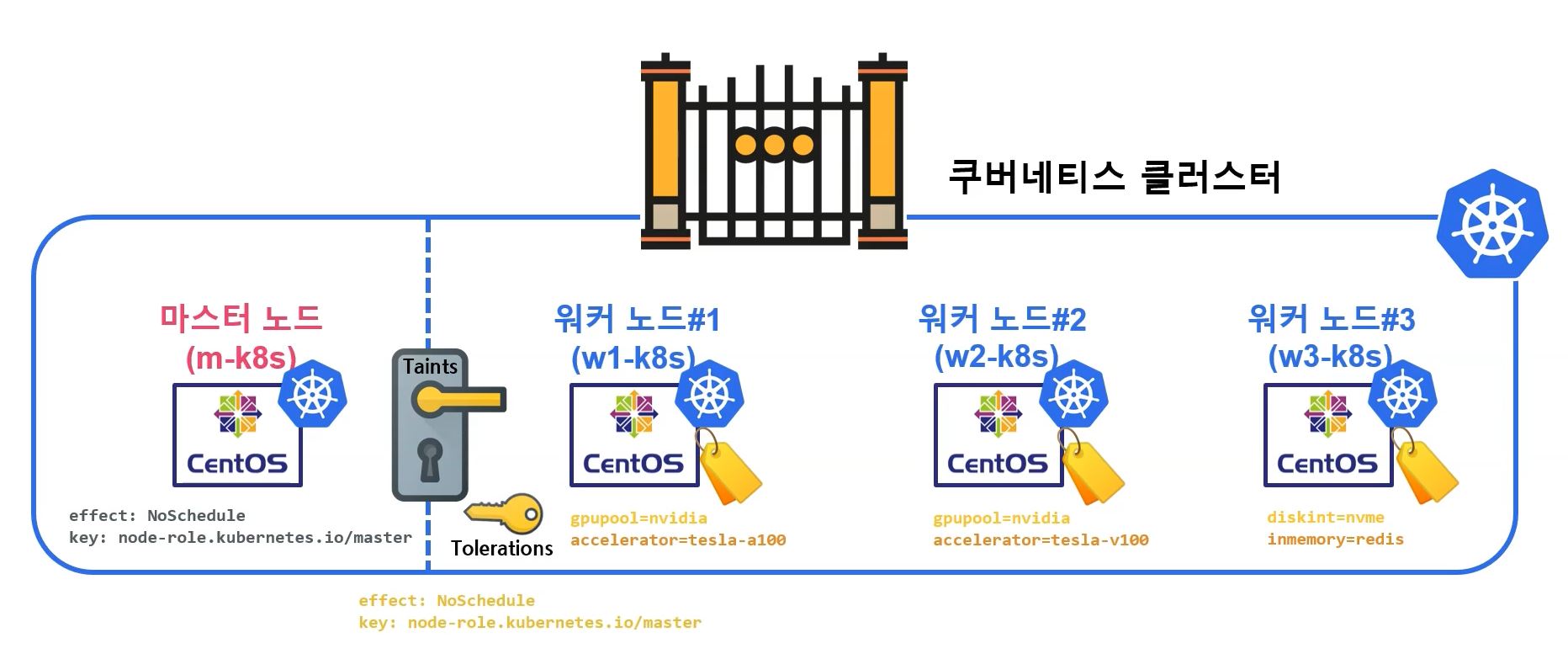
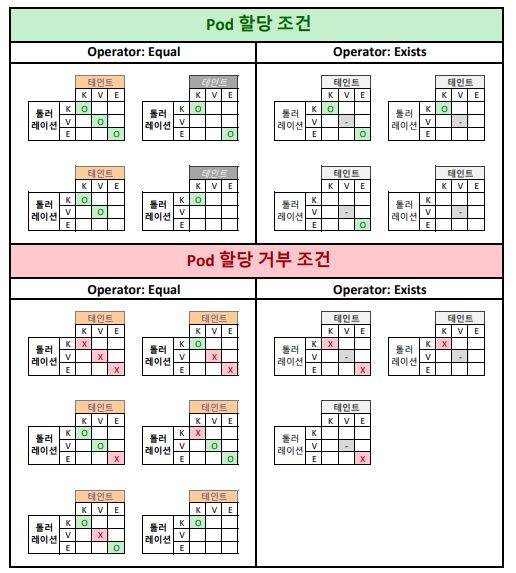
- Effect
- NoSchedule : Only deploy with Telerations
- PreferNoSchedule : When there is no more nodes to deploy, ignore Taints setting
- NoExecute : Reschedule and delete pods which has no telerations
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: daemonset-w-tolerations
labels:
app: daemonset-w-tolerations
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: daemonset-w-tolerations
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: daemonset-w-tolerations
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master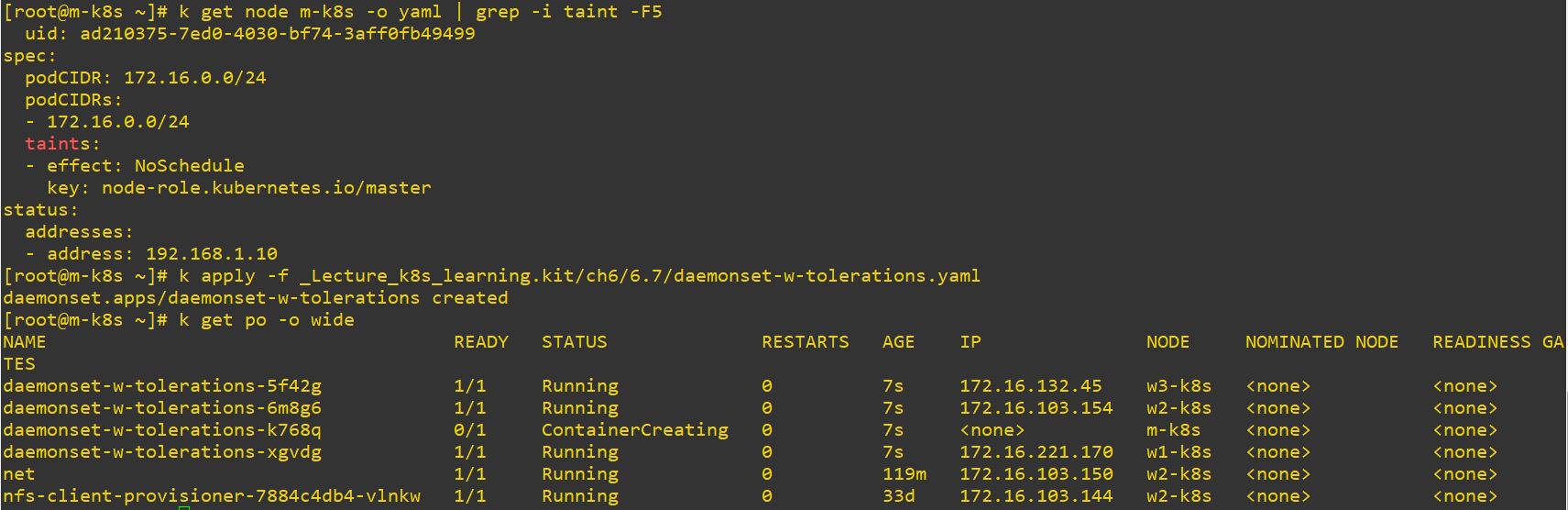
- When key has kaster, then DaemonSet can be deployed in master also.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-after-taints
name: deploy-after-taints
spec:
replicas: 6
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-after-taints
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-after-taints
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx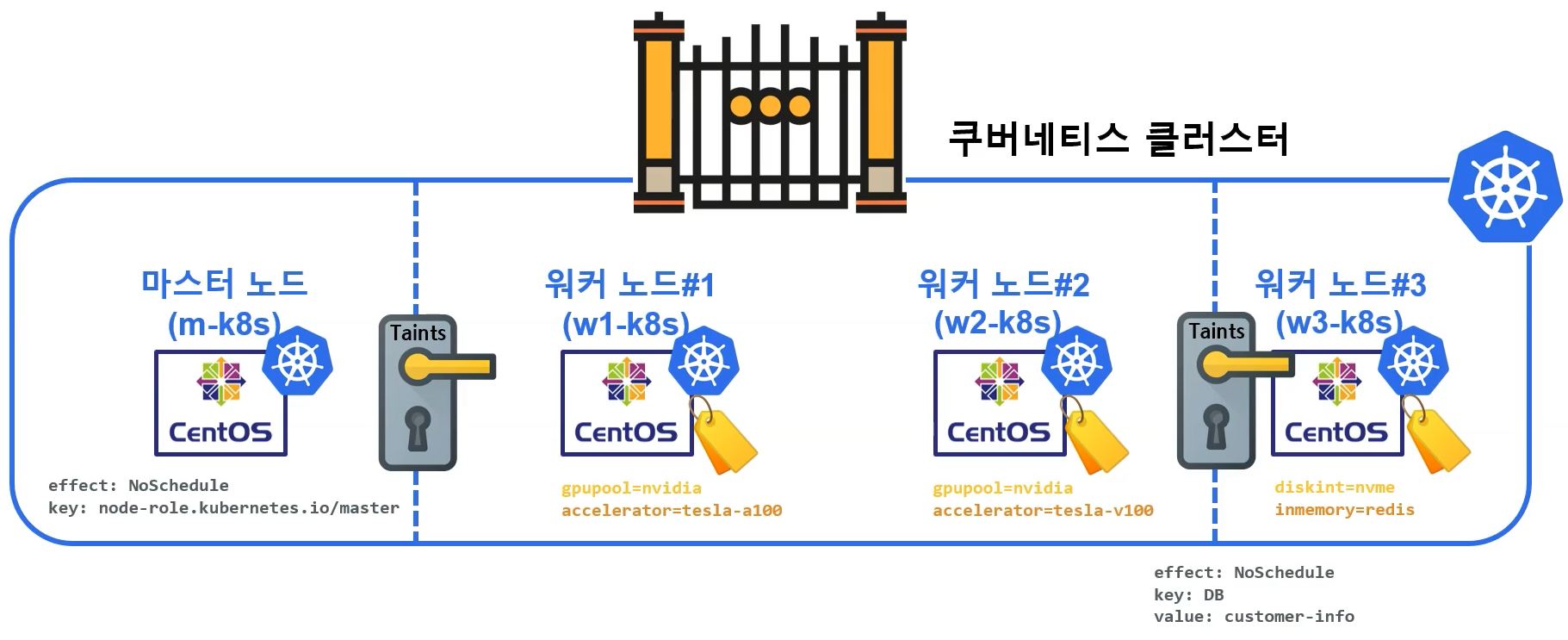
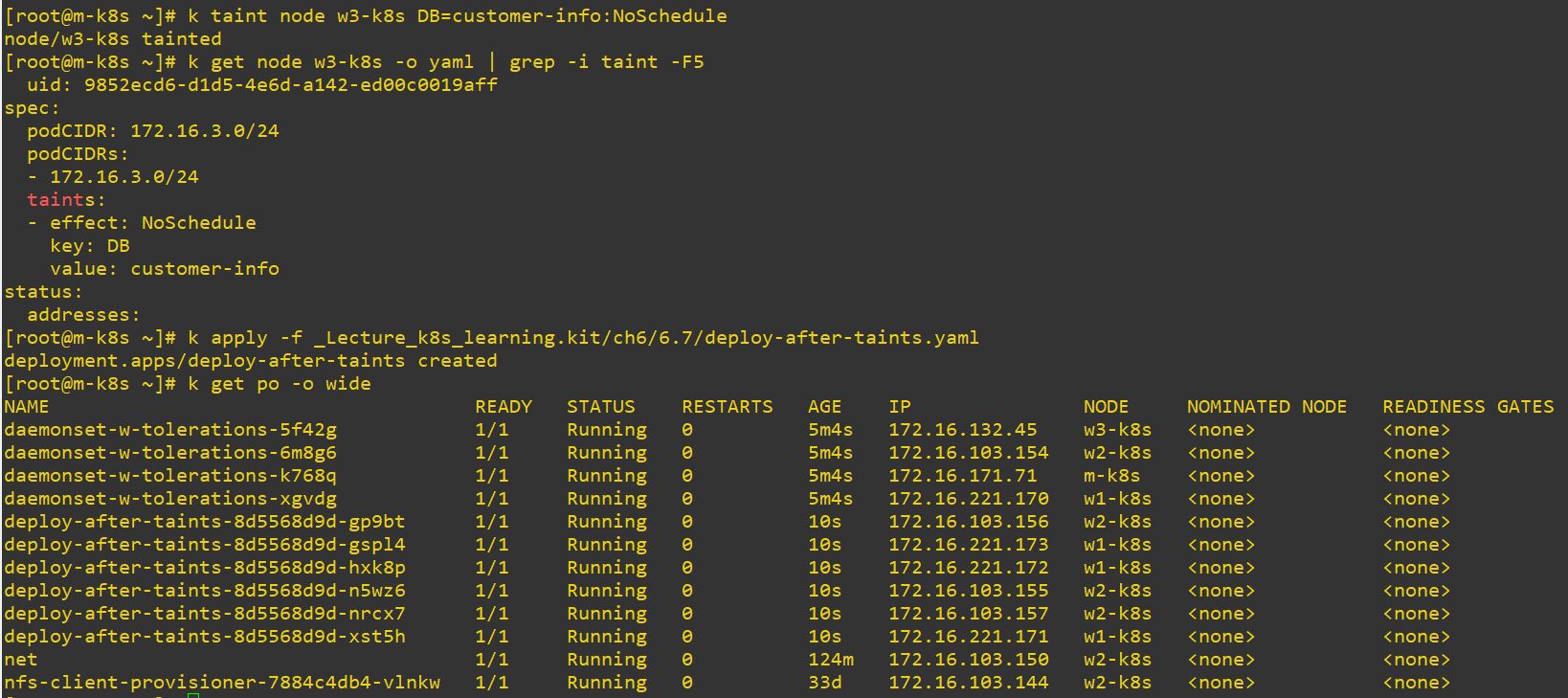
- Pod cannot be deployed on w3-k8s, because w3-k8s has taint and pod has no teleration.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-w-tolerations
name: deploy-w-tolerations
spec:
replicas: 6
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-w-tolerations
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-w-tolerations
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
tolerations: # it has telerations
- effect: NoSchedule
key: DB
value: customer-info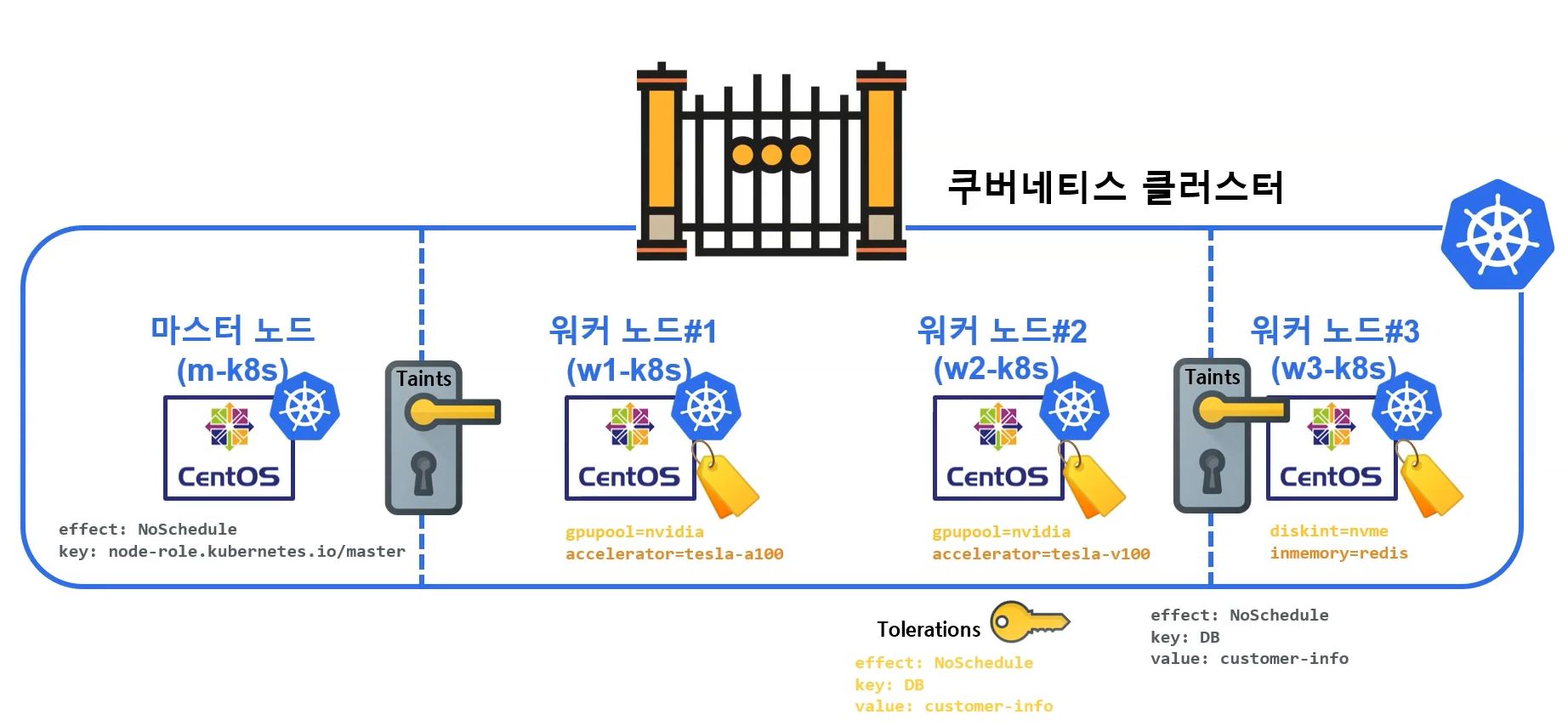
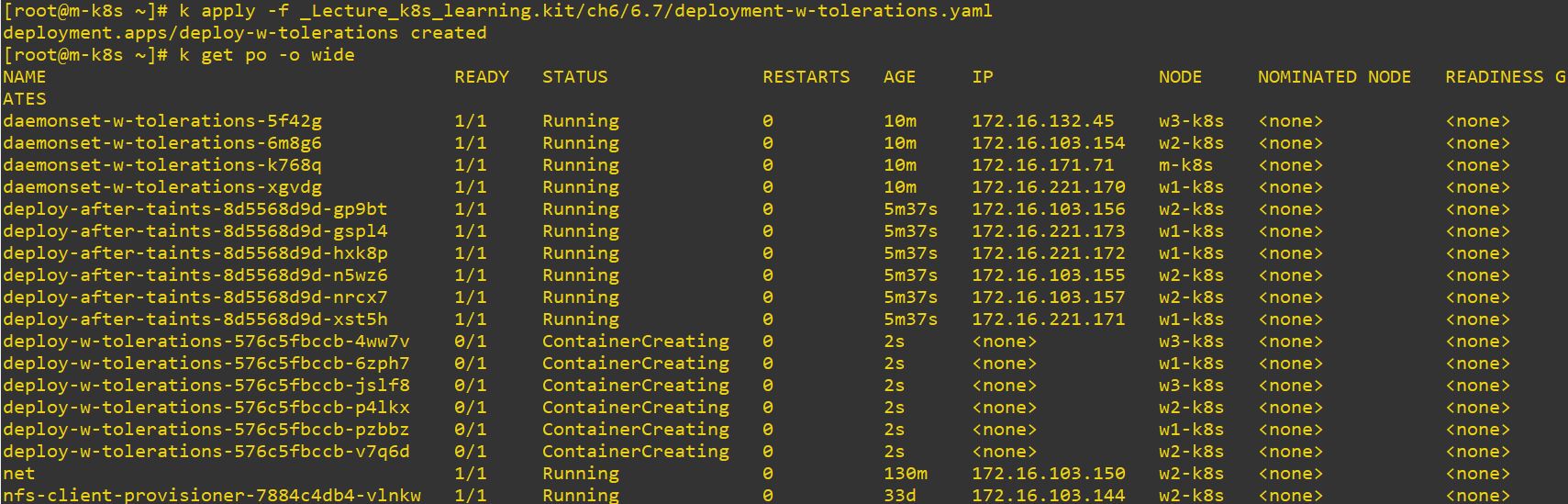
- Pod cab be deployed on w1-k8s, w2-k8s and w3-k8s, because pod has teleration.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-w-tolerations-nodeaffinity
name: deploy-w-tolerations-nodeaffinity
spec:
replicas: 6
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-w-tolerations-nodeaffinity
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-w-tolerations-nodeaffinity
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: DB
value: customer-info
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions: # it prefer node who has inmemory-redis label
- key: inmemory
operator: In
values:
- redis
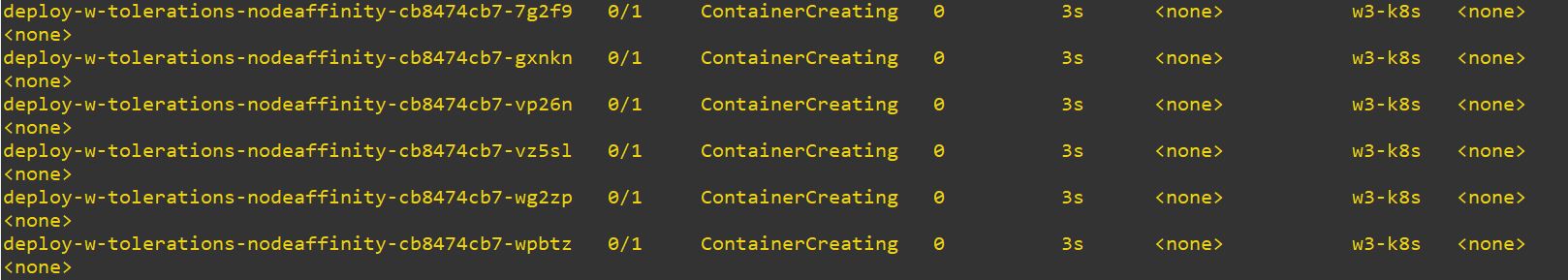
#!/usr/bin/env bash
kubectl patch node w1-k8s -p '{"spec":{"taints":[]}}'
kubectl patch node w2-k8s -p '{"spec":{"taints":[]}}'
kubectl patch node w3-k8s -p '{"spec":{"taints":[]}}'
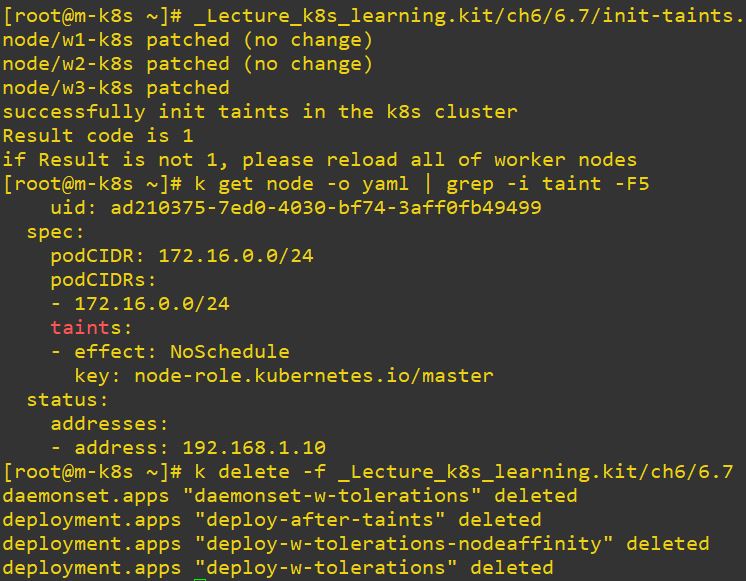
CODE=$(kubectl get node -o yaml | grep -i taints | wc -l) # Check status of taints
echo "successfully init taints in the k8s cluster"
echo "Result code is $CODE"
echo "if Result is not 1, please reload all of worker nodes"- Above code is for deleting taints on nodes.
- Or you can jsut rerun nodes to delte taints.
Pod Composition and Management
Label
- Same with node label.
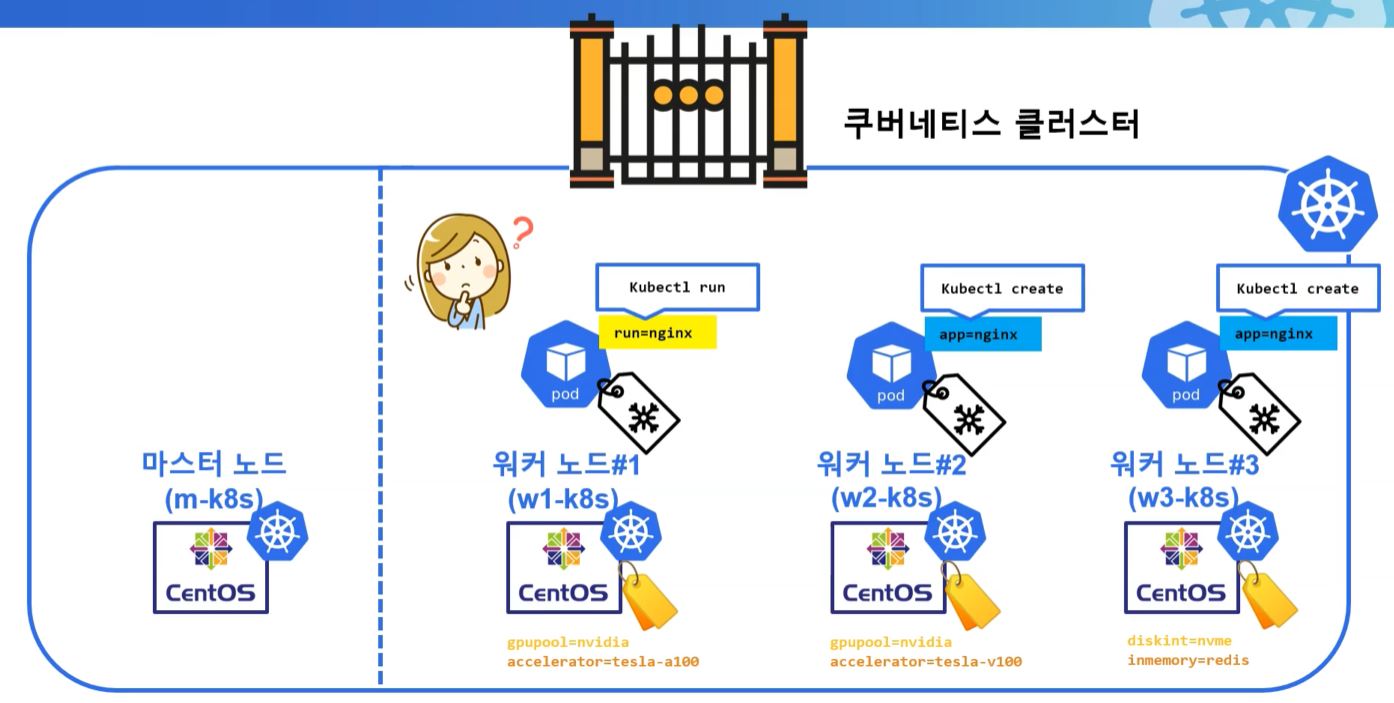
run=nginxis created fromkubectl runandapp=nginxis created fromkubectl create.
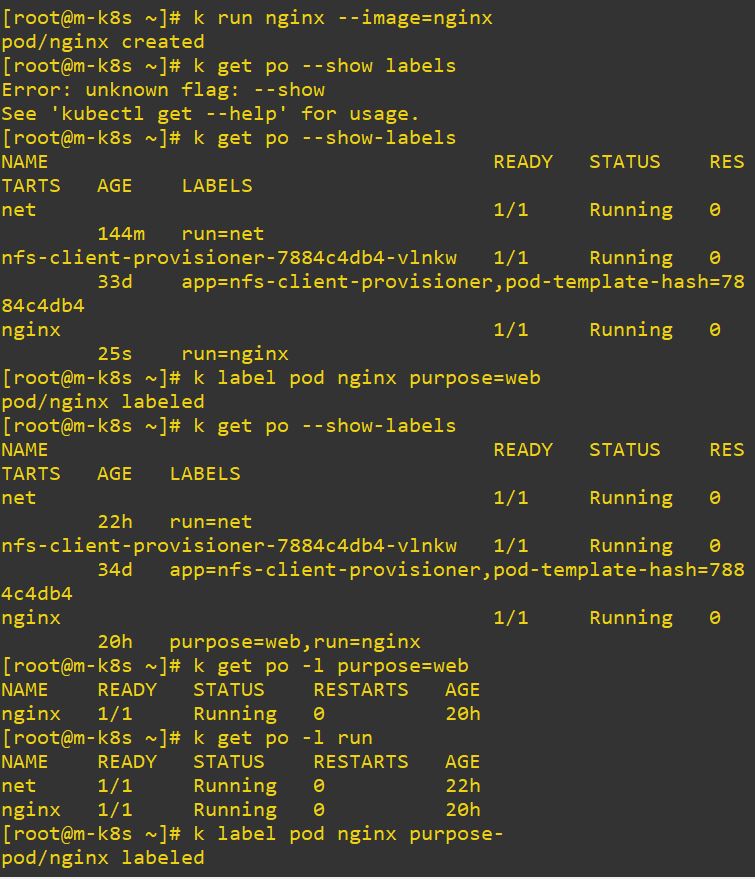
- Use
k label pod [pod] [label]to create custom label on pod.
Static Pod
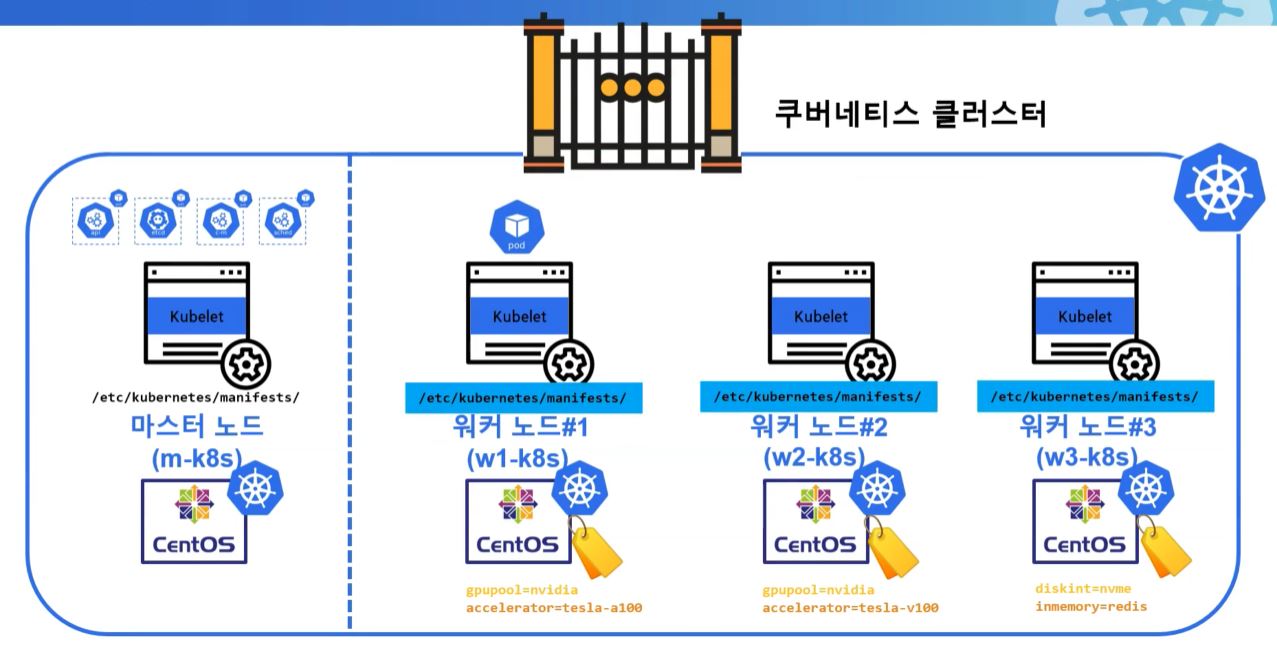
- Static Pod deploys etcd, controler manager and scheduler.
- Kubelet read yaml file and create api, etcd, customer manager and scheduler.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: static-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx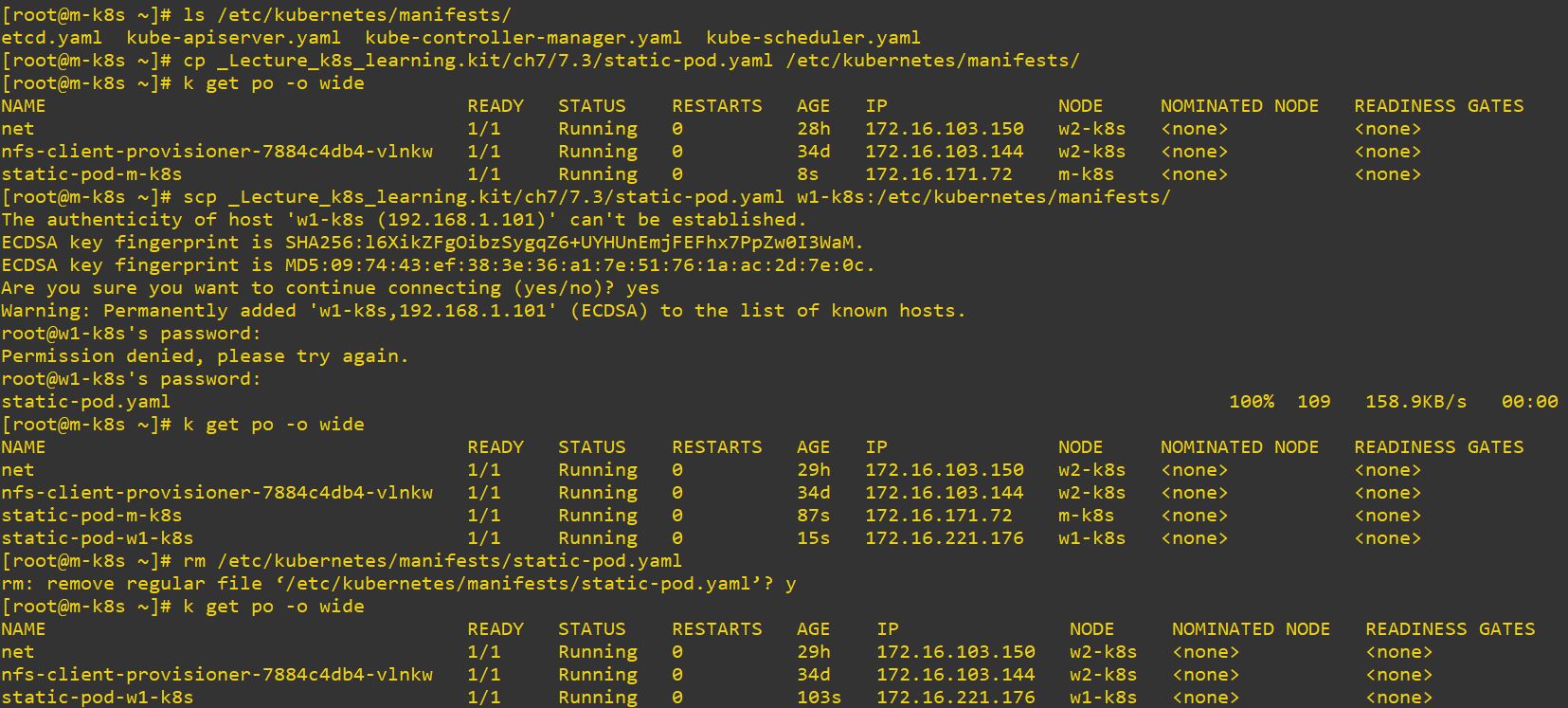

- Use
cp [Your Code Path] [Target Path]to copy yaml code - Use
scp [Your Code Path] [Target Node]:[Target Path]to copy yaml code on other node - Use
rm [Target Path]to remove copied yaml code - You can only remove yaml code on accessed node. It means, to delete copied yaml code on other node, you should access other node.
restartPolicy
- Options
- Always : always restart
- Never : never restart
- OnFails : only restart when it failed
- Typo makes also restarting when the pod has OnFails option.
- Deployment only accept Always option, because Job is only once but deployment is continue.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
run: pod-always
name: pod-always
spec:
containers:
- image: sysnet4admin/net-tools
name: net-tools
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- nslookup kubernetes
restartPolicy: Always 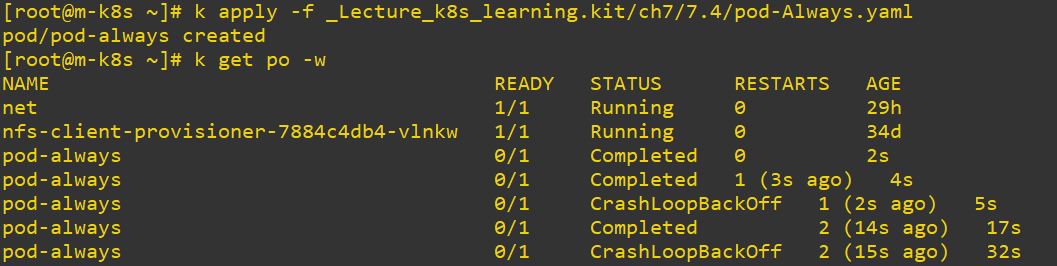
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
run: pod-never
name: pod-never
spec:
containers:
- image: sysnet4admin/net-tools
name: net-tools
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- nslookup kubernetes
restartPolicy: Never 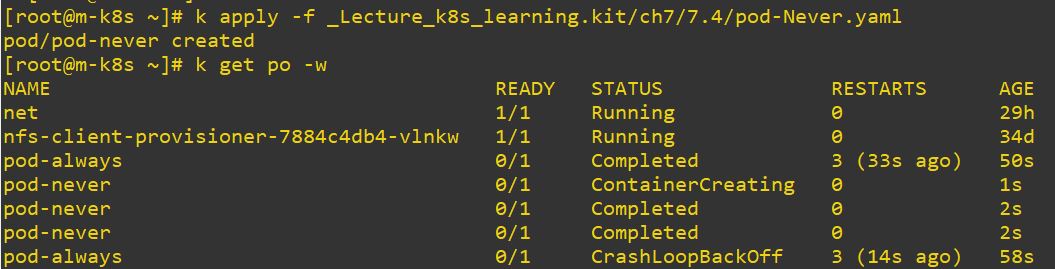
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
run: pod-onfailure
name: pod-onfailure
spec:
containers:
- image: sysnet4admin/net-tools
name: net-tools
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- nslookup kubernetes
restartPolicy: OnFailure 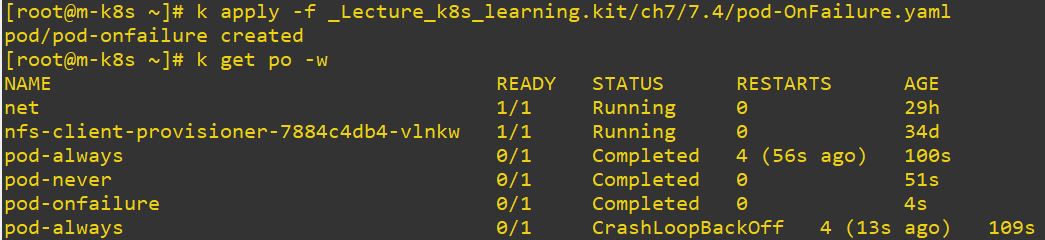
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-never-failure
name: deploy-never-failure
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-never-failure
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-never-failure
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
restartPolicy: Never # Never cannot be used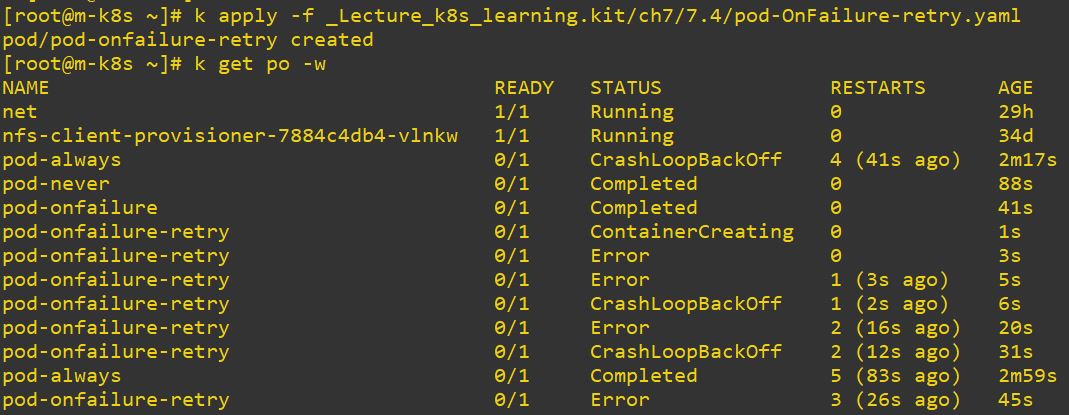
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-onfailure-failure
name: deploy-onfailure-failure
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-onfailure-failure
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-onfailure-failure
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
restartPolicy: OnFailure # Never cannot be used
Probe
- startupProbe
- Probe container status
- Kill container and execute with restartPolicy
- livenessProbe
- Probe container’s action
- Kill container and execute with restartPolicy
- readinessProbe
- Probe containers’s application whether can resolve requests
- Unpass traffic
livenessProbe
- Check Options
- exec : Execute container’s command
- httpGet : Get response from HTTP GET command
- tcpSocket : Check container’s address or port is alive
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
run: liveness-exec
name: liveness-exec
spec:
containers:
- name: tardy-nginx
image: sysnet4admin/tardy-nginx
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- cat
- /tmp/healthy-on
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 10 #it cannot start properly 
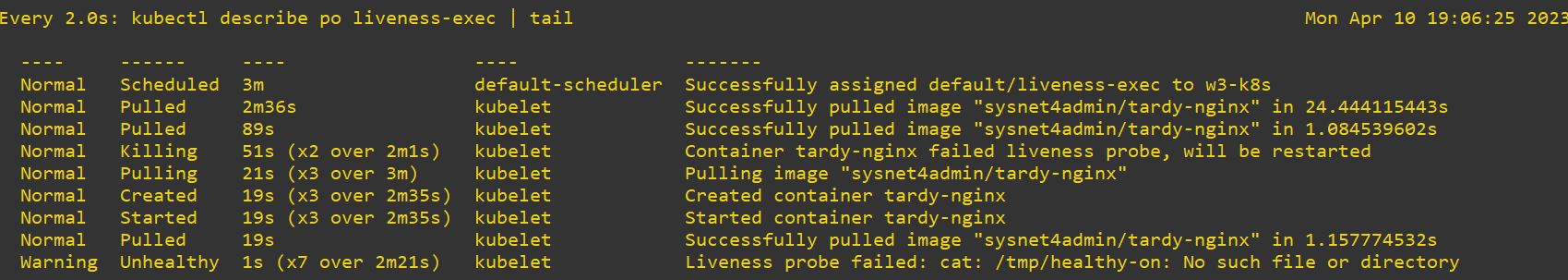
watch "kubectl describe po liveness-exec | tail"show changing continue- This cannot be worked, because initialDelaySeconds is 10 and preiodSeconds is also 10. It will repeat delay and initial infinity.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
run: liveness-httpget
name: liveness-httpget
spec:
containers:
- name: healthz-nginx
image: sysnet4admin/healthz-nginx
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthz
port: 80
httpHeaders:
- name: purpose
value: health-check
initialDelaySeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 3
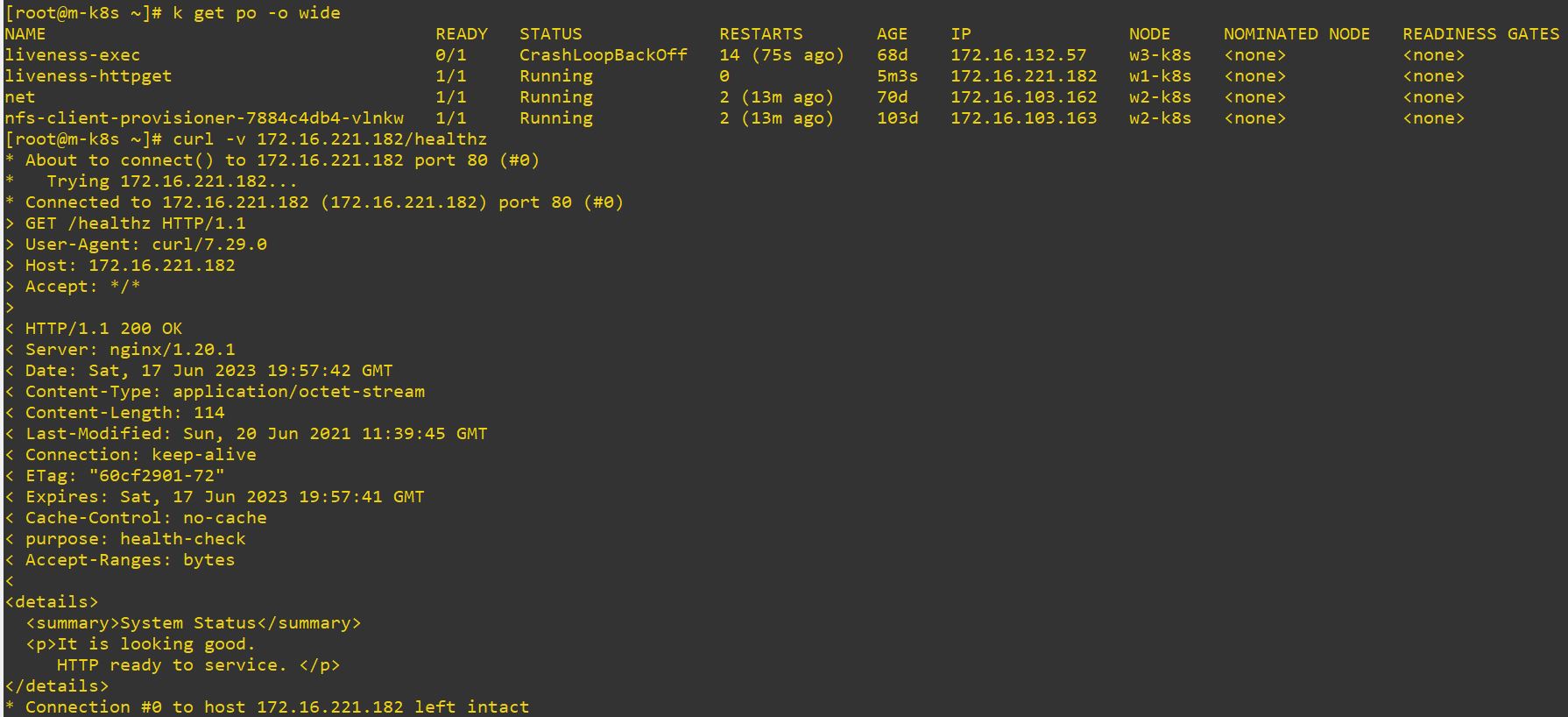
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
run: liveness-tcpsocket
name: liveness-tcpsocket
spec:
containers:
- name: healthz-nginx
image: sysnet4admin/healthz-nginx
livenessProbe:
tcpSocket:
port: 80
initialDelaySeconds: 3
periodSeconds: 3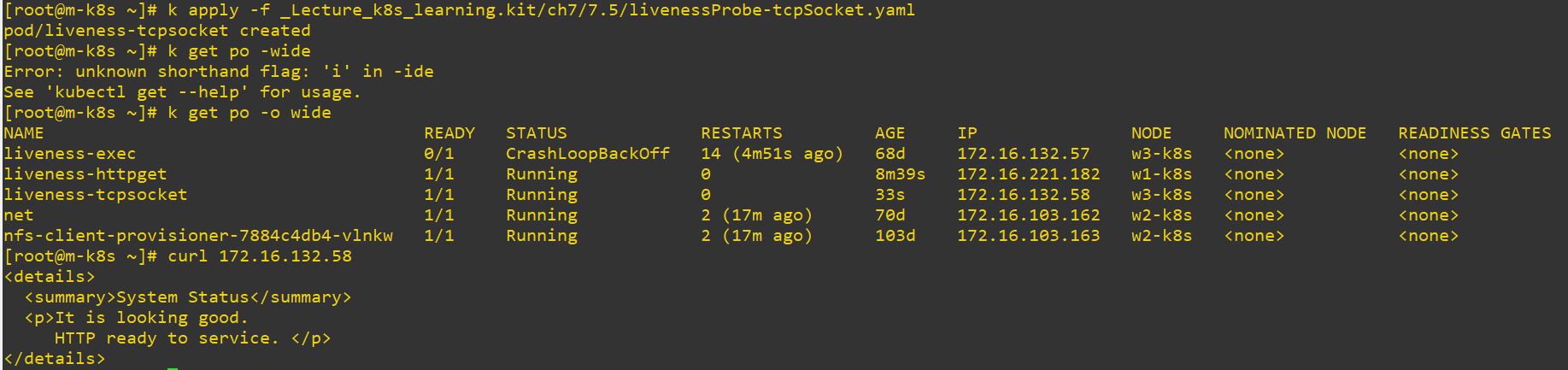
readinessProbe
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
run: readiness-exec
name: readiness-exec
spec:
containers:
- name: tardy-nginx
image: sysnet4admin/tardy-nginx
readinessProbe: // we will use a pod
exec:
command:
- cat
- /tmp/healthy-on
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 5 // we will give short periodSecond.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service // service is for removing endpoint.
metadata:
name: readiness-exec-lb
spec:
selector:
run: readiness-exec
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: LoadBalancer- This application will not be killed because readinessProbe doesn’t rerun the application.
- readinessProbe just remove the endpoint.
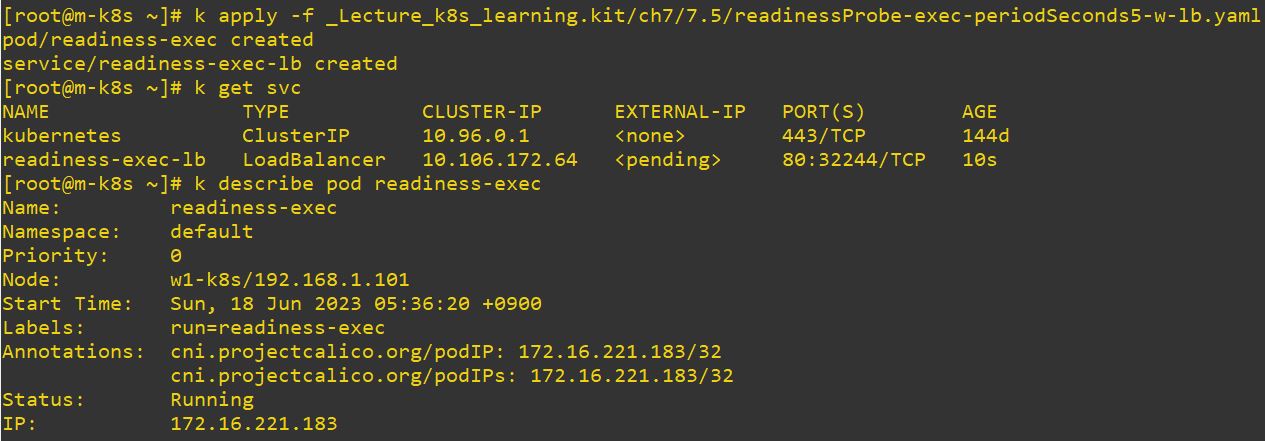
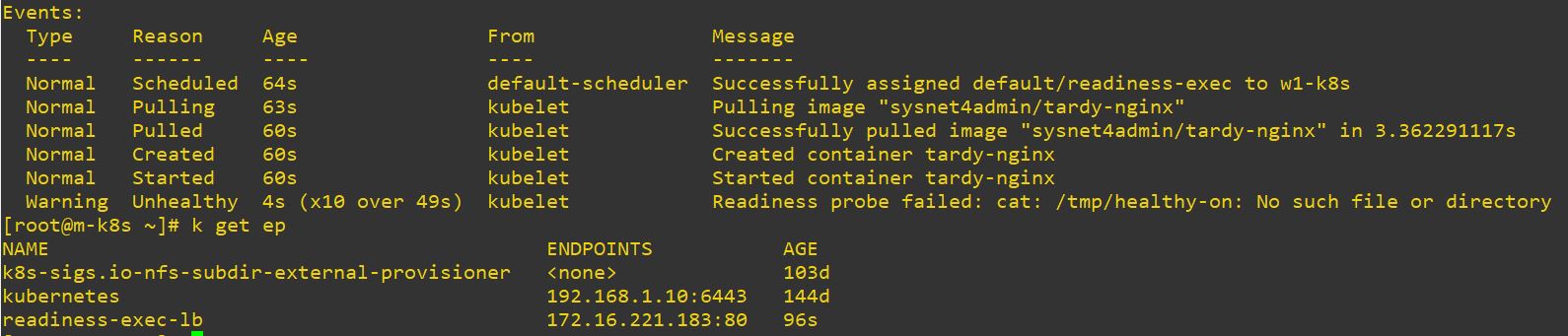
- How readinessProbe remove entpoint
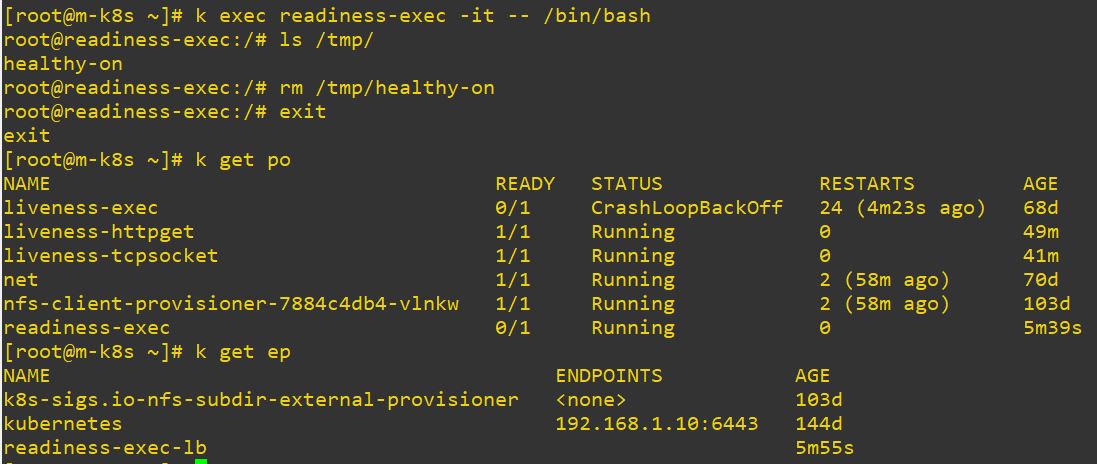
- How readinessProbe resume entpoint
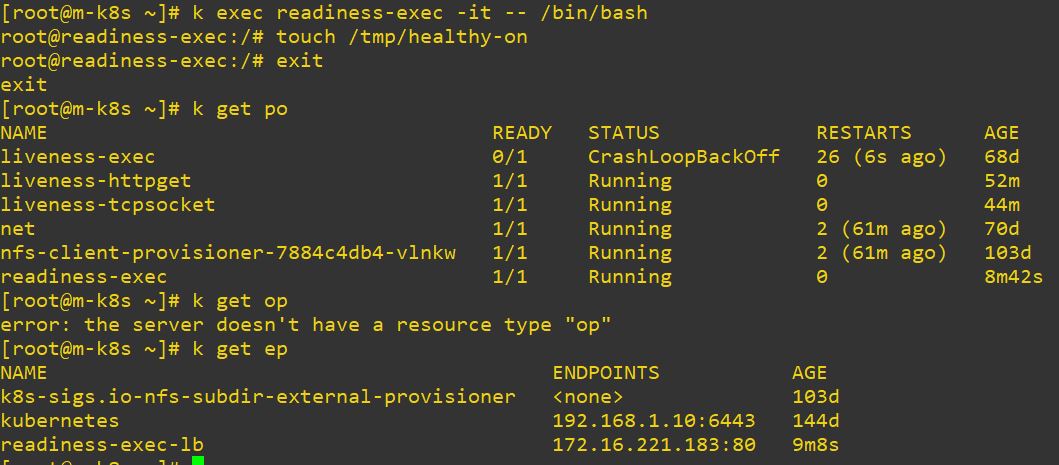
startupProbe
- startupProve is not used be alone because this is for bootup check.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
run: startup-w-others
name: startup-w-others
spec:
containers:
- name: tardy-nginx
image: sysnet4admin/tardy-nginx
startupProbe: // startupProbe
exec:
command:
- cat
- /tmp/healthy-on
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 60
livenessProbe: // livenessProbe
exec:
command:
- cat
- /tmp/healthy-on
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 10 // This is not matter because startupProbe has already made the image.
readinessProbe: // readinessProbe
exec:
command:
- cat
- /tmp/healthy-on
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 5
Init Container
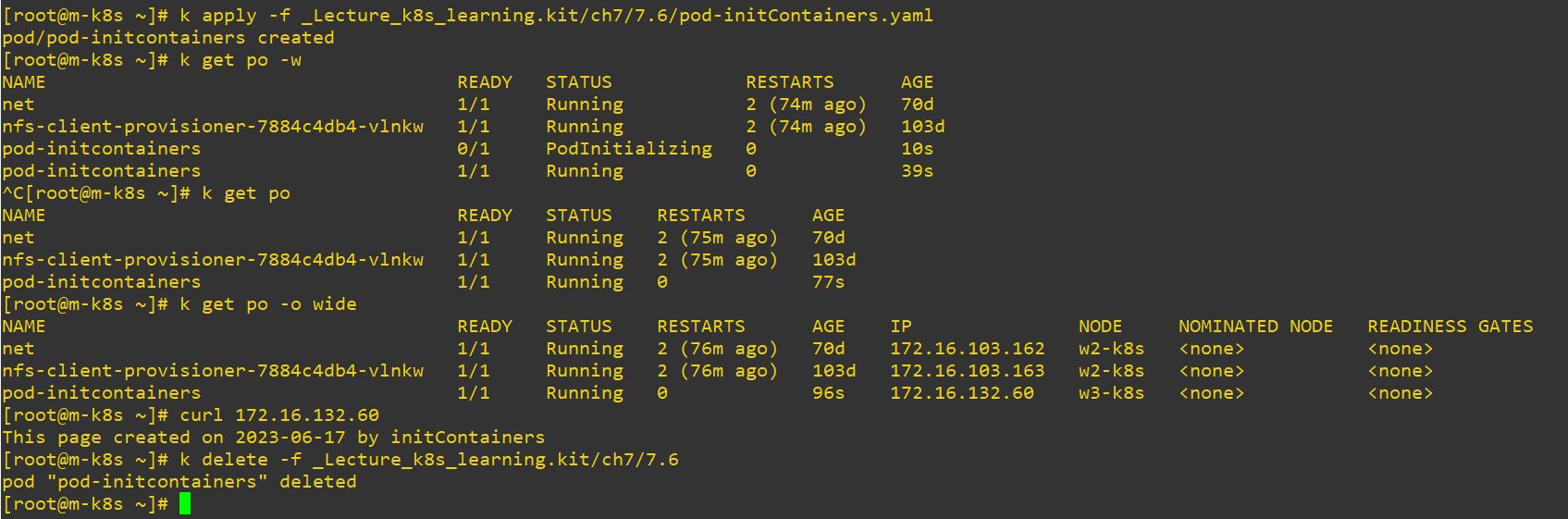
- InitContainer make easier contratuctor for pod.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-initcontainers
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: web-page
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
name: empty-directory
initContainers:
- name: html-builder
image: alpine
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /html-dir
name: empty-directory
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- echo "This page created on $(date +%Y-%m-%d) by initContainers" > /html-dir/index.html;
volumes:
- name: empty-directory
emptyDir: {}- pod initializing is from initContainer.
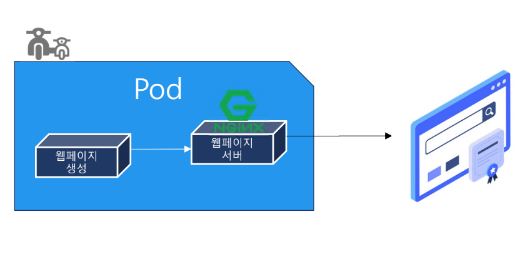
Multi Container
Sidecar
- First container make Web page and second container make server(e.g, NginX).
- This second container presents first conainer’s web page.
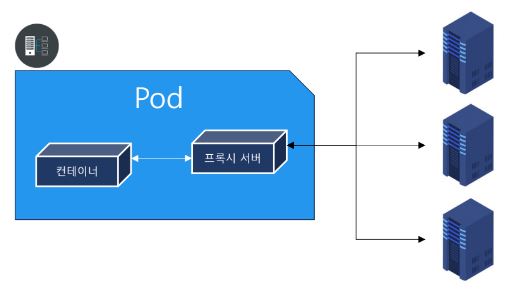
Ambassador
- Second container is Proxy server and this second container takes over to present first container.
- It means, second container communicates with extern servers.
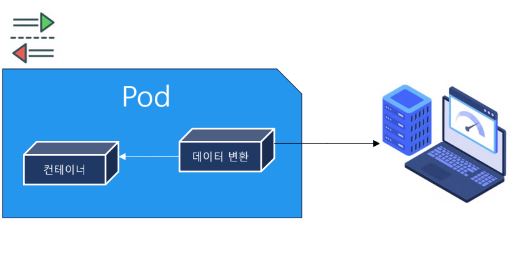
Adapter
- First container make data and second container translate this data.
- Second container expose this translated data to external.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-conf
data:
default.conf: |
server {
listen 80;
server_name nginx;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
location /stub_status {
stub_status;
allow 127.0.0.1;
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
allow 172.16.0.0/16;
deny all; #deny all other hosts
}
}apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-adapter
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: web-page
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/nginx/conf.d
name: nginx-conf
- name: adapter
image: nginx/nginx-prometheus-exporter:0.9.0
env:
- name: SCRAPE_URI
value: http://localhost/stub_status
ports:
- containerPort: 9113
volumes:
- name: nginx-conf
configMap:
name: nginx-conf
items:
- key: default.conf
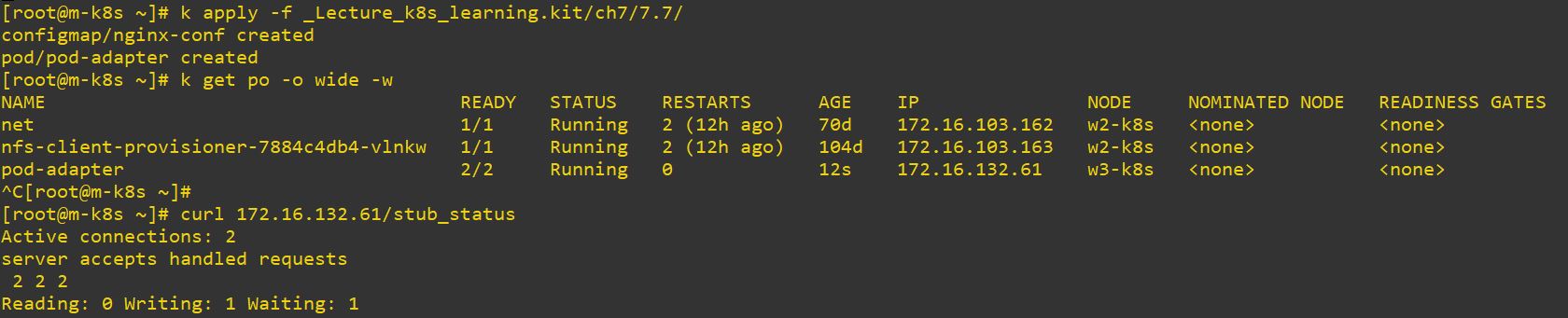
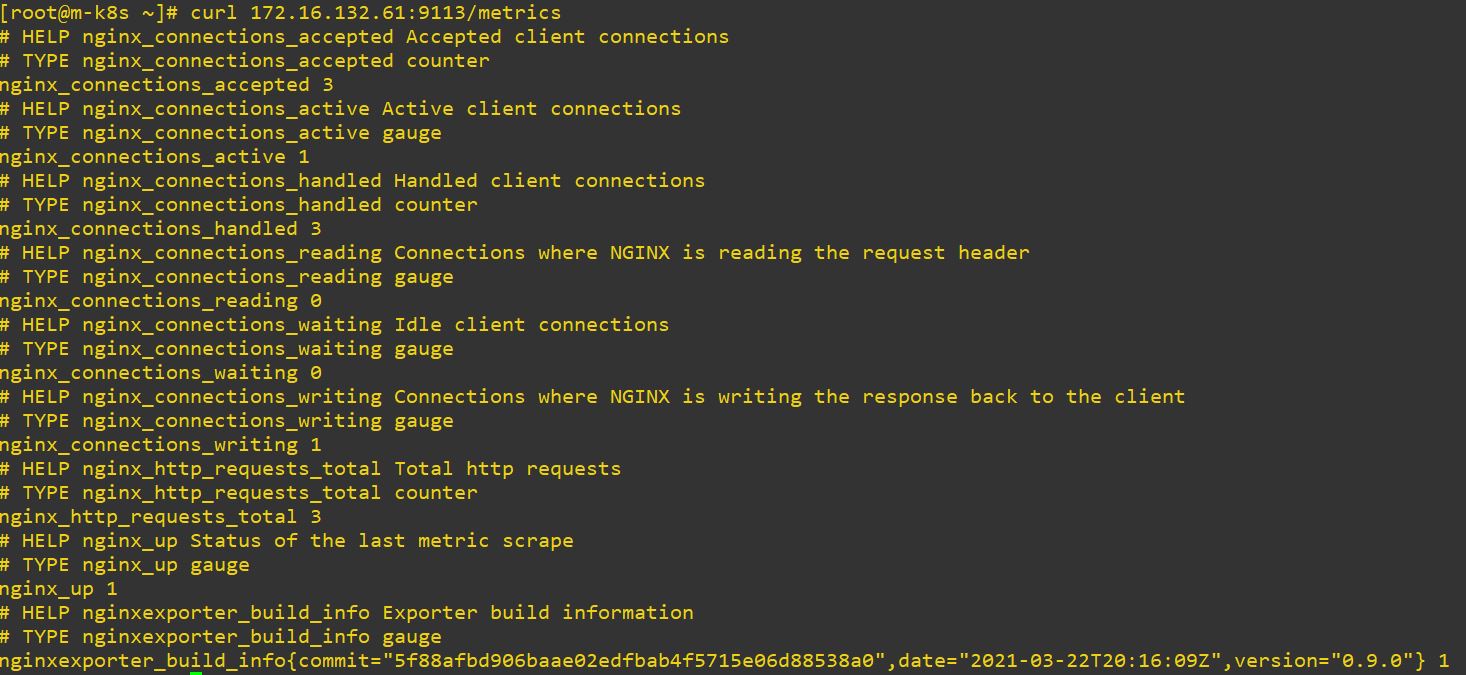
path: default.conf- In this case, first container is NginX(server) and second container is Prometheus(translator).
Pod Affinity and Anti-Affinity
- You can use Pod affinity to group your pods.
- You can use Anti-Affinity to exclude your pods from groupping pods.
Affinity
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
run: sleepy
affinity: leader
name: w1-affinity-leader
spec:
containers:
- image: sysnet4admin/sleepy
name: sleepy
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/hostname: w1-k8s- Pod will be deployed on w1 always.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-podaffinity
name: deploy-podaffinity
spec:
replicas: 4
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-podaffinity
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-podaffinity
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
affinity:
podAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: affinity
operator: In
values:
- leader
# If you want to change topologyKey,
# modify the admission controller, or disable.
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname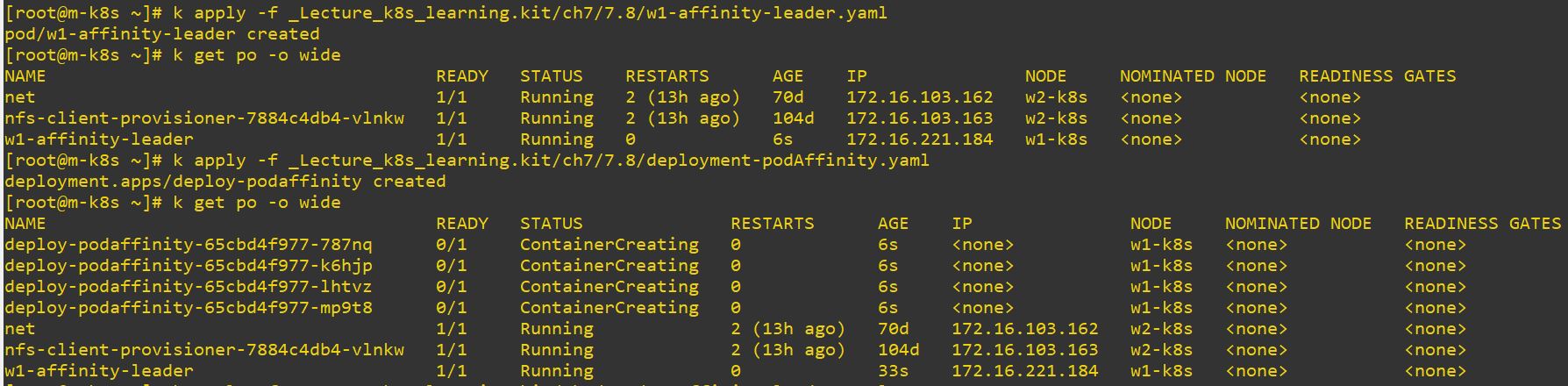
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
run: sleepy
affinity: leader
name: w3-affinity-leader
spec:
containers:
- image: sysnet4admin/sleepy
name: sleepy
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/hostname: w3-k8s- Newly created Pods will be deployed on w3 always.
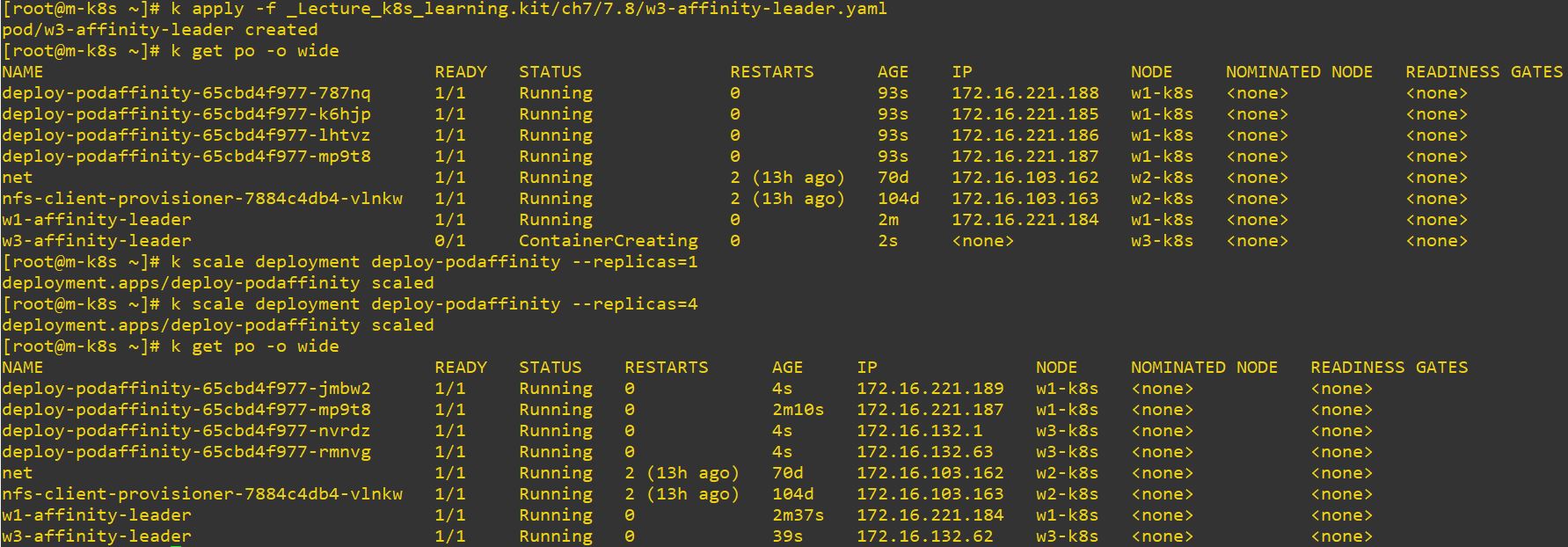
Anti-Affinity
- Anti affinity will deploy pods, where has no affinity.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-anti-podaffinity
name: deploy-anti-podaffinity
spec:
replicas: 4
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-anti-podaffinity
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-anti-podaffinity
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: affinity
operator: In
values:
- leader
# If you want to change topologyKey,
# modify the admission controller, or disable.
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname- In this case, this pods will be deployed on w2, because w1 and w3 has affinity already from previous commands.
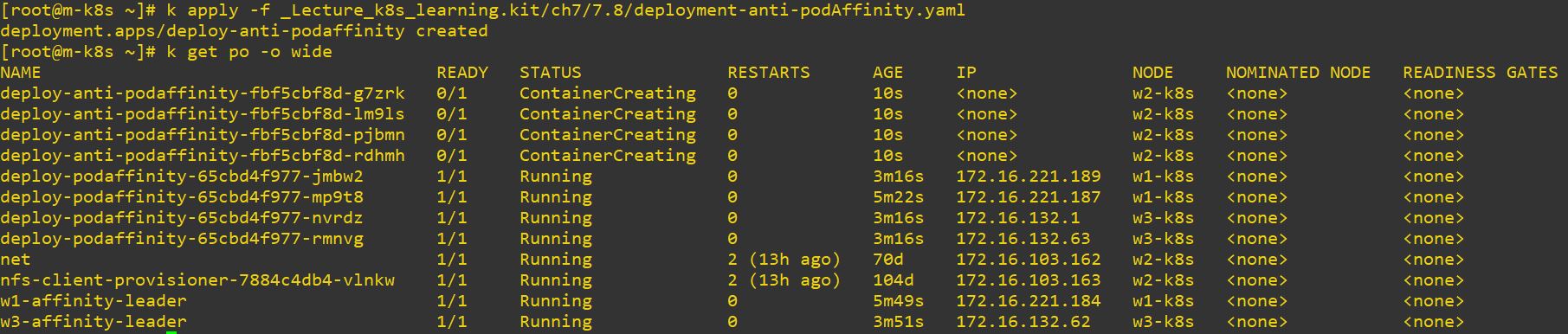
TopologySpreadConstaints
- TopologySpreadConstaints can group pods with balance eventhough specific situations.
- At first, cluster read the count of nodes and set this all nodes as region.
- Then devides this nodes and set this devided noodes as zone.
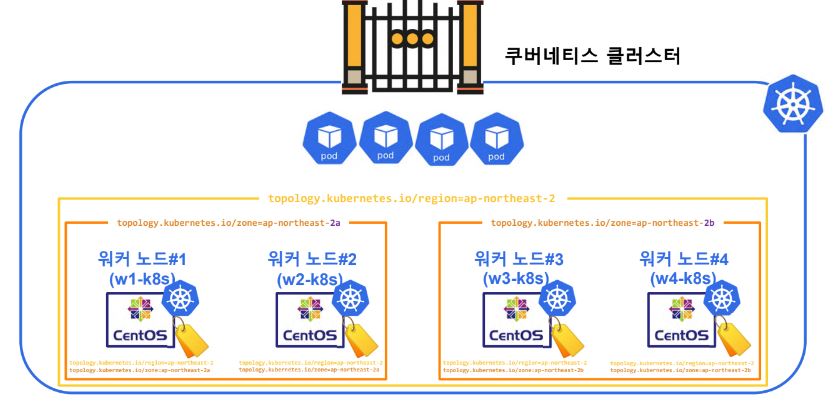
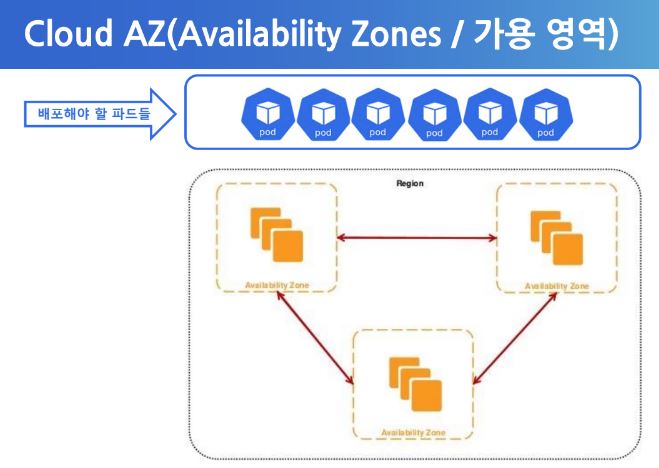
- Before we practice, we need one more worker node to make even.

#!/usr/bin/env bash
kubectl label node w1-k8s topology.kubernetes.io/region=ap-northeast-2 topology.kubernetes.io/zone=ap-northeast-2a
kubectl label node w2-k8s topology.kubernetes.io/region=ap-northeast-2 topology.kubernetes.io/zone=ap-northeast-2a
kubectl label node w3-k8s topology.kubernetes.io/region=ap-northeast-2 topology.kubernetes.io/zone=ap-northeast-2b
kubectl label node w4-k8s topology.kubernetes.io/region=ap-northeast-2 topology.kubernetes.io/zone=ap-northeast-2b- This will create label on each node(e.gregion and zone).
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-topologyspreadconstraints
name: deploy-topologyspreadconstraints
spec:
replicas: 4
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-topologyspreadconstraints
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-topologyspreadconstraints
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
topologySpreadConstraints:
- maxSkew: 1 // difference of each section should be not bigger then 1
topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/region // make same key
whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule // If this condition is false, it will not schedule any pods more.
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-topologyspreadconstraints // it will use this label, so pods are 4.
- maxSkew: 1
topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone // make same zone
whenUnsatisfiable: DoNotSchedule
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-topologyspreadconstraints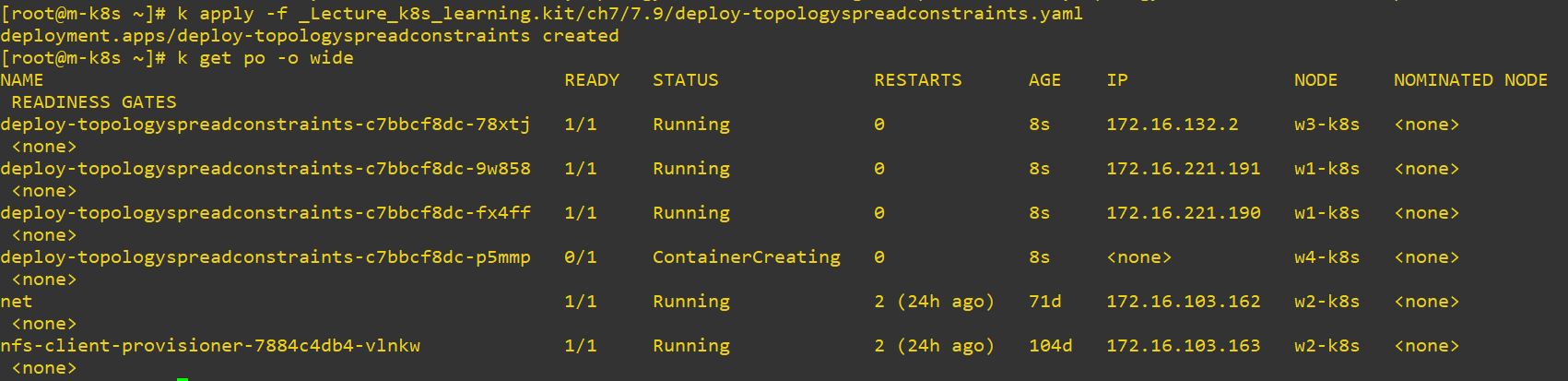
- w2 has some pods before we try this command, so topology devide like, 2 pods on w1, 1 pod on w3 and 1 pod on w4.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy12-load-w3
name: deploy12-load-w3
spec:
replicas: 12
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy12-load-w3
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy12-load-w3
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
nodeName: w3-k8s- This will make 12 pods on w3.
- And rerun topology, then it will devide like, 2 pods on w1 and 2 pods on w4.
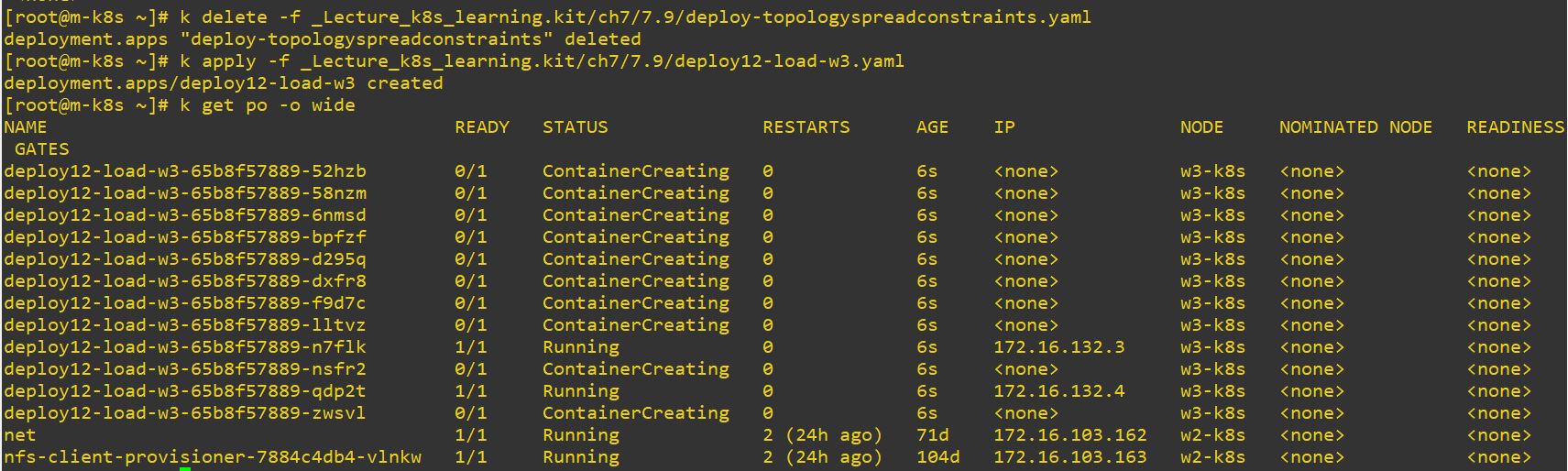
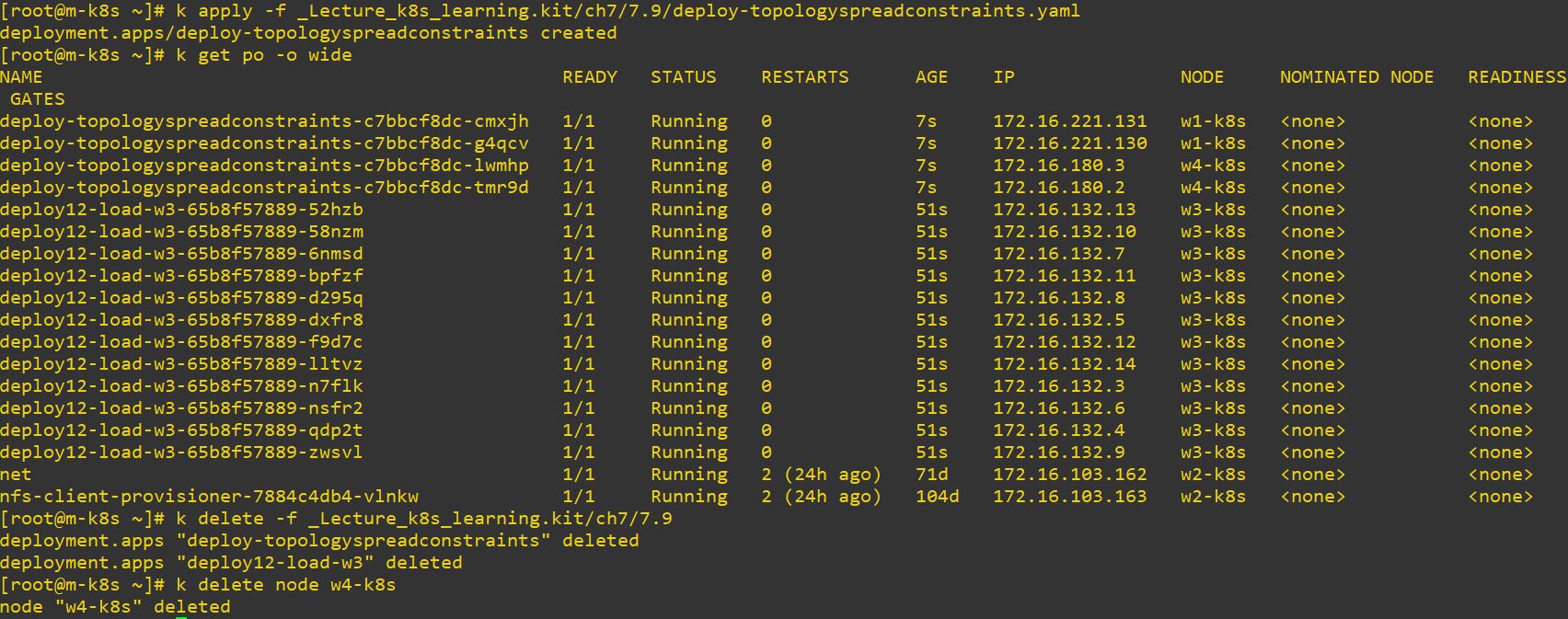
- Please remove w4 in virtual box!
Cluster Management
Access Control
RBAC(Role-Based Access Control)
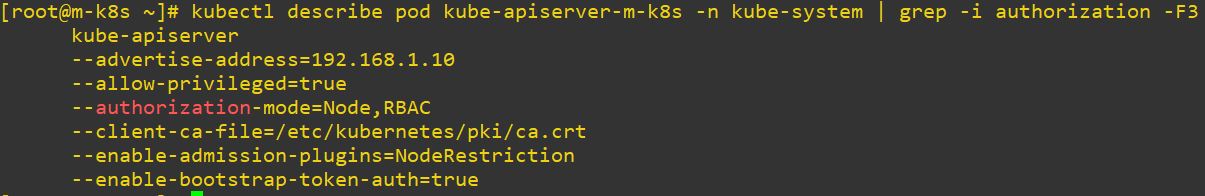
- Node : set access permission from kubelet of scheduled node.
- ABAC : Attribute-based access control
- RBAC : set access permission from role.
- Webhook : Based on HTTP Post get Payload and control Authorization.
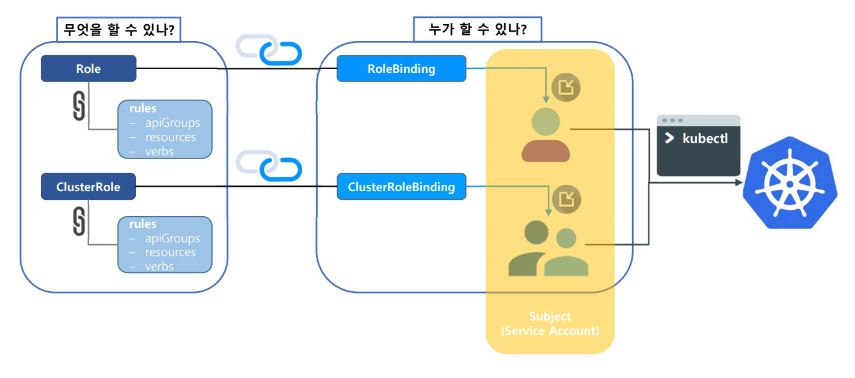
-
Set role with behavior permission and set role group.
-
Context(Kubernetes Cluster)
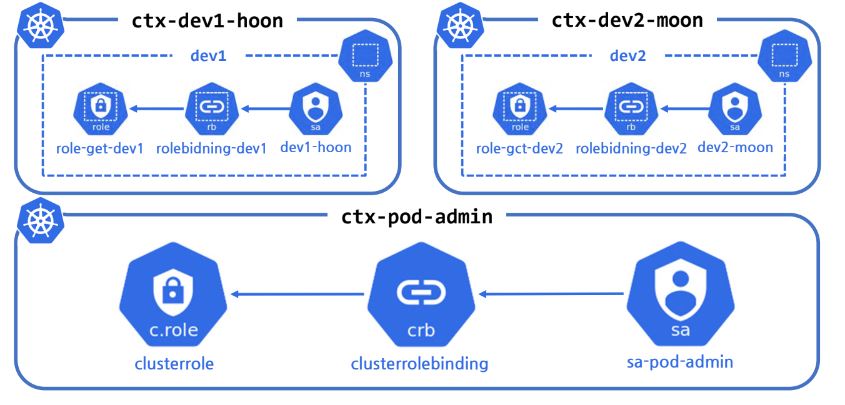
- dev1 is EKS(AWS).
- dev2 is AKS(Azure).
- dev3 is GKE(Google).
-
Context makes cluster and has access control data.
-
Practice
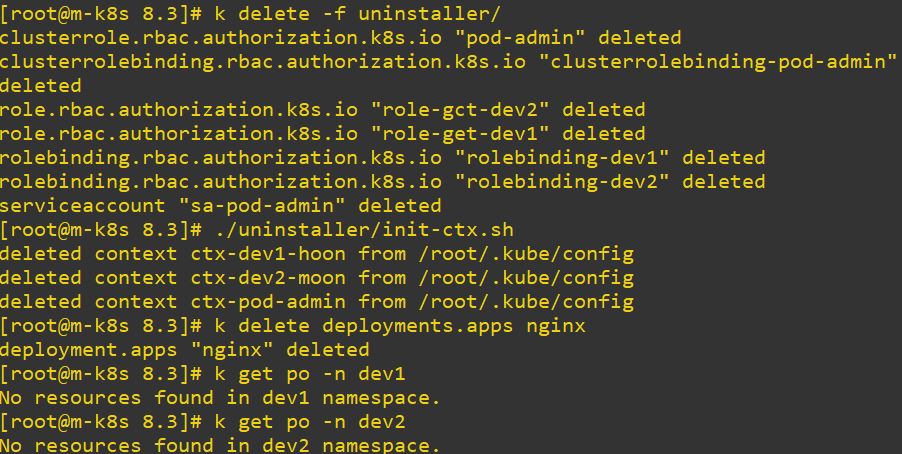
- Create namespace and account for dev1, dev 2 and cluster
# dev1 namespace and account
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: dev1
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: dev1-hoon
namespace: dev1
---
# dev2 namespace and account
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: dev2
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: dev2-moon
namespace: dev2# account for clusterrole
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: sa-pod-admin- Create Role and bind this role and account for dev1
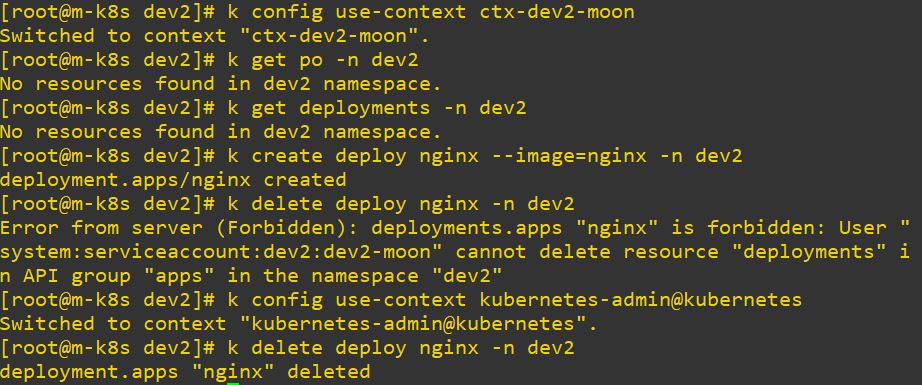
- Role dev1 has get and list permission. So error is occured, when it try to create.
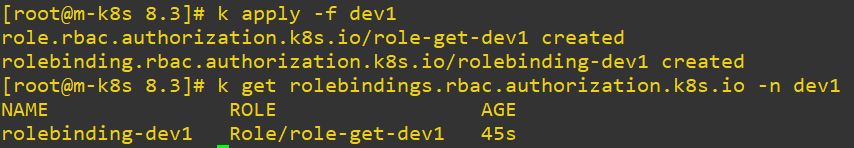
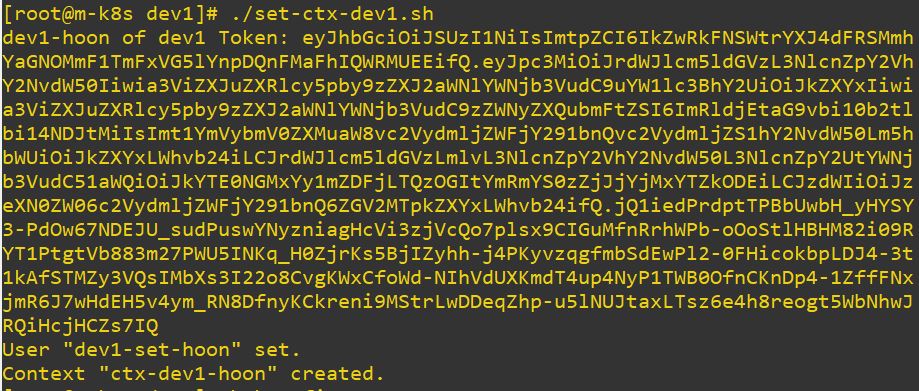
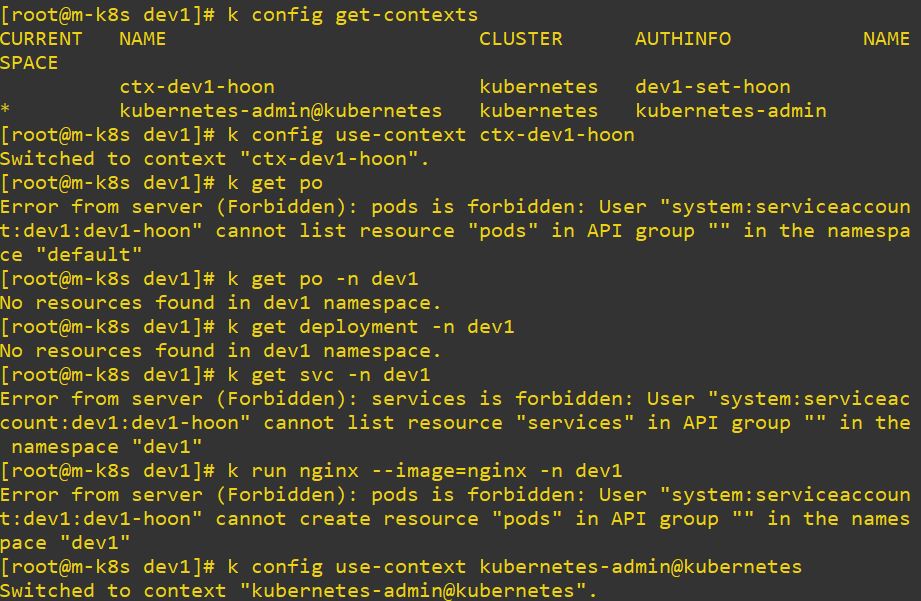
# dev1 Role
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: dev1
name: role-get-dev1
rules:
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["pods", "deployments"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]# dev1 Role Binding
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: rolebinding-dev1
namespace: dev1
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: dev1-hoon
apiGroup: ""
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: role-get-dev1
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io- Create Role and bind this role and account for dev2
- Role dev2 has get, list and create permission. So error is occured, when it try to delete.
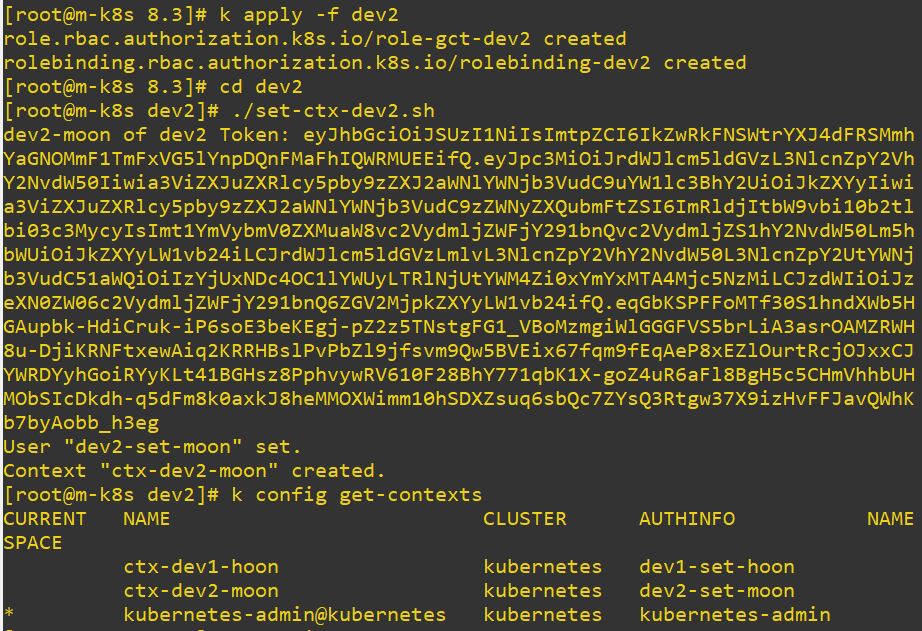
# dev2 Role
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: dev2
name: role-gct-dev2
rules:
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["pods", "deployments"]
verbs: ["get", "list","create"]# dev2 Role Binding
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: rolebinding-dev2
namespace: dev2
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: dev2-moon
apiGroup: ""
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: role-gct-dev2
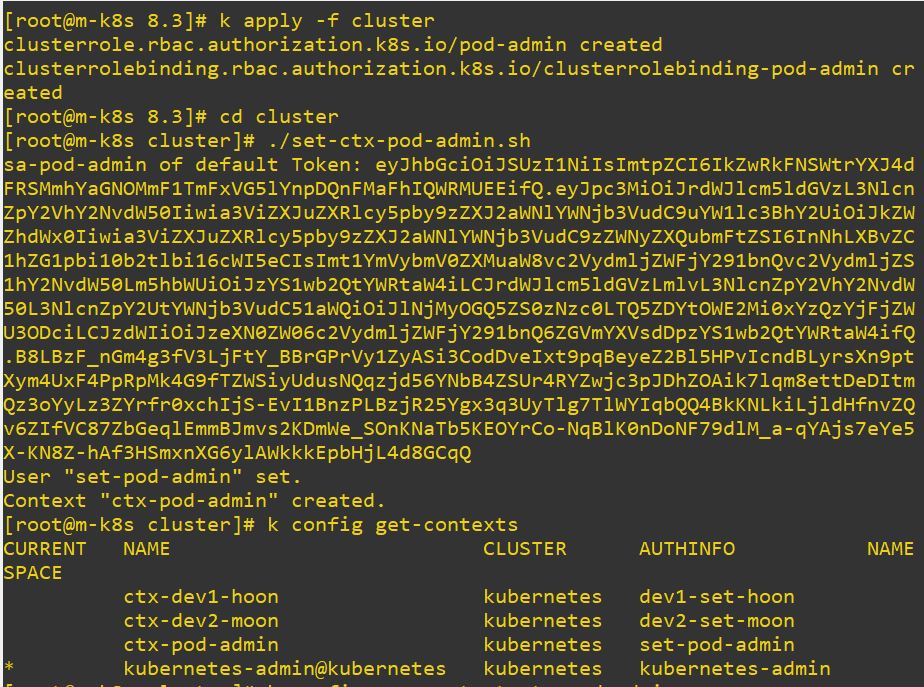
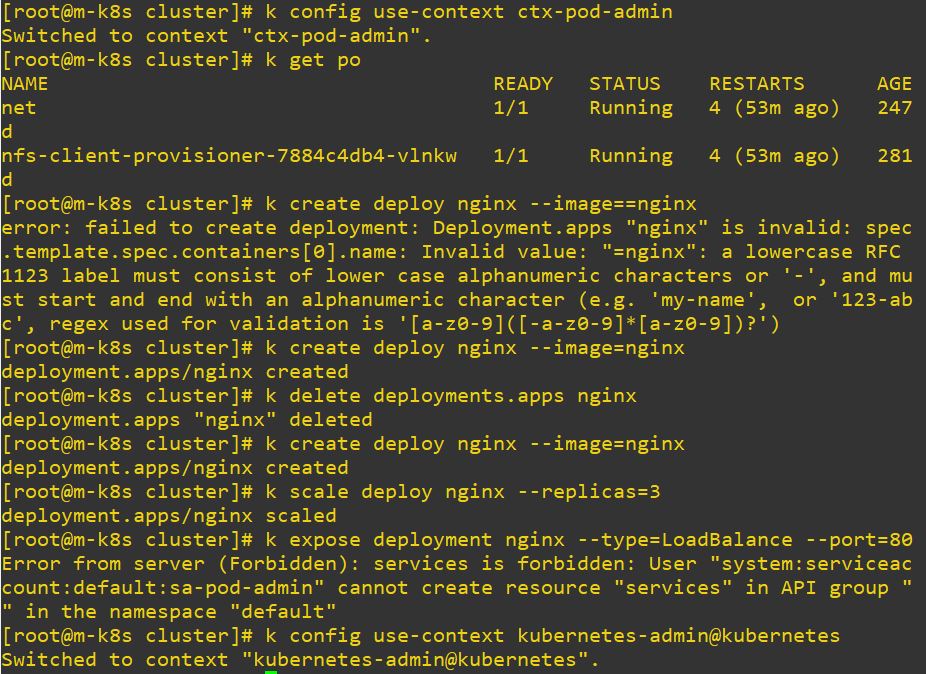
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io- Create Role and bind this role and account for cluster
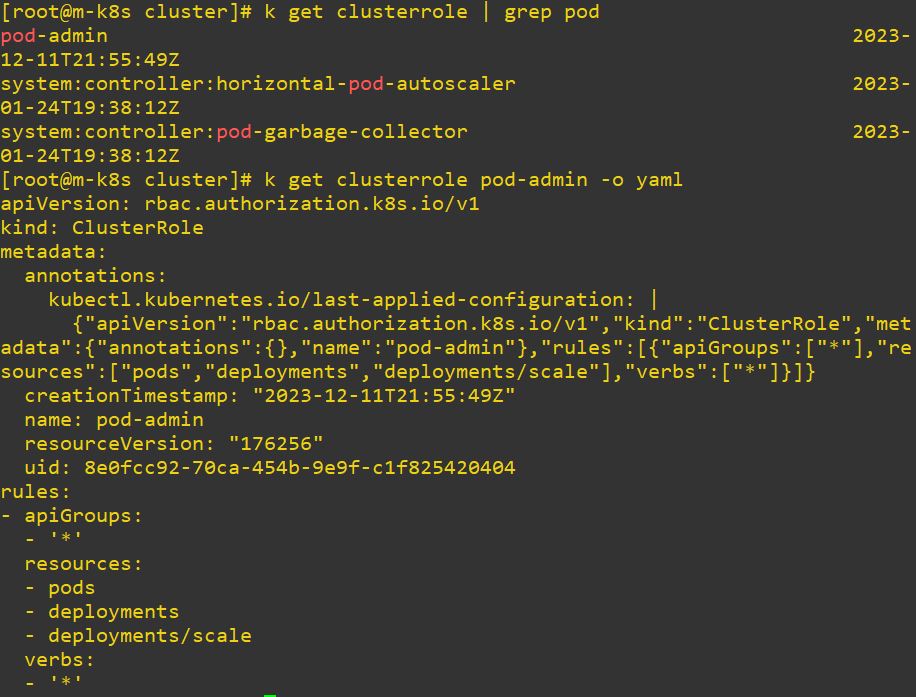
- Role cluster has every thing on verb but it is accepted for pods, deployments, and deployment scale. So when it try to use service, it occures error.
# Cluster Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: pod-admin
rules:
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["pods","deployments","deployments/scale"]
verbs: ["*"]# Cluster Role Binding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: clusterrolebinding-pod-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: sa-pod-admin
apiGroup: ""
# need namespace for CRB subjects
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: pod-admin
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io-
If you want to find with specific word, use “ grep”.
Resource Management
Resource Quota
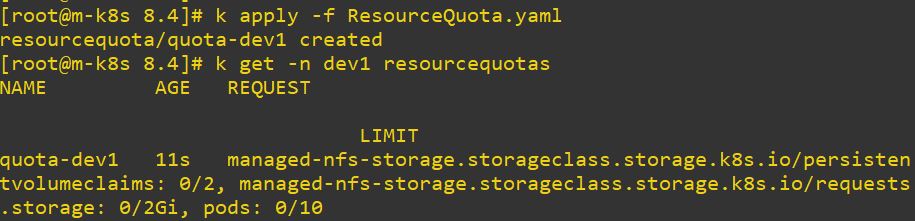
- Limitation for resource
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: quota-dev1
namespace: dev1
spec:
hard:
pods: 10
managed-nfs-storage.storageclass.storage.k8s.io/persistentvolumeclaims: "2"
managed-nfs-storage.storageclass.storage.k8s.io/requests.storage: "2Gi"
#persistentvolumeclaims: "2"
#requests.storage: "2Gi"-
So when we try to take attributes with more than limited value, it occures error.
-
Error with storage
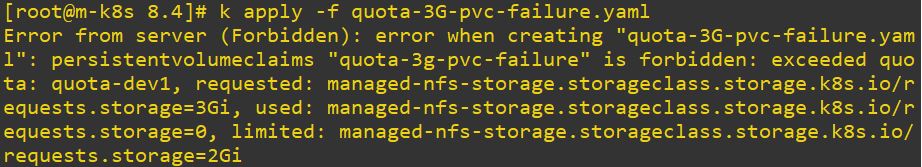
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: quota-3g-pvc-failure
namespace: dev1
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 3Gi
storageClassName: managed-nfs-storage - Error with pvc
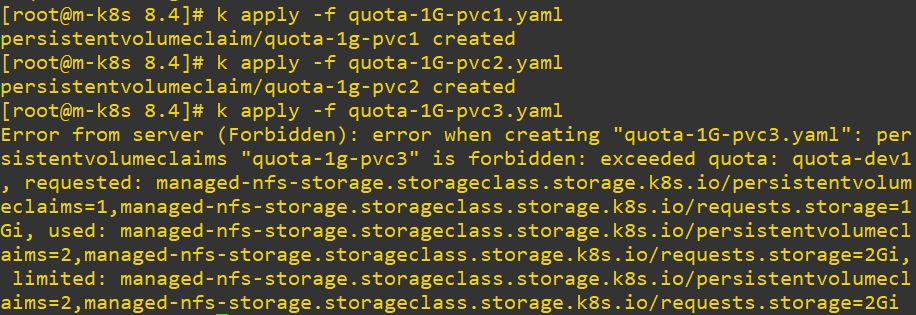
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: quota-1g-pvc1
namespace: dev1
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: managed-nfs-storage apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: quota-1g-pvc2
namespace: dev1
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: managed-nfs-storage apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: quota-1g-pvc3
namespace: dev1
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: managed-nfs-storage - Error with pods

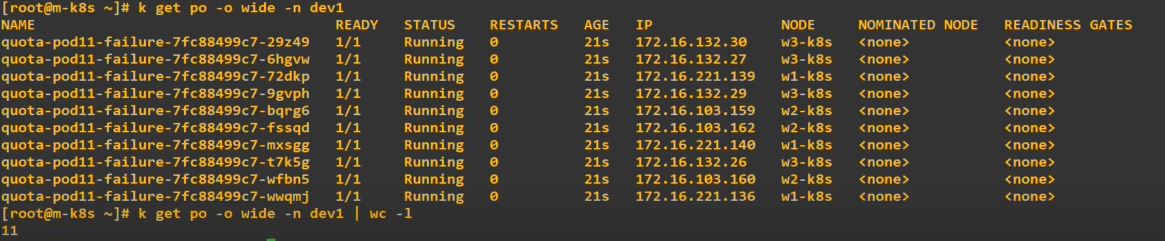
- It will try to make 11 pods but error is occured when it try to make 11th pod.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: quota-pod11-failure
namespace: dev1
spec:
replicas: 11
selector:
matchLabels:
app: quota-pod11-failure
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: quota-pod11-failure
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx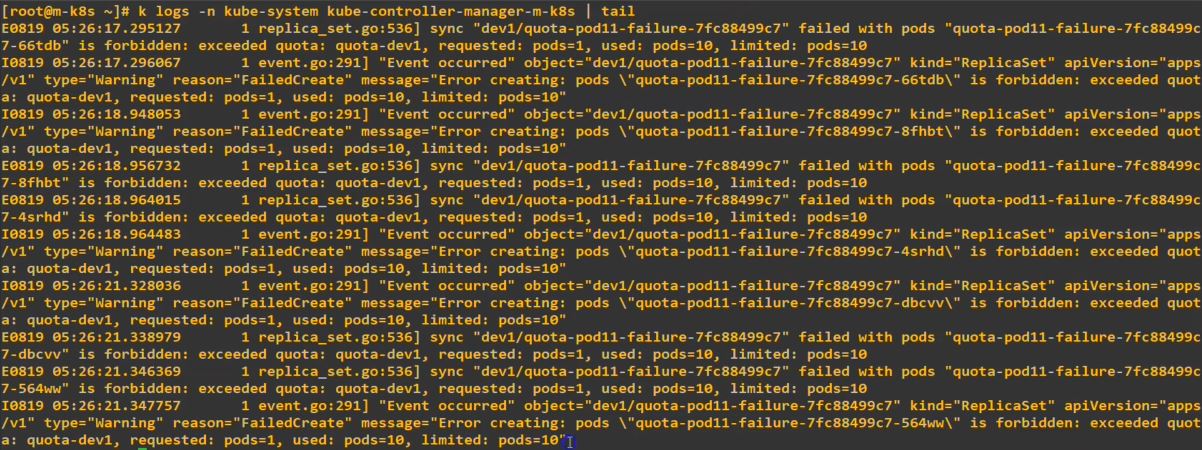

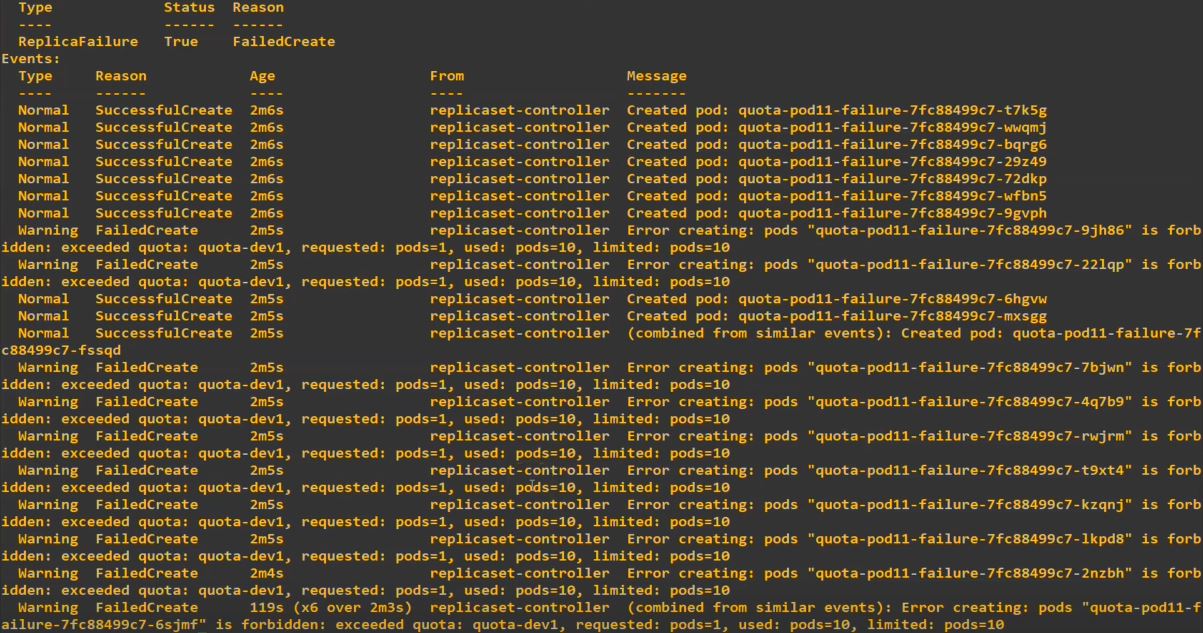
- 176.jpg command is ‘k describe -n dev1 replicasets.apps quota-pod11-failure-7fc88499c7’
LimitRange
- LimitRange is effective object to process objective requests.
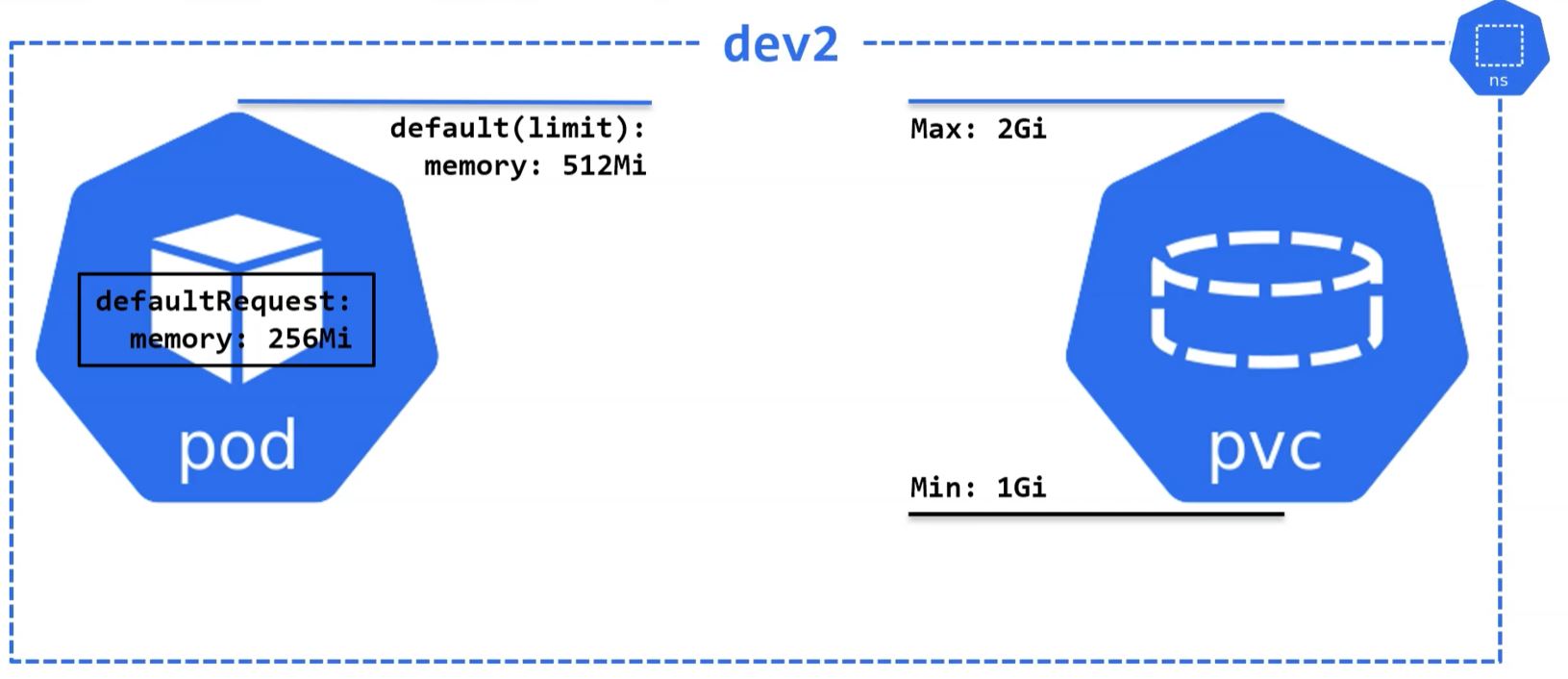
apiVersion: v1
kind: LimitRange
metadata:
name: limits-dev2
namespace: dev2
spec:
limits:
- type: PersistentVolumeClaim
max:
storage: 2Gi
min:
storage: 1Gi
- type: Container
default:
memory: 512Mi
defaultRequest:
memory: 256Mi- Pod’s minimum memory size would be 256 Mi and maximum would be 512 Mi.
- PVC’s minimum memory size would be 1 Gi and maximum would be 2 Gi.
-
Like this, we can set LimitRange in namespace.
- G vs Gi
- For example, 5G means 5 Gigabytes while 5 Gibibytes.
- 5 G = 5000000 KB / 5000 MB
- 5 Gi = 5368709.12 KB / 5368.70 MB
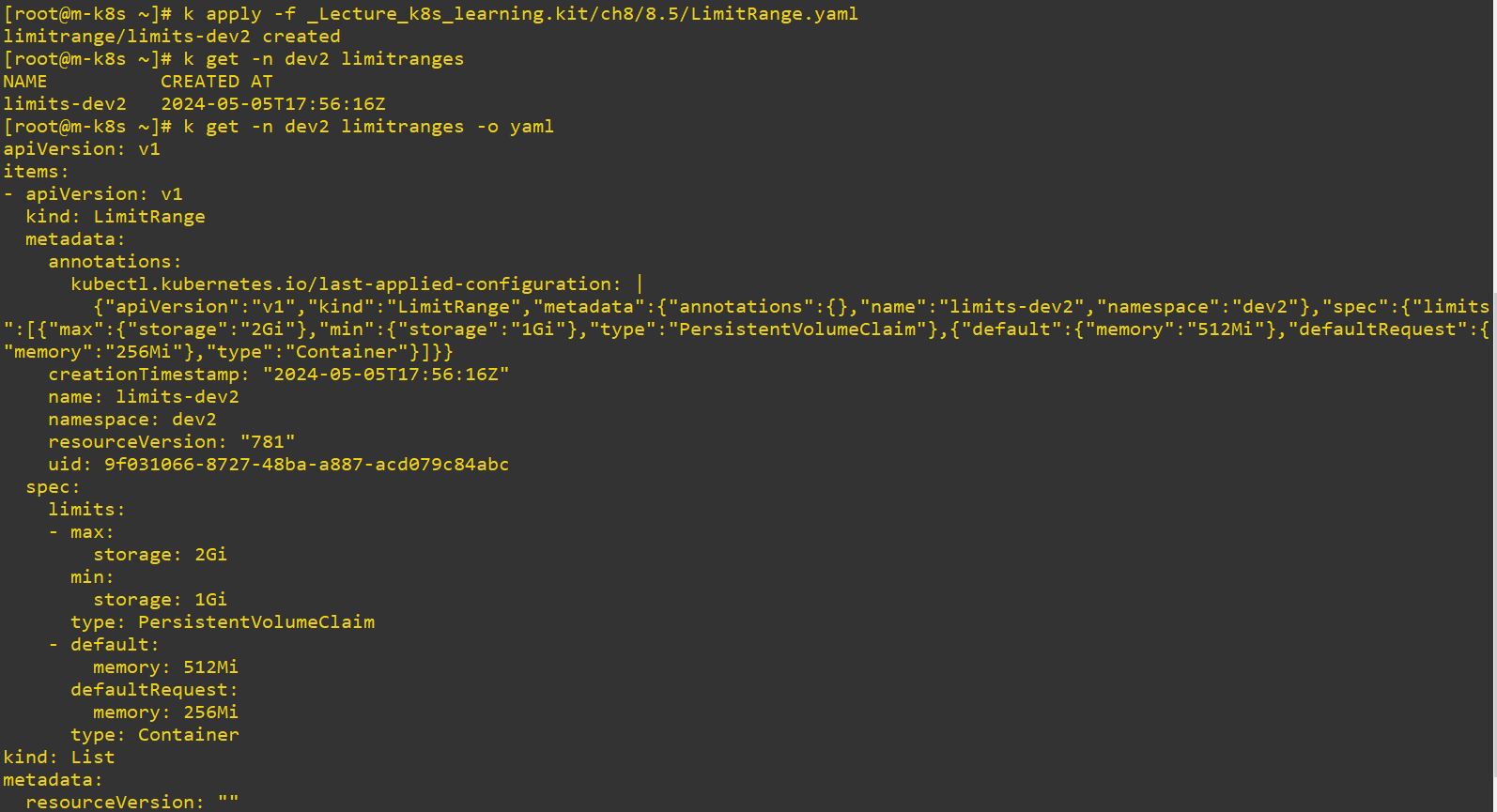
- Now, dev2 has Limit Ranges with minimum 256 Mi and maximum 512 Mi.
- And when we request more resource on that namespace(our case is dev2), it occurs error like below.
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: limits-3g-pvc-failure
namespace: dev2
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 3Gi
storageClassName: managed-nfs-storage 
- But when we reauest appropriate resources, it will be created on namespace well.
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: limits-1g-pvc
namespace: dev2
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: managed-nfs-storage 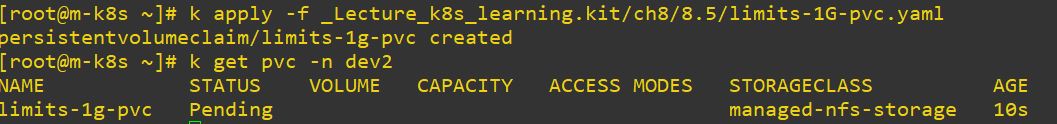
- Extra experimence
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: limits-defaultrequest
namespace: dev2
spec:
replicas: 6 # will be out of memory
selector:
matchLabels:
app: limits-defaultrequest
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: limits-defaultrequest
spec:
containers:
- name: chk-log
image: sysnet4admin/chk-log
volumeMounts:
- name: pvc-vol
mountPath: /audit
volumes:
- name: pvc-vol
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: limits-1g-pvc
nodeName: w3-k8s # only here for testing purpose- Worker nodes have 1.5 Gi per each.
- We will test on w3-k8s to create 6 pods with minimum size 256 Mi.(6 x 256 Mi = 1.5 Gi)
- It should occur out of memory error because total needed memory is bigger than 1.5 Gi. (ex. pod memory)
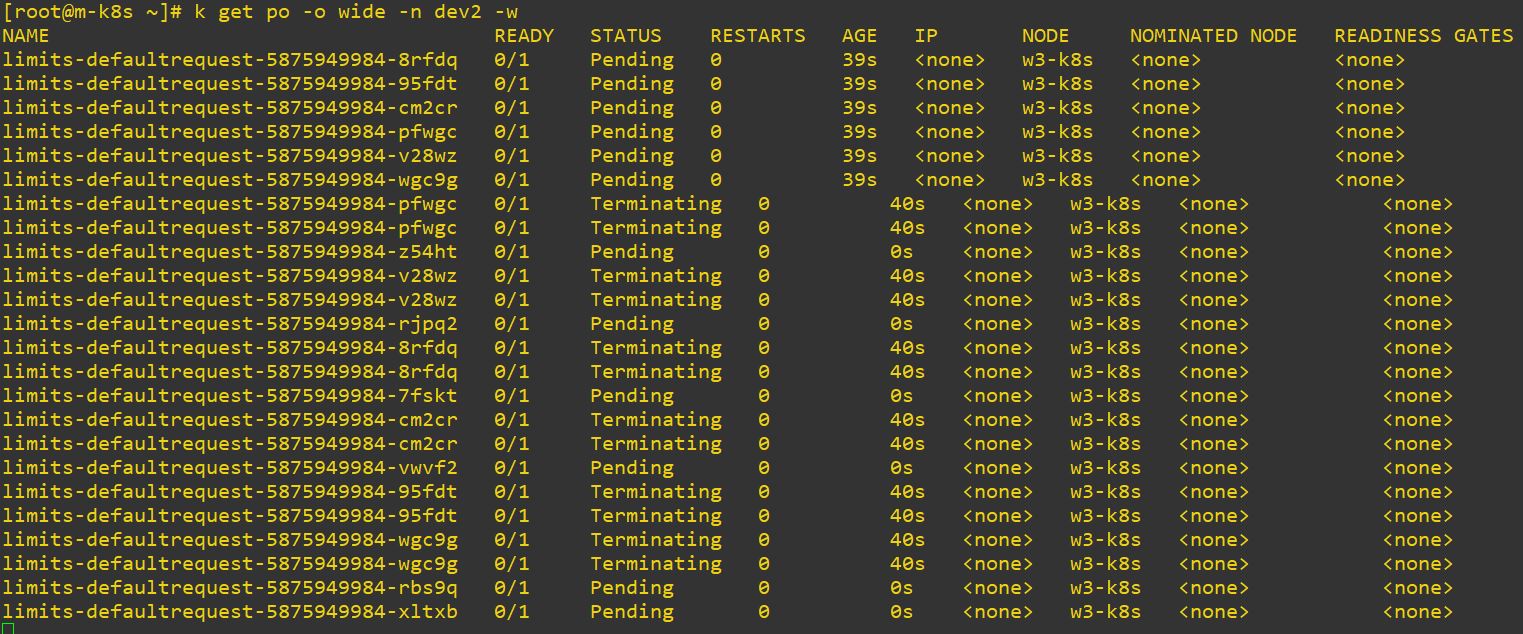
- So please delete ASAP if you tested this code.
Network Policy
- Ingress Traffic : Traffic getting in to server through firewall
- Egress Traffic : Traffic getting out from server through firewall
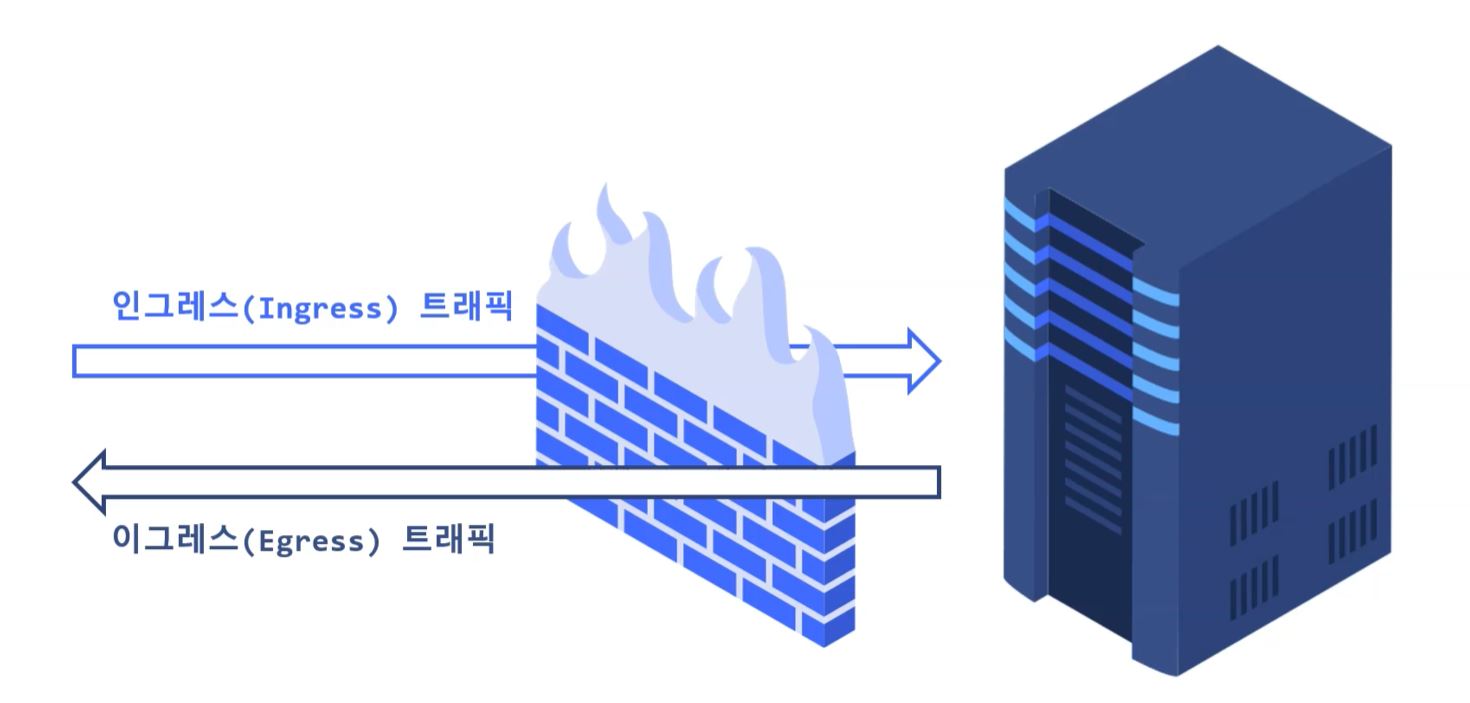
Network Policy in Kubernetes
- Ingress : set direction of netrowk
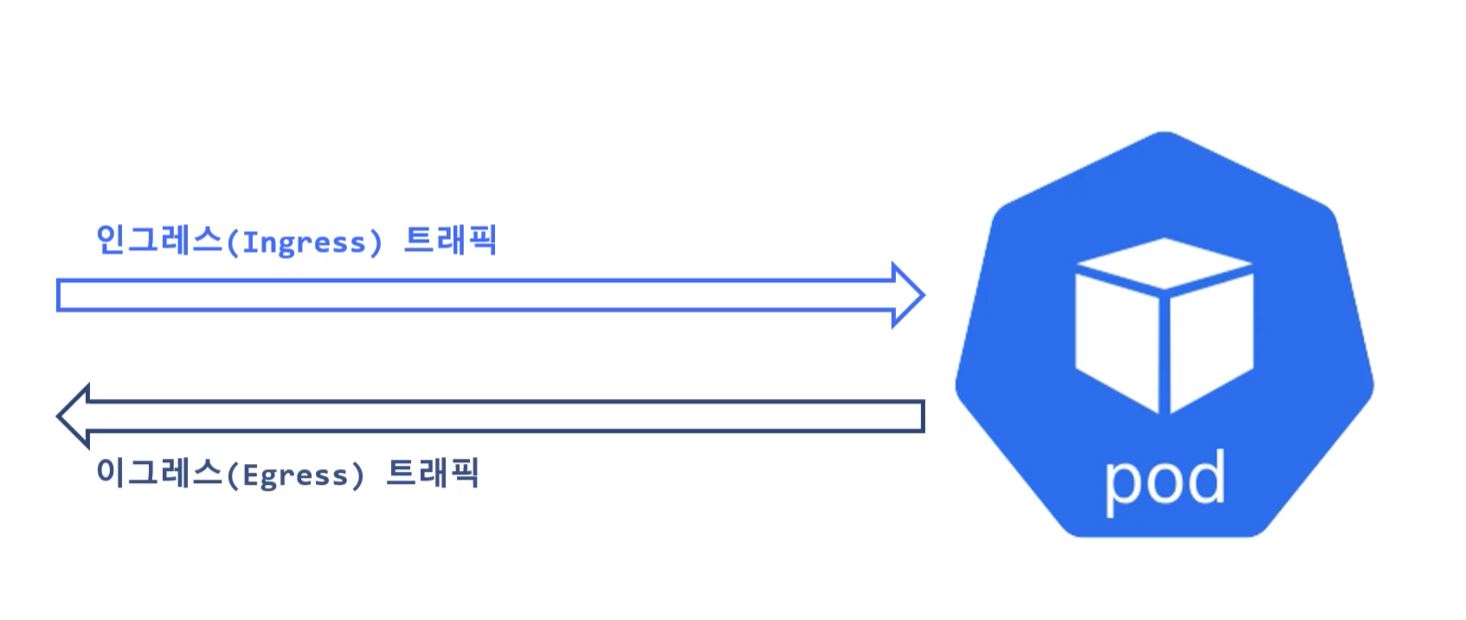
- Before you run experiments, check you have net tools.
- If you don’t have net tools, run this
0-1-net-tools-ifn-default.yamland0-2-net-tools-ifn-dev[1-2].yamlfirst.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: net
spec:
containers:
- image: sysnet4admin/net-tools-ifn
name: netapiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: net-dev1
namespace: dev1
spec:
containers:
- image: sysnet4admin/net-tools-ifn
name: net
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: net-dev2
namespace: dev2
spec:
containers:
- image: sysnet4admin/net-tools-ifn
name: net- Experiment 1 : Deny all
- if label’s role is sensitive, then deny all.
- This blocks every network transport in the pod.
- Because Ingress and Egress are just declared and there is no description for transporting.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
role: sensitive
app: chk-info
name: deploy-deny-all
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
role: sensitive
app: chk-info
template:
metadata:
labels:
role: sensitive
app: chk-info
spec:
containers:
- image: sysnet4admin/chk-info
name: chk-info
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: chk-info
name: deploy-deny-all
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: chk-info
type: LoadBalancerapiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: networkpolicy-deny-all
namespace: default
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels:
role: sensitive
policyTypes:
- Ingress
- Egress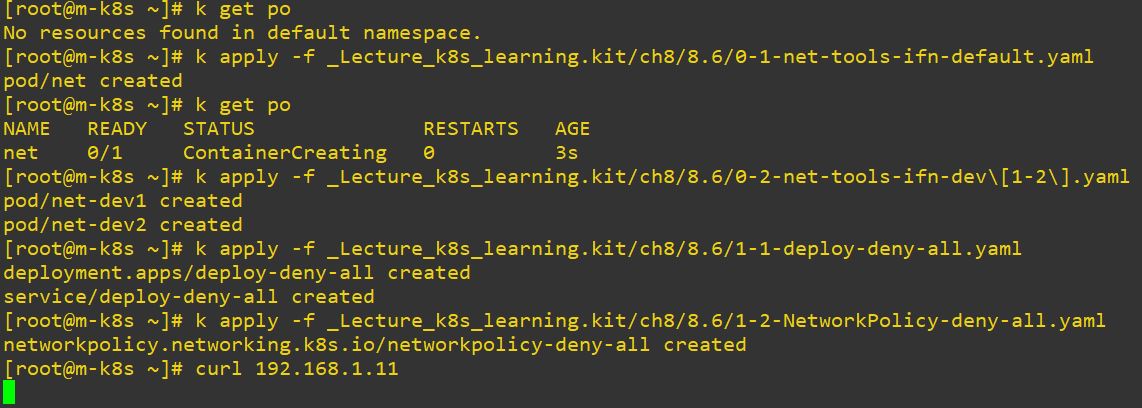
-
It doesn’t work to get in the server, so please delete pods and policy after experiment.
-
Experiment 2 : Process with machted label
- if label’s role is internal, Ingress and Egress will be processed with mached label.
- In this case, Ingress will get in through chk-info app and Egress will get out though chk-info app.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: networkpolicy-podselector
namespace: default
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels:
role: internal
policyTypes:
- Ingress
- Egress
ingress:
- from:
- podSelector:
matchLabels:
app: chk-info
egress:
- to:
- podSelector:
matchLabels:
app: chk-info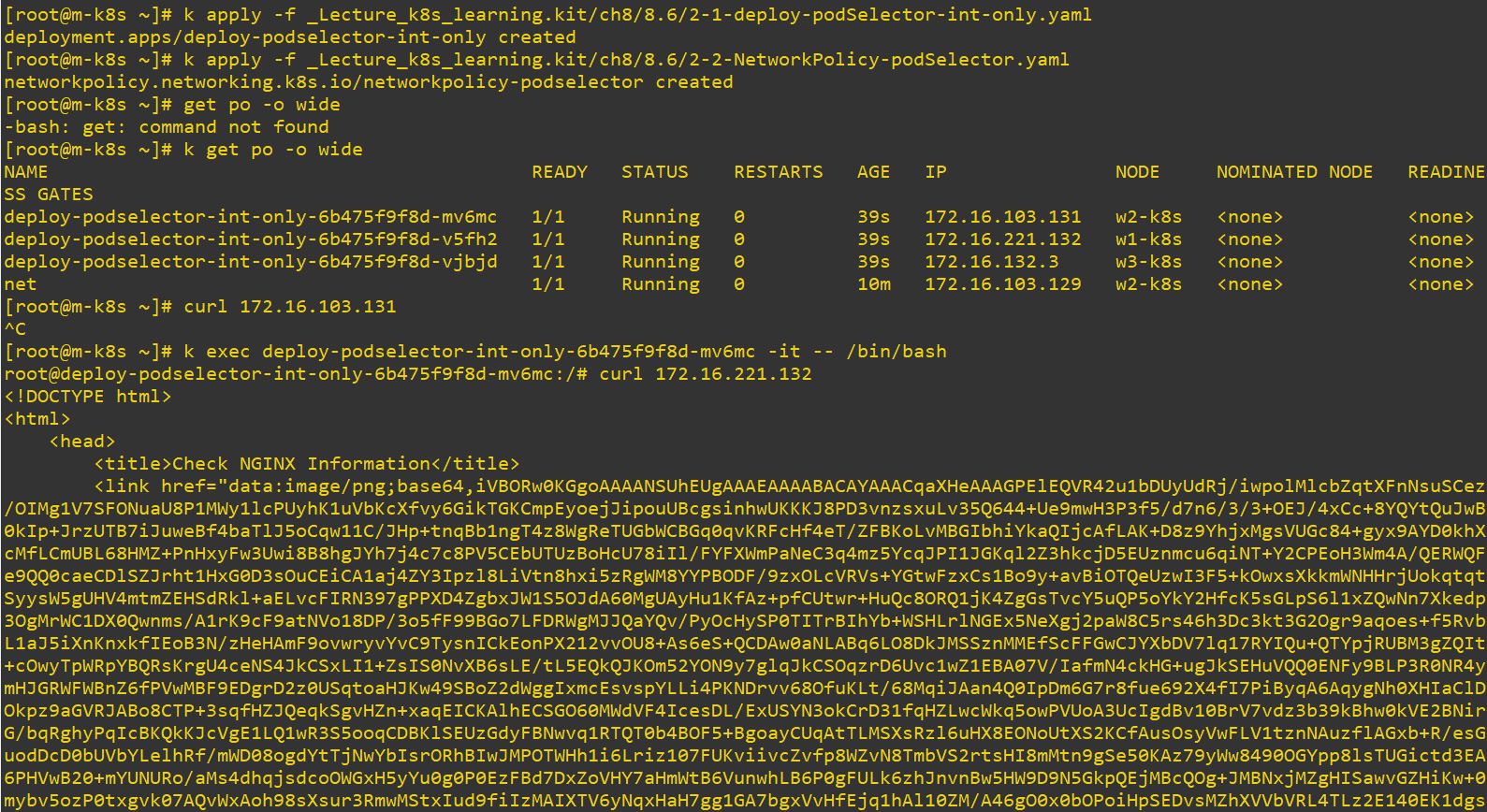
- Those pods can connect with only each others, it means transport occurs only inside of them.
- That is the reason, why we cannot connect the pod outside.
-
Please delete pods and policy before going to next expriment.
- Experiment 3-1 : Using IP block as criterion
podSelector:{}means there is no criterion for label. So it will accept every labels.- In this case, Ingress will get in through ip 172.16.0.1 - 172.16.255.254 and Egress will get out through ip 172.16.0.1 - 172.16.127.254.
- So half of IPs cannot transport.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: networkpolicy-ipblock
namespace: default
spec:
podSelector: {}
policyTypes:
- Ingress
- Egress
ingress:
- from:
- ipBlock:
# 172.16.0.1 - 172.16.255.254
cidr: 172.16.0.0/16
egress:
- to:
- ipBlock:
# 172.16.0.1 - 172.16.127.254
cidr: 172.16.0.0/17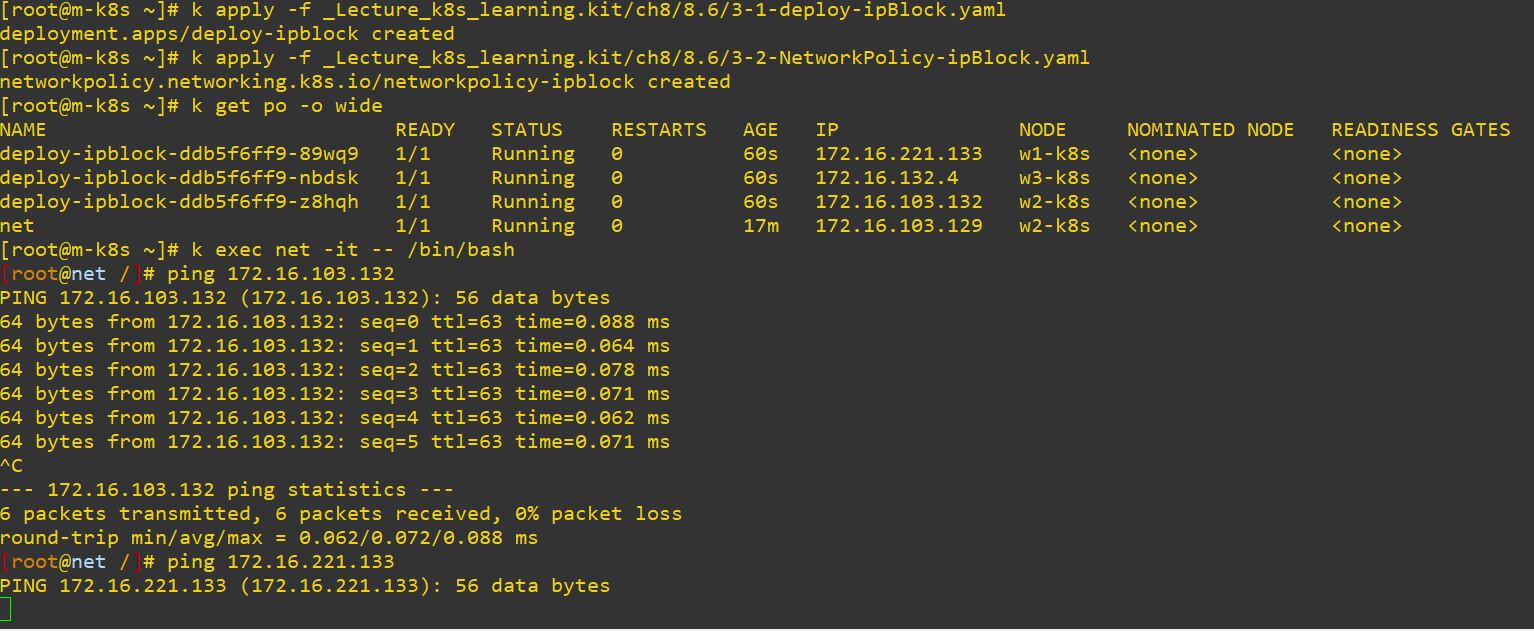
- I can use only
172.16.103.132, others are over 127. - I executed net pod first with
k exec net -it -- /bin/bashand then connected withping 172.16.103.132. - Of course, I cannot connected with
ping 172.16.221.133because of the policy. -
Please delete pods and policy for the next.
- Experiment 3-2 : Using IP block as criterion
- You can also except a specific IPs for transporting with
except. - That excepted node should not be transported.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: networkpolicy-ipblock-except
namespace: default
spec:
podSelector: {}
policyTypes:
- Ingress
- Egress
ingress:
- from:
- ipBlock:
cidr: 172.16.0.0/16
# change your CIDR to shut it down
#except:
# - 172.16.n.n/24
egress:
- to:
- ipBlock:
cidr: 172.16.0.0/16
# change your CIDR to shut it down
#except:
# - 172.16.n.n/24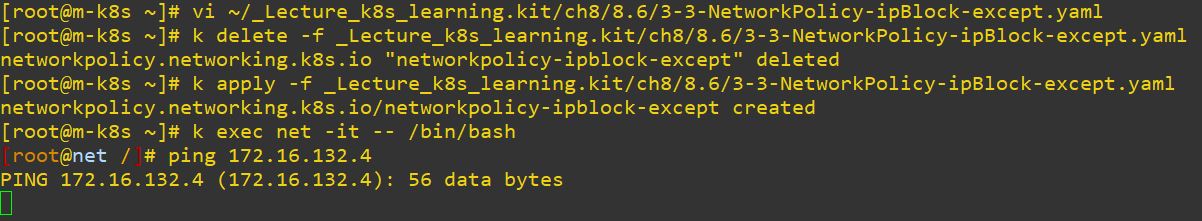
- In my case, I blocked
172.16.132.0/24for Ingress and Egress. - You can also change above code with
vicommand. -
Please delete pods and policy for the next.
- Experiment 4 : Using namespace as criterion
- In this case, Ingress is only getting in through dev2.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: networkpolicy-namespaceselector-dev2
namespace: dev2
spec:
podSelector: {}
policyTypes:
- Ingress
- Egress
ingress:
- from:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
kubernetes.io/metadata.name: dev2
egress:
- {}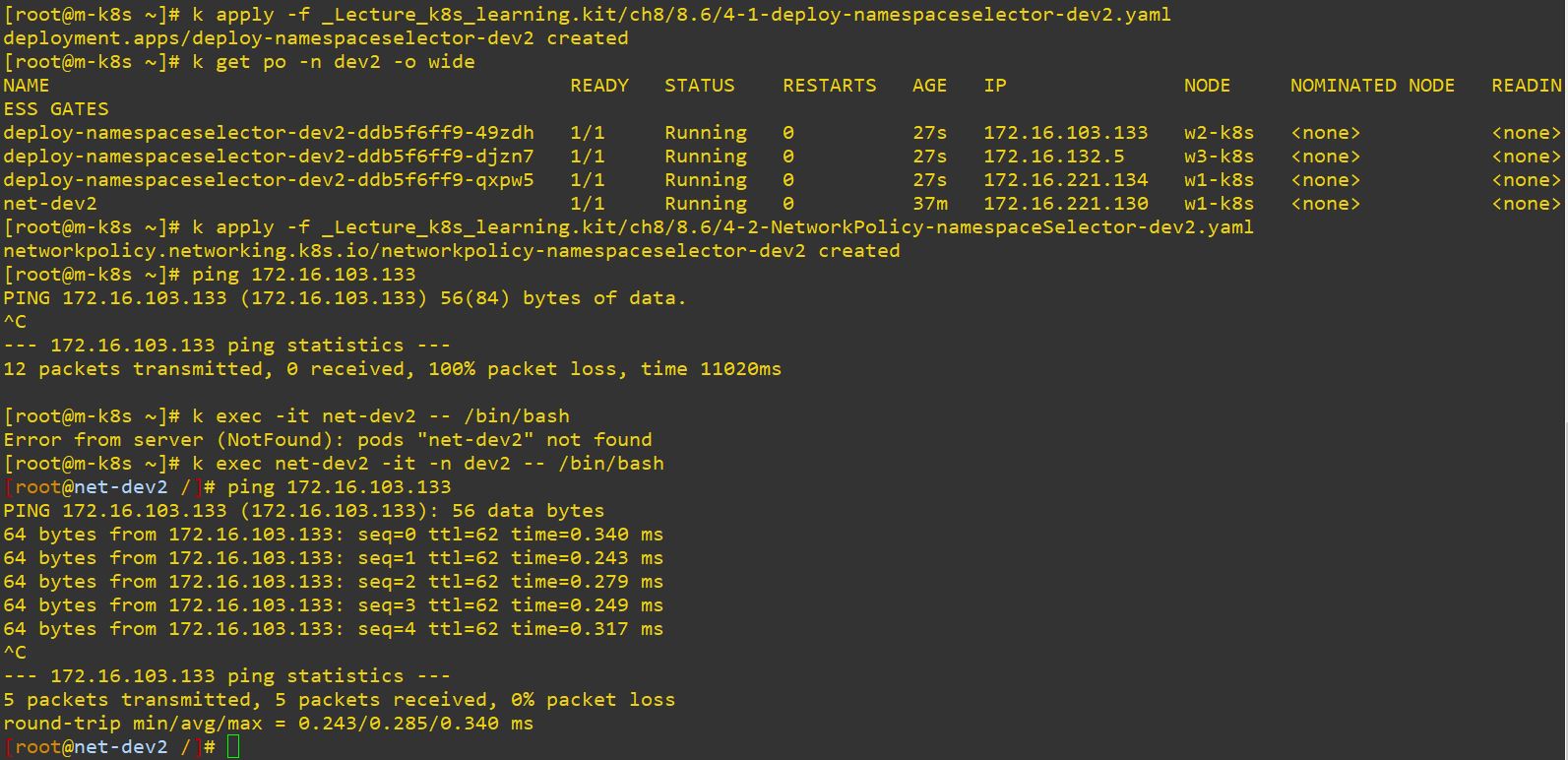
- So it doesn’t work, when you are not in dev2.
- But it works, when you are in dev2 because of the policy.
- Please delete pods and policy for the next.
Application Construction and Management
- Version upgrade
- Auto-Scale
- Deployment with Web UI
ConfigMap
- ConfigMap is for additional or changiable settings and messages.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: sleepy-config
data:
STATUS: "SLEEP AGAIN"
NOTE: "TestBed Configuration"
# create a form with data type
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-configmapref
name: deploy-configmapref
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-configmapref
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-configmapref
spec:
containers:
- image: sysnet4admin/sleepy
name: sleepy
command: ["/bin/sh","-c"]
args:
- |
echo "sleepy $STATUS"
echo "NOTE: $NOTE"
sleep 3600
# $ means, we will use a specific variable here with same name
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
name: sleepy-config
# reference container 'sleepy-config' and it will be used as a environment variable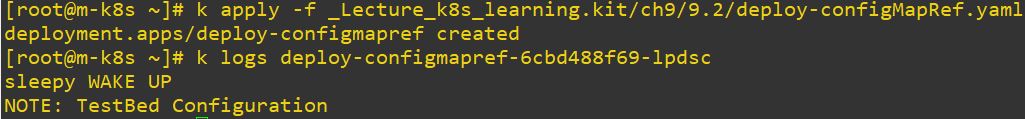
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-configmapkeyref
name: deploy-configmapkeyref
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-configmapkeyref
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-configmapkeyref
spec:
containers:
- image: sysnet4admin/sleepy
name: sleepy
command: ["/bin/sh","-c"]
args:
- |
echo "sleepy $APP_STATUS"
sleep 3600
env:
- name: APP_STATUS # mandantory field
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: sleepy-config
key: STATUS
# reference key STATUS in 'sleepy-config' and this STATUS renamed to APP_STATUS
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-vol-configMap
name: deploy-vol-configmap
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-vol-configmap
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-vol-configmap
spec:
containers:
- image: sysnet4admin/sleepy
name: sleepy
command: ["/bin/sh","-c"]
args:
- |
sleep 3600
volumeMounts:
- name: appconfigvol
mountPath: /etc/sleepy.d
# mount ConfigMap as a volume
# read ConfigMap and mount it on the directory
# take values when we need
volumes:
- name: appconfigvol
configMap:
name: sleepy-config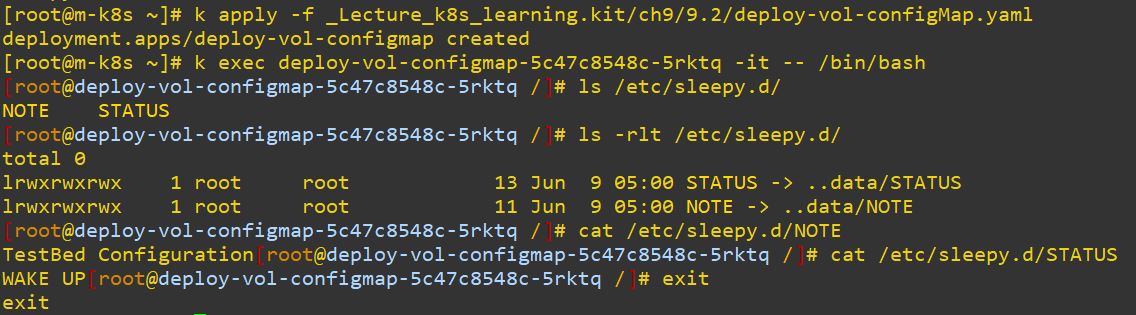
- If ConfigMap is changed, then environment variables gonna be also changed.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: sleepy-config
data:
STATUS: "SLEEP AGAIN" # changed
NOTE: "TestBed Configuration"
- Metallb can choose IP range by ConfigMap in load balance service.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
namespace: metallb-system
name: config
data:
config: |
address-pools:
- name: metallb-ip-range
protocol: layer2
addresses:
- 192.168.1.11-192.168.1.19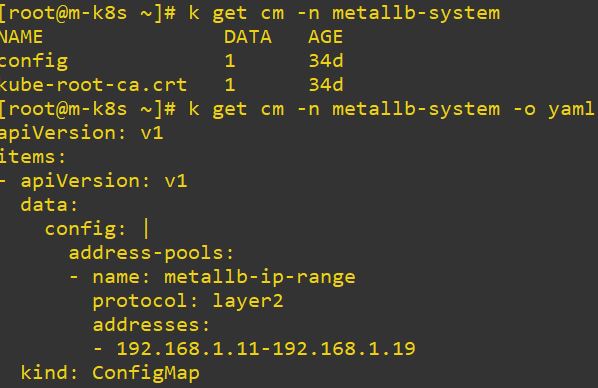
Secret
- for security(ex. id or password)
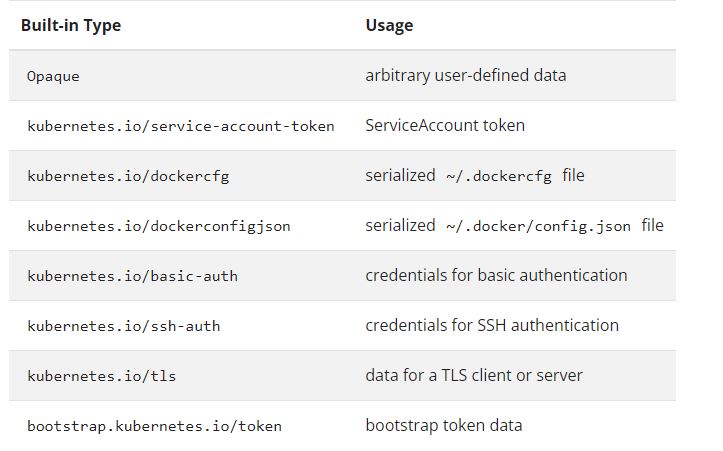
- Secret Types
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: mysql-cred
namespace: default
data: # base64
username: ZGItdXNlcg==
password: bGVlaHVobGVl
type: Opaque # default value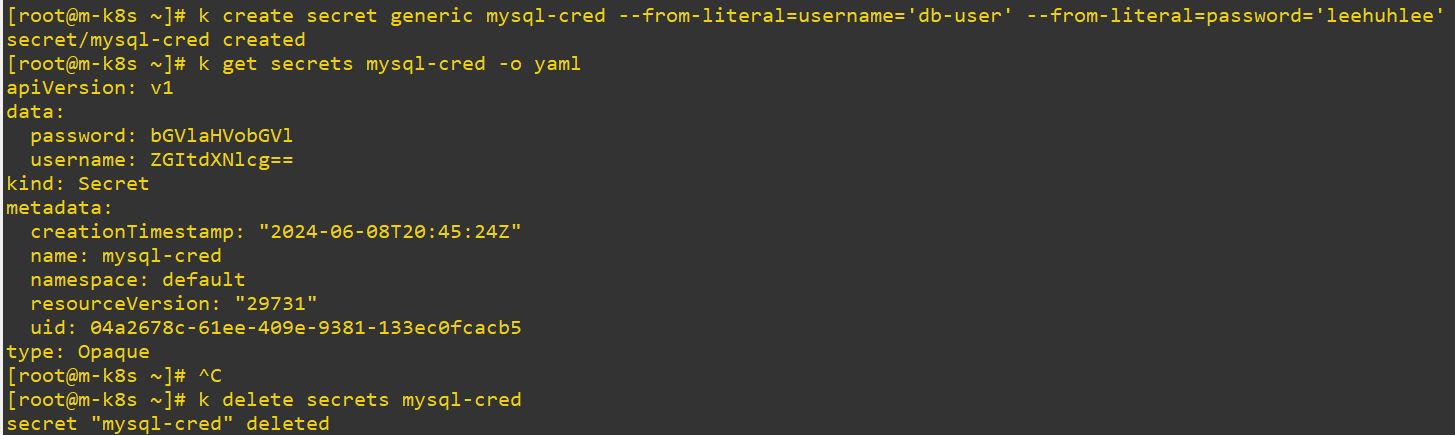
- This endoding keys can be decoded by
echo {your key} | base64 --decode
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
run: deploy-secretkeyref
name: deploy-secretkeyref
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-secretkeyref
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-secretkeyref
spec:
containers:
- image: sysnet4admin/mysql-auth
name: mysql-auth
env:
# Need to init mysql
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: rootpassword
# Custom auth
- name: MYSQL_USER_ID
valueFrom: # similar with ConfigMapRef
secretKeyRef:
name: mysql-cred # secret name
key: username # db-user
- name: MYSQL_USER_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mysql-cred
key: password # leehuhlee
ports:
- containerPort: 3306
volumeMounts:
- name: mysql-pvc
mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
volumes:
- name: mysql-pvc
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mysql-pvc
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: mysql-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 20Gi
storageClassName: managed-nfs-storage - Secret and ConfigMap can be changed with
kubectl edit. - It means, when pod is dead and reveal, Secret and ConfigMap can be changed automatically.
- If Secret and ConfigMap should not or will not be changed, use
immutable.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: mysql-cred
namespace: default
data:
username: ZGItdXNlcg==
password: bGVlaHVobGVl
type: Opaque
immutable: true- After deploy secret, you cannot change this file again.
Roll Out
- Rolling Update
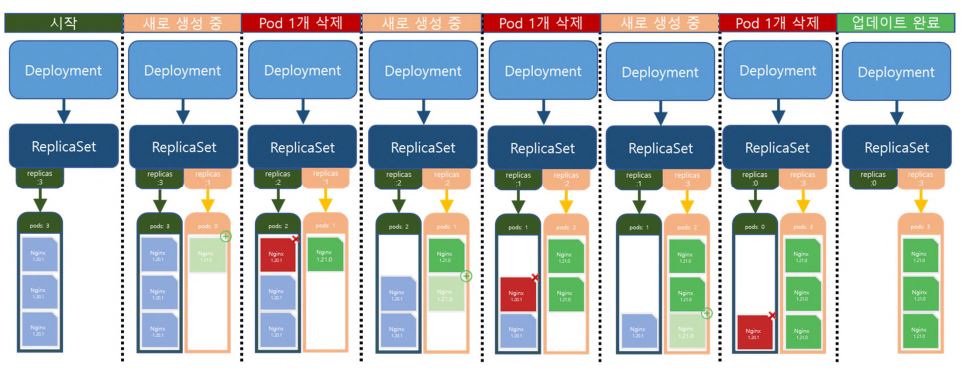
- Kubernetes updates 1 by 1 to continue services.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-rollout
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-rollout
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-rollout
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.20.1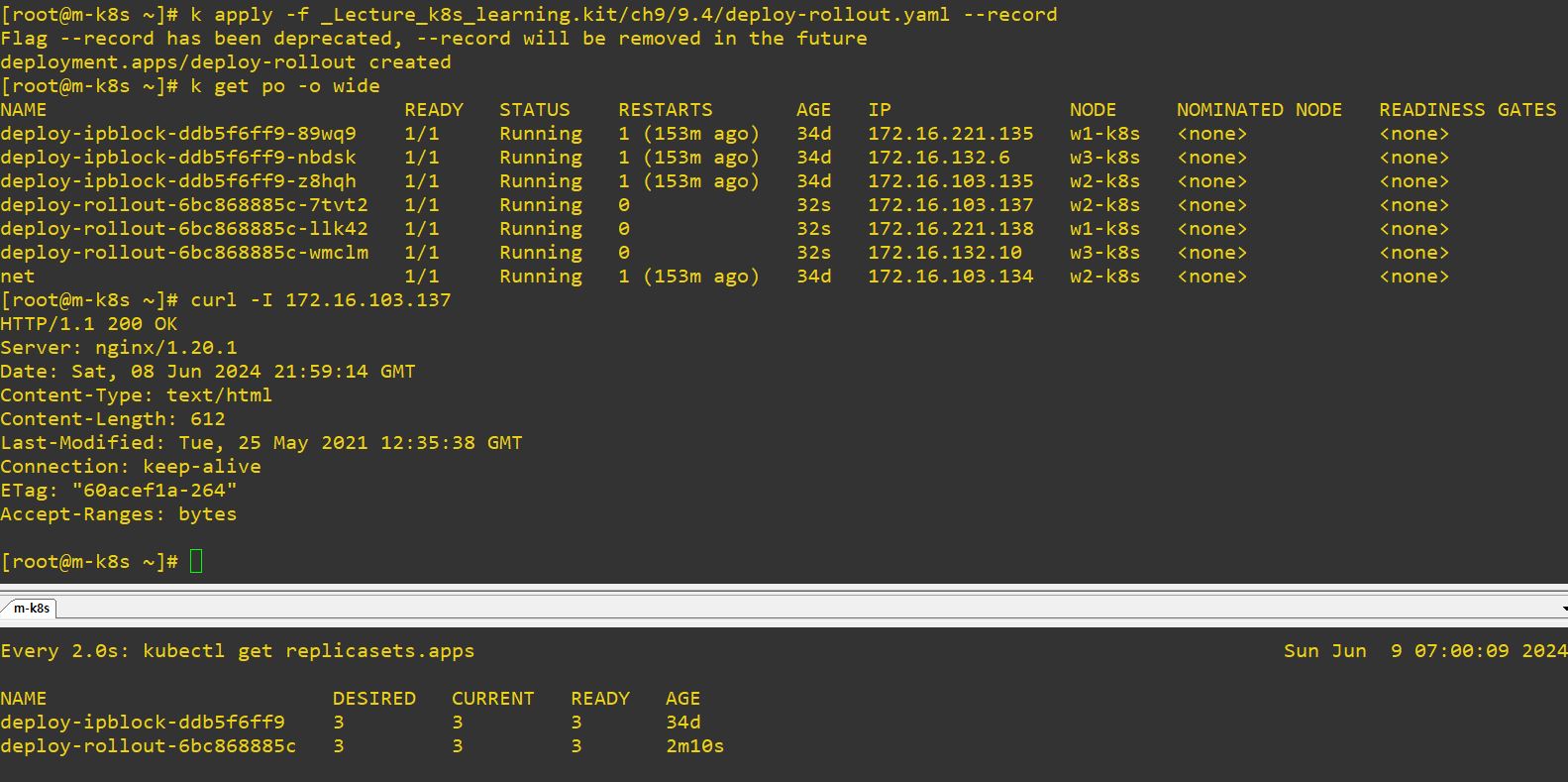
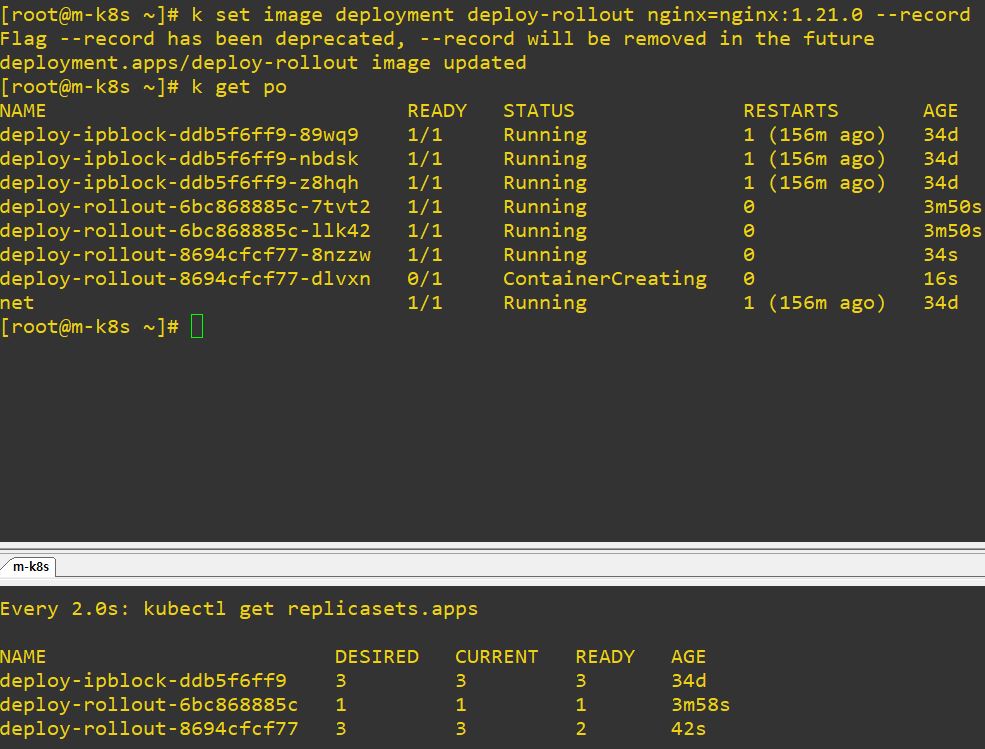
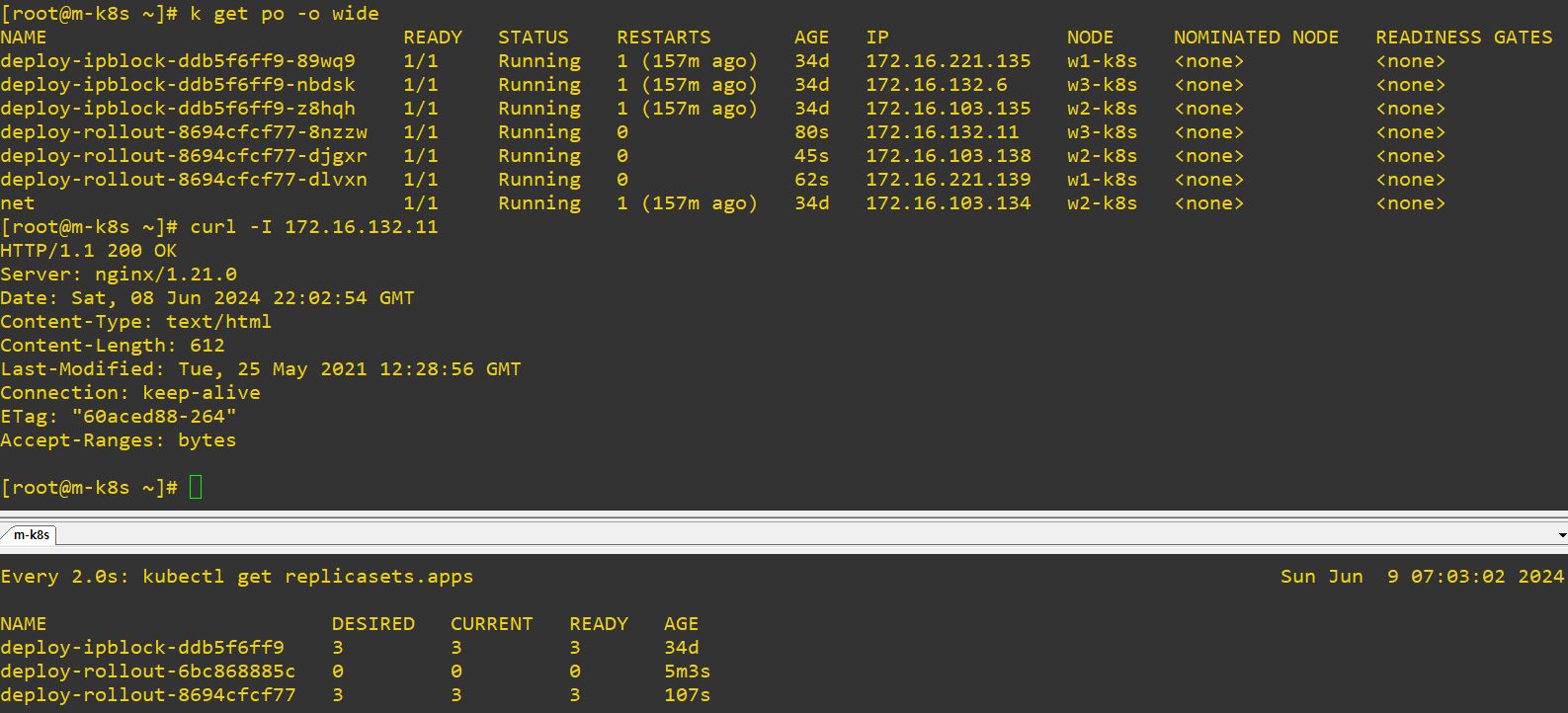
- update with unexisting version.
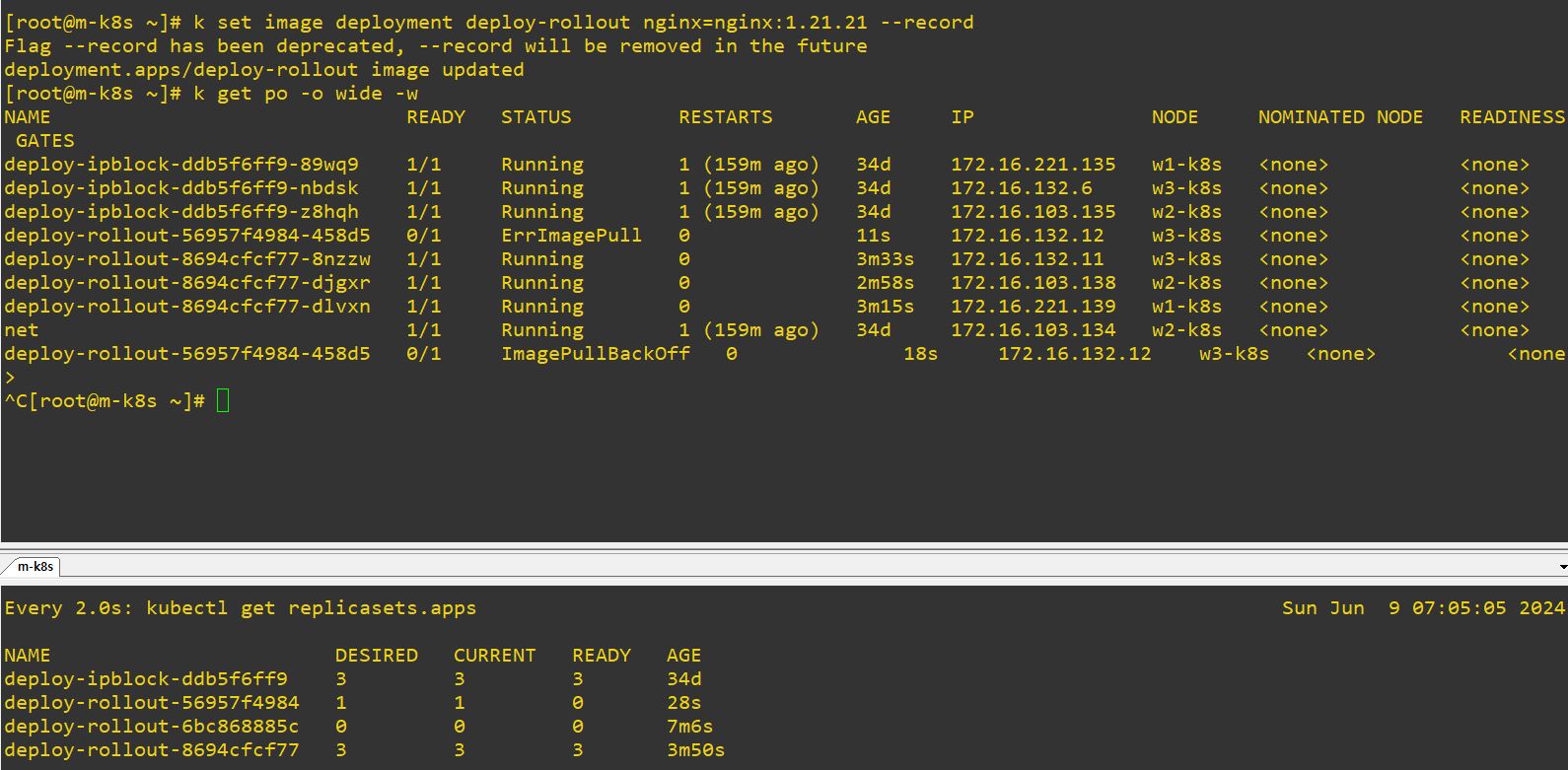
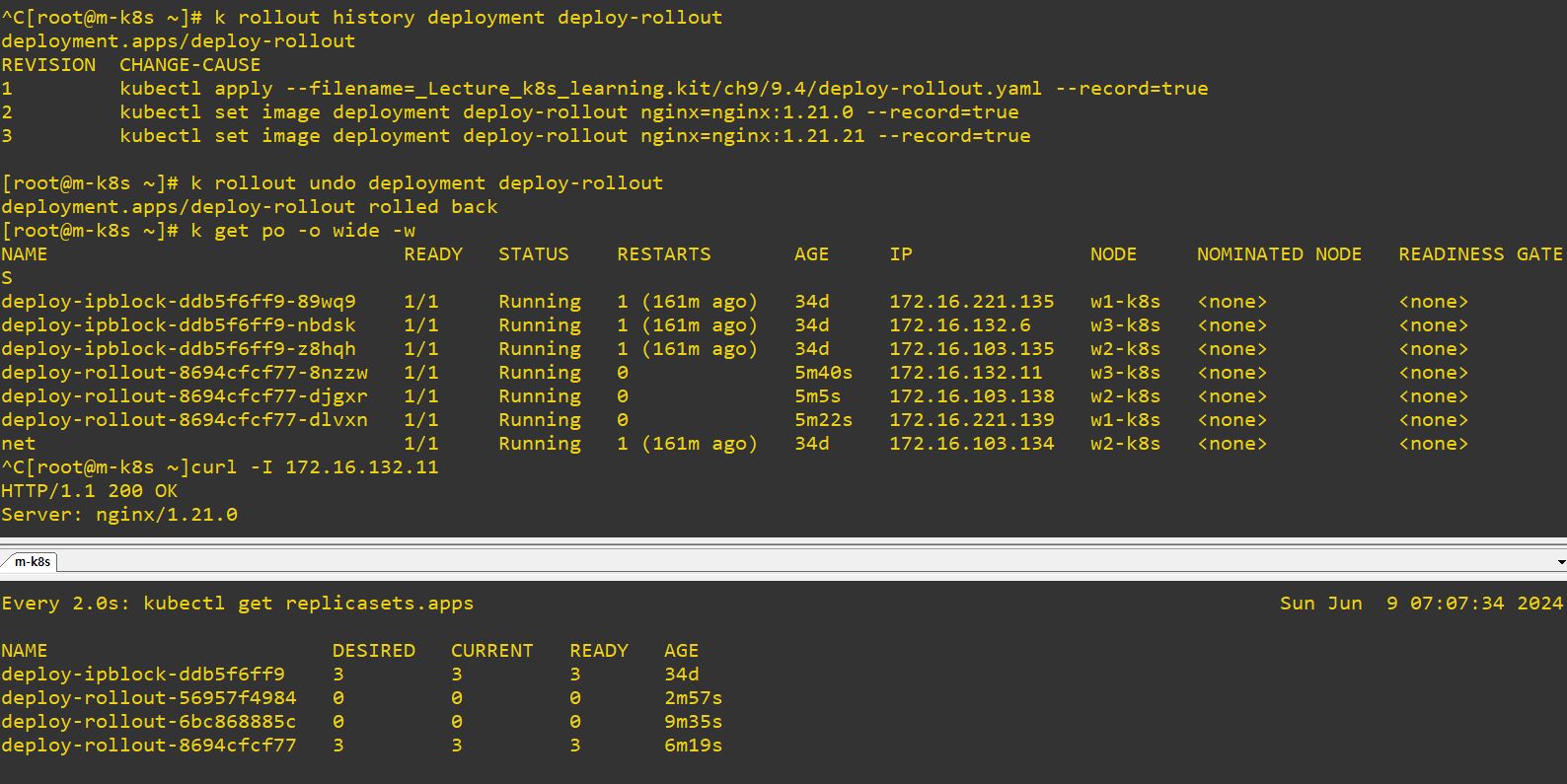
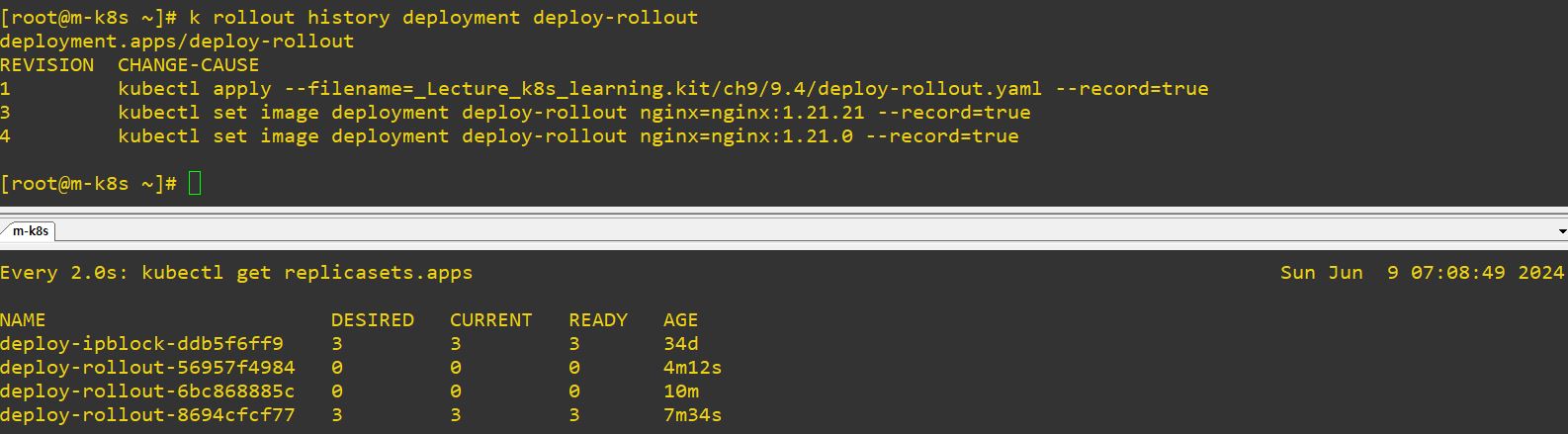
- update with specific version.
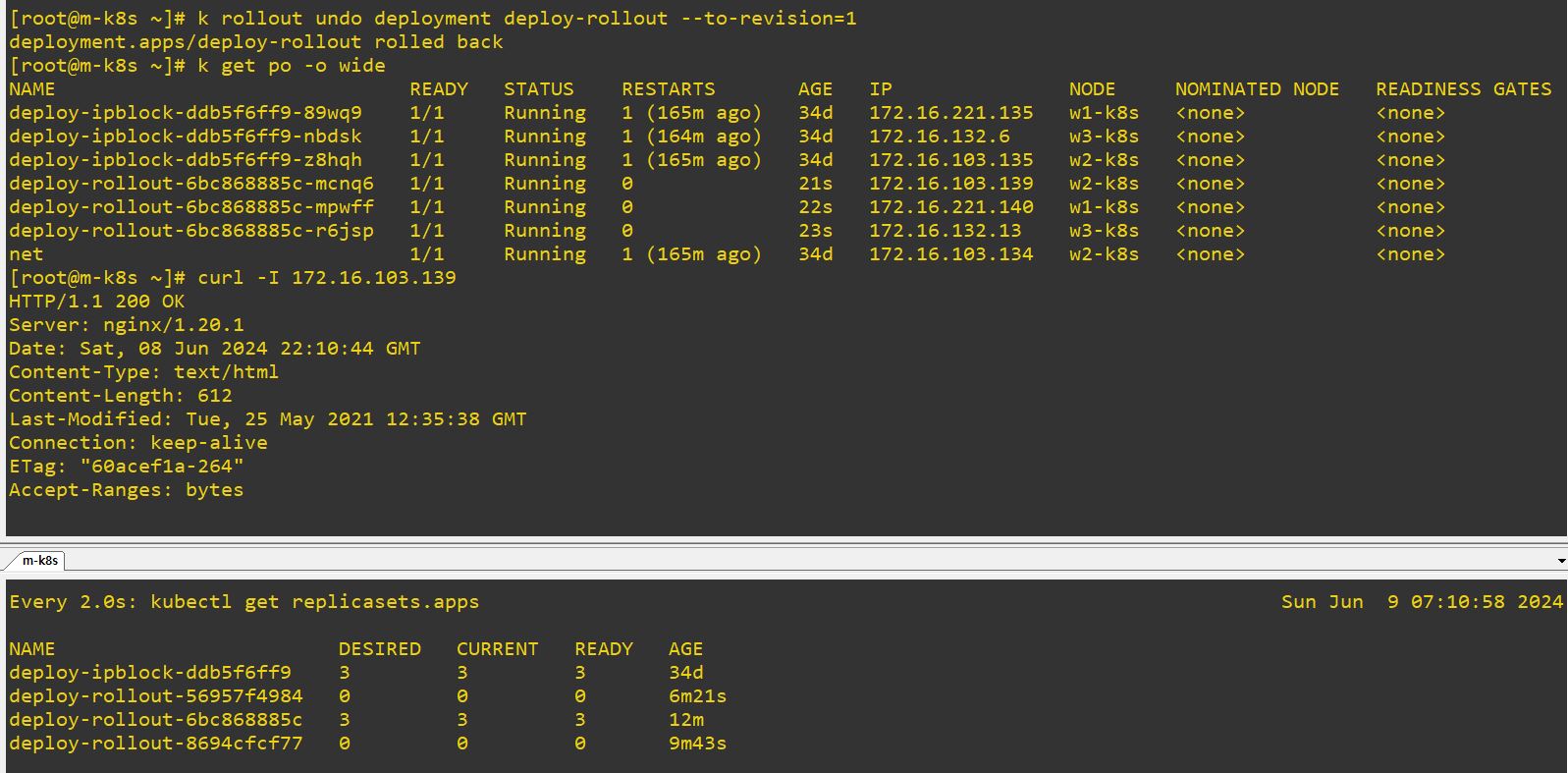
Kustomize
- Dynamic deplyoment
- Metallb can deploy several application at once.
apiVersion: policy/v1beta1
kind: PodSecurityPolicy
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: controller
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
allowedCapabilities: []
allowedHostPaths: []
defaultAddCapabilities: []
defaultAllowPrivilegeEscalation: false
fsGroup:
ranges:
- max: 65535
min: 1
rule: MustRunAs
hostIPC: false
hostNetwork: false
hostPID: false
privileged: false
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
requiredDropCapabilities:
- ALL
runAsUser:
ranges:
- max: 65535
min: 1
rule: MustRunAs
seLinux:
rule: RunAsAny
supplementalGroups:
ranges:
- max: 65535
min: 1
rule: MustRunAs
volumes:
- configMap
- secret
- emptyDir
---
apiVersion: policy/v1beta1
kind: PodSecurityPolicy
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: speaker
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
allowedCapabilities:
- NET_RAW
allowedHostPaths: []
defaultAddCapabilities: []
defaultAllowPrivilegeEscalation: false
fsGroup:
rule: RunAsAny
hostIPC: false
hostNetwork: true
hostPID: false
hostPorts:
- max: 7472
min: 7472
- max: 7946
min: 7946
privileged: true
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
requiredDropCapabilities:
- ALL
runAsUser:
rule: RunAsAny
seLinux:
rule: RunAsAny
supplementalGroups:
rule: RunAsAny
volumes:
- configMap
- secret
- emptyDir
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: controller
namespace: metallb-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: speaker
namespace: metallb-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: metallb-system:controller
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ''
resources:
- services
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ''
resources:
- services/status
verbs:
- update
- apiGroups:
- ''
resources:
- events
verbs:
- create
- patch
- apiGroups:
- policy
resourceNames:
- controller
resources:
- podsecuritypolicies
verbs:
- use
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: metallb-system:speaker
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ''
resources:
- services
- endpoints
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups: ["discovery.k8s.io"]
resources:
- endpointslices
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- ''
resources:
- events
verbs:
- create
- patch
- apiGroups:
- policy
resourceNames:
- speaker
resources:
- podsecuritypolicies
verbs:
- use
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: config-watcher
namespace: metallb-system
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ''
resources:
- configmaps
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: pod-lister
namespace: metallb-system
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ''
resources:
- pods
verbs:
- list
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: controller
namespace: metallb-system
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ''
resources:
- secrets
verbs:
- create
- apiGroups:
- ''
resources:
- secrets
resourceNames:
- memberlist
verbs:
- list
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources:
- deployments
resourceNames:
- controller
verbs:
- get
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: metallb-system:controller
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: metallb-system:controller
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: controller
namespace: metallb-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: metallb-system:speaker
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: metallb-system:speaker
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: speaker
namespace: metallb-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: config-watcher
namespace: metallb-system
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: config-watcher
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: controller
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: speaker
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: pod-lister
namespace: metallb-system
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: pod-lister
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: speaker
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
name: controller
namespace: metallb-system
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: controller
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: controller
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
component: speaker
name: speaker
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: metallb
component: speaker
template:
metadata:
annotations:
prometheus.io/port: '7472'
prometheus.io/scrape: 'true'
labels:
app: metallb
component: speaker
spec:
containers:
- args:
- --port=7472
- --config=config
env:
- name: METALLB_NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
- name: METALLB_HOST
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.hostIP
- name: METALLB_ML_BIND_ADDR
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.podIP
# needed when another software is also using memberlist / port 7946
# when changing this default you also need to update the container ports definition
# and the PodSecurityPolicy hostPorts definition
#- name: METALLB_ML_BIND_PORT
# value: "7946"
- name: METALLB_ML_LABELS
value: "app=metallb,component=speaker"
- name: METALLB_ML_SECRET_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: memberlist
key: secretkey
image: quay.io/metallb/speaker:main
name: speaker
ports:
- containerPort: 7472
name: monitoring
- containerPort: 7946
name: memberlist-tcp
- containerPort: 7946
name: memberlist-udp
protocol: UDP
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
add:
- NET_RAW
drop:
- ALL
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
hostNetwork: true
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
serviceAccountName: speaker
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 2
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
operator: Exists
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: metallb
component: controller
name: controller
namespace: metallb-system
spec:
revisionHistoryLimit: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: metallb
component: controller
template:
metadata:
annotations:
prometheus.io/port: '7472'
prometheus.io/scrape: 'true'
labels:
app: metallb
component: controller
spec:
containers:
- args:
- --port=7472
- --config=config
env:
- name: METALLB_ML_SECRET_NAME
value: memberlist
- name: METALLB_DEPLOYMENT
value: controller
image: quay.io/metallb/controller:main
name: controller
ports:
- containerPort: 7472
name: monitoring
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- all
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
securityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 65534
fsGroup: 65534
serviceAccountName: controller
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0Kustomize process
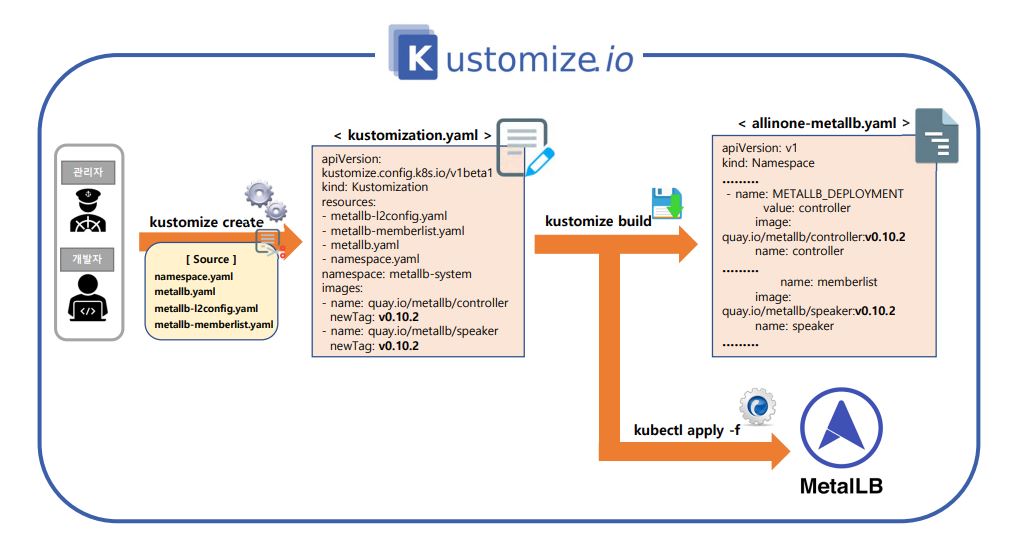
- We can change dynamically kustomization.yaml file with sources by
kustomize create. - And then we can create upgrade build file with
kustomize build. - Finally you can upgrade with
kubectl apply -f.
- Delete MetalLB
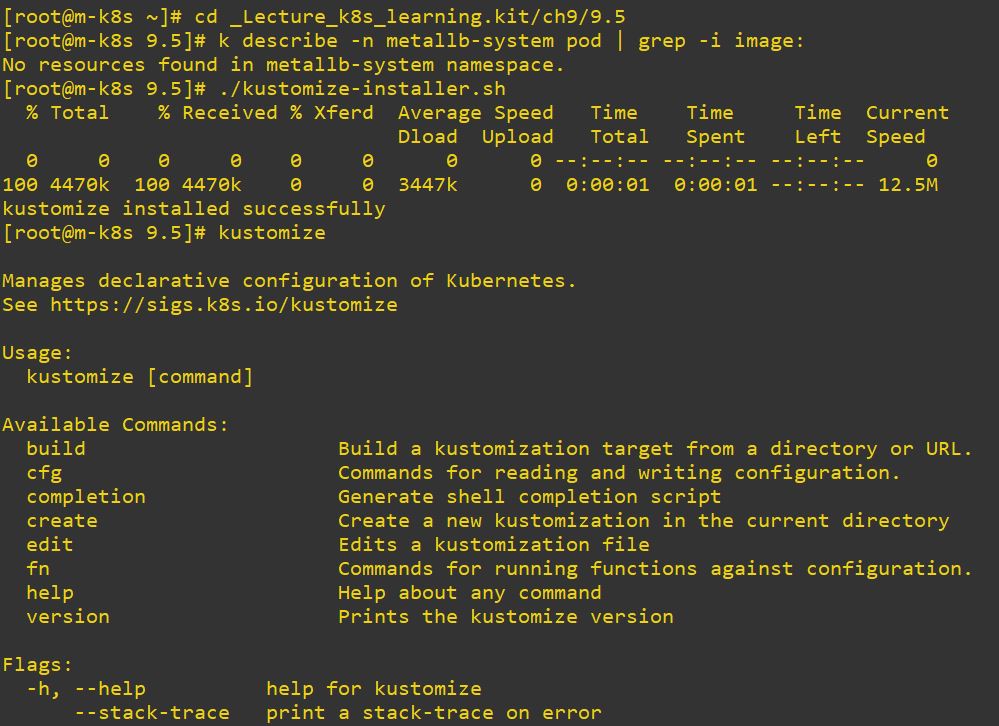
- Check MetalLB is deleted and install kustomize
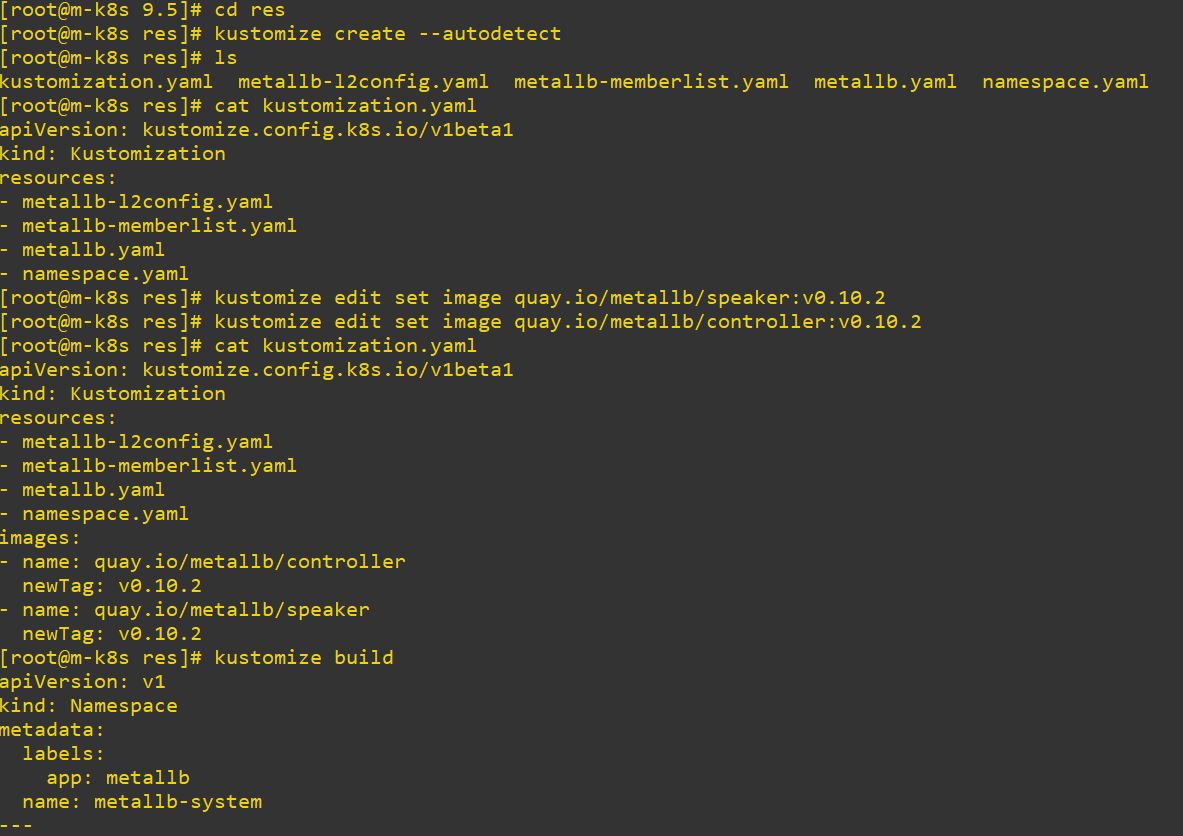
- Create kustomize and edit version
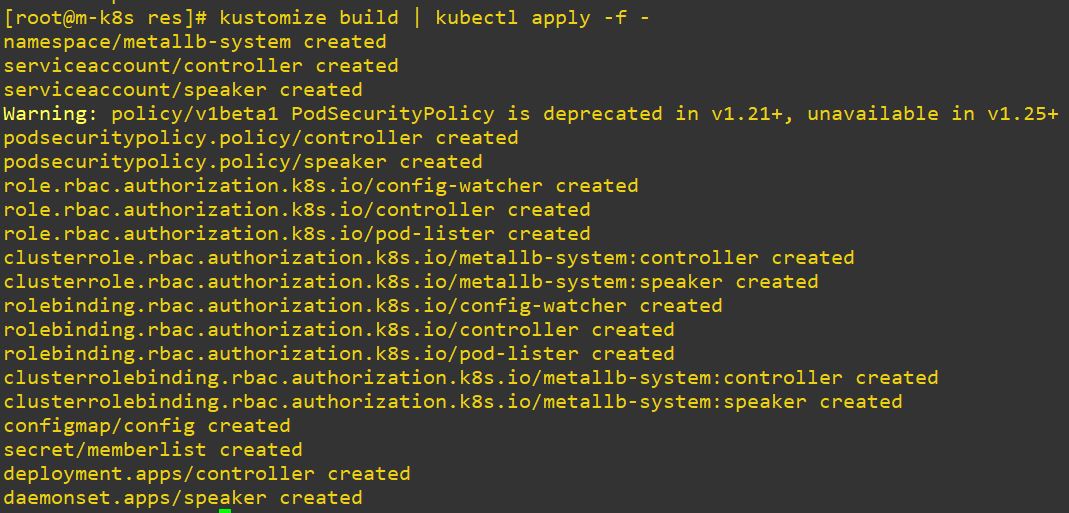
- Deploy MetalLB
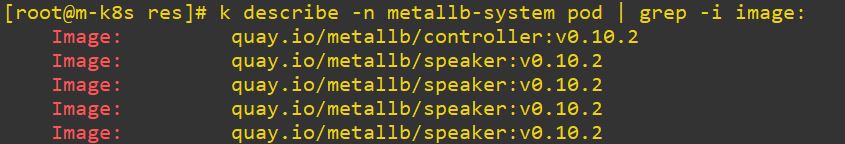
- Chcek MetalLB is deployed
helm
- helm make dynamic deploy easier.
- helm > kustomize.io > kubectl
- User’s work with helm is just setting storage and intalling release
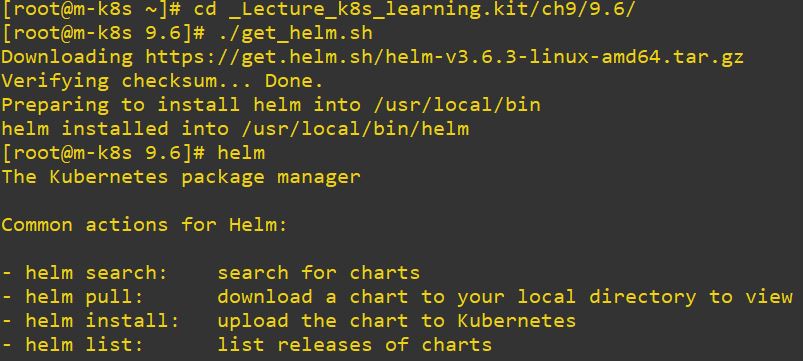
- Install helm
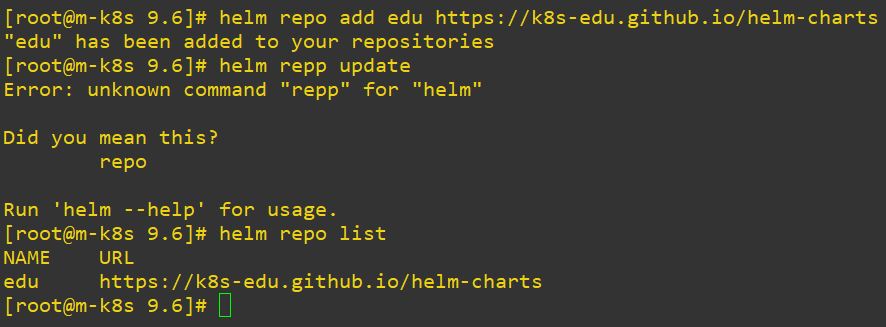
- Set storage
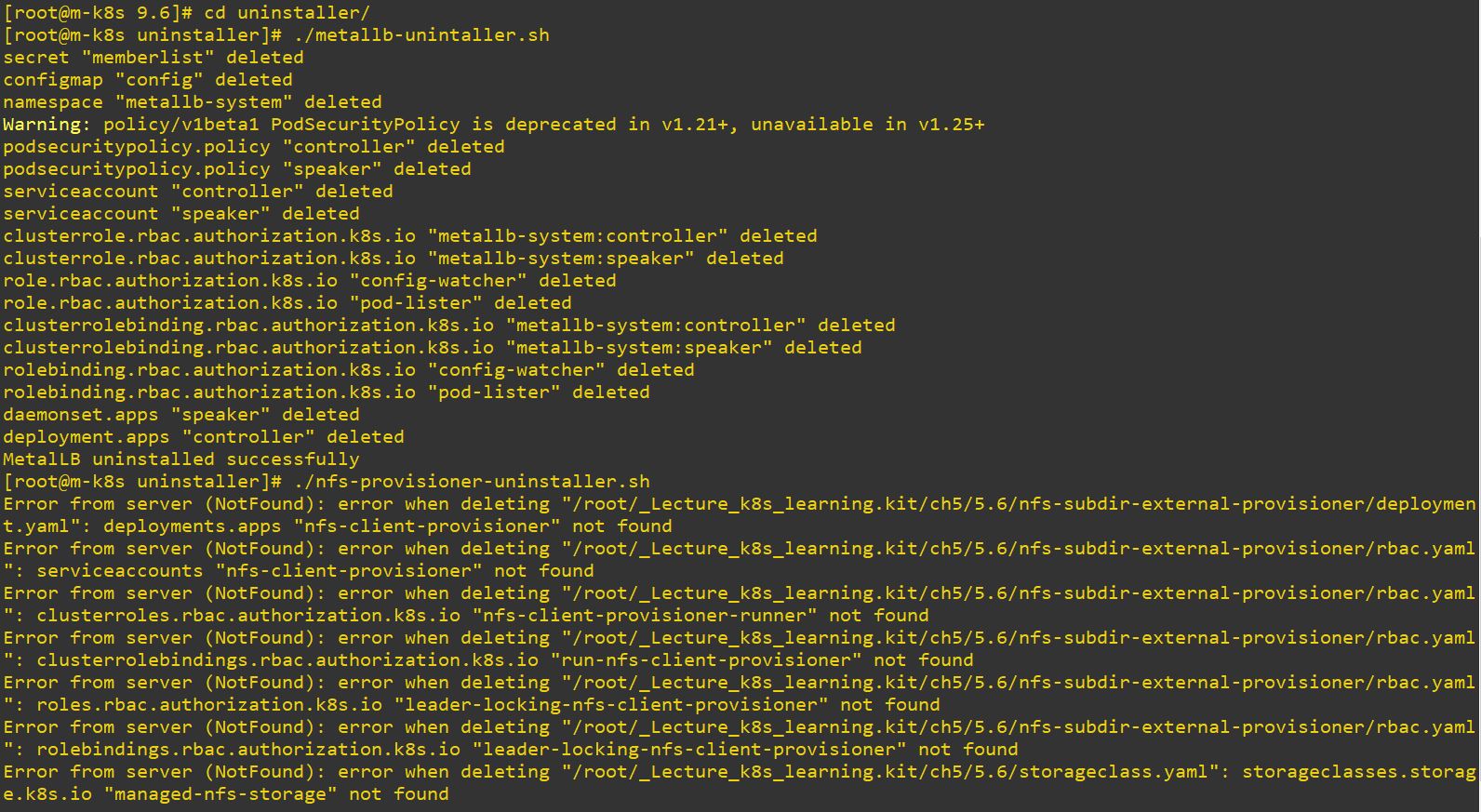
- Delete oldest metalLB and NFS provisioner because we will use only helm
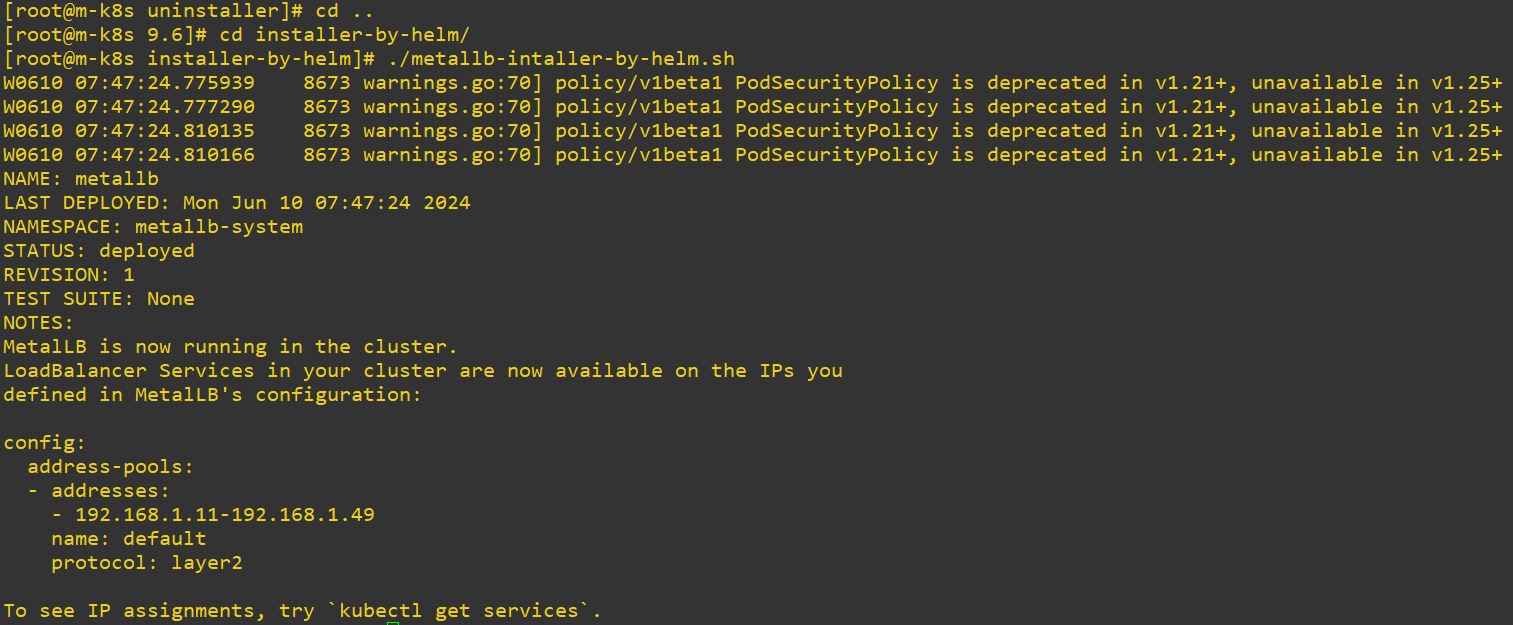
- Install metalLB with helm
- This is
metallb-installer-by-helm.sh
helm install metallb edu/metallb \
--create-namespace \
--namespace=metallb-system \
--set controller.image.tag=v0.10.2 \
--set speaker.image.tag=v0.10.2 \
-f ~/_Lecture_k8s_learning.kit/ch9/9.6/installer-by-helm/l2-config-by-helm.yaml- helm will install metalLB with namespace
metallb-systemand image version0.10.2. - helm will apply config with this.
configInline:
address-pools:
- name: default
protocol: layer2
addresses:
- 192.168.1.11-192.168.1.49
- Install metalLB with helm
- This is
nfs-provisioner-installer-by-helm.sh
helm install nfs-provisioner edu/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner \
--set nfs.server=192.168.1.10 \
--set nfs.path=/nfs_shared/dynamic-vol \
--set storageClass.name=managed-nfs-storage- Uninstall metalLB with helm, if you need.

Metrics-Server
- Mornitoring resources, like CPU and memory.
- Each kubelet in worker node sends measured value to Metrics-Server.
- And user can get measured value from Metrics-Server with API.
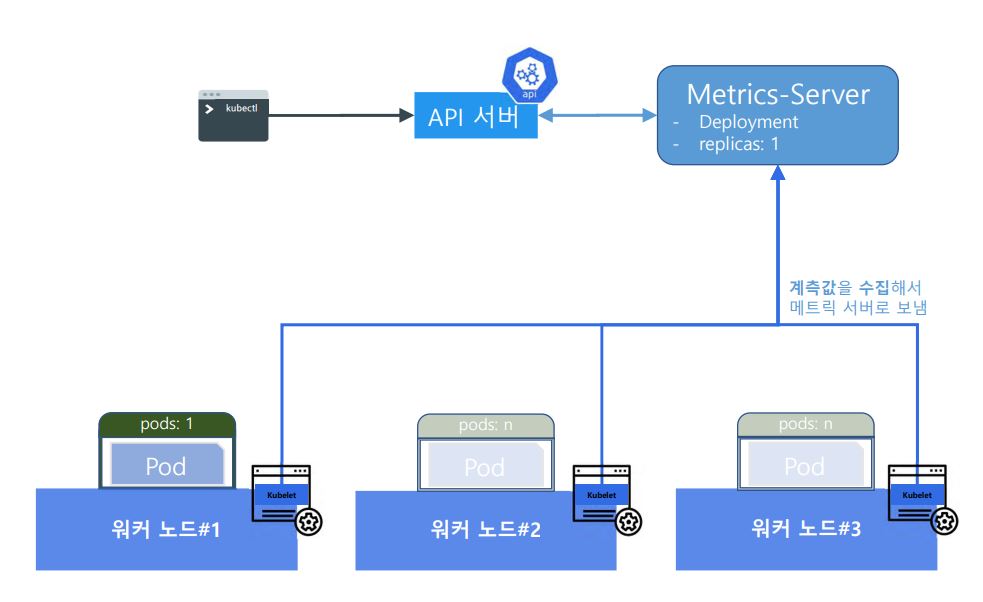
- If current system has not kustomization,
kubectl apply -k .will read and excute all referenced kustomization files. - You can see measured value by
k top
HPA (Horizontal Pod Autoscaler)
- Sync with Metrics-Server
- Scale pods automatically
- Applications will be managed automatically depends on kubernetes resources’ status.
- HPA is for linear load increasing or predictable load.
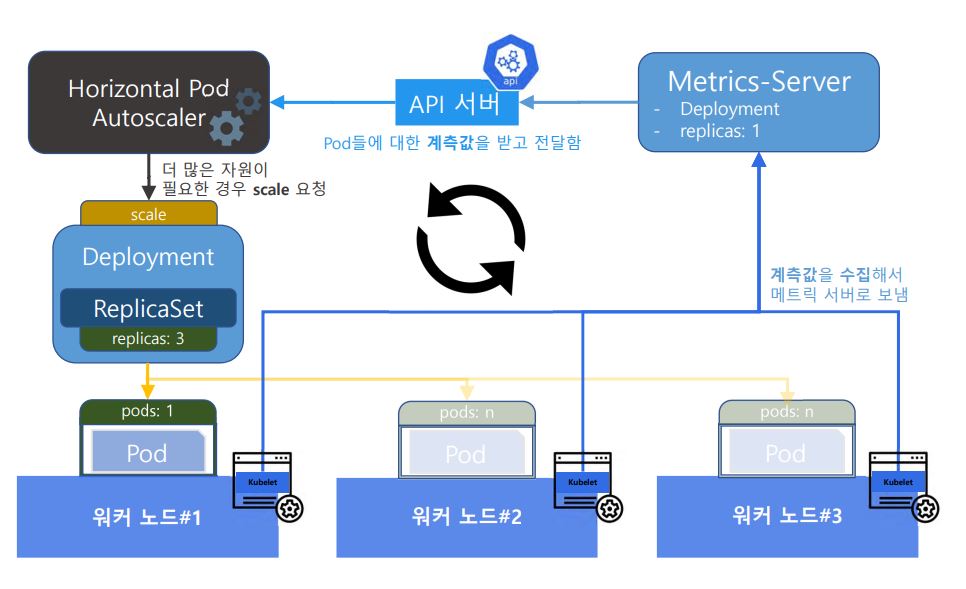
- API Server sends measured value about pods to HPA.
- HPA applies resources to appropriate deployment when they has to be needed.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-4-hpa
labels:
app: deploy-4-hpa
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: deploy-4-hpa
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: deploy-4-hpa
spec:
containers: # Set resources for containers
- name: chk-hn
image: sysnet4admin/chk-hn
resources:
requests: # min
cpu: "10m"
limits: # max
cpu: "20m"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: lb-deploy-4-hpa
spec:
selector:
app: deploy-4-hpa
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: LoadBalancer- Active HPA with below code or command
k autoscale deployment deploy-4-hpa --min=1 --max=10 --cpu-percent=50 - You can create below code by
k autoscale deployment deploy-4-hpa --min=1 --max=10 --cpu-percent=50 --dry-run=client -o yaml
apiVersion: autoscaling/v1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: deploy-4-hpa
spec:
maxReplicas: 10
minReplicas: 1
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: deploy-4-hpa
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 50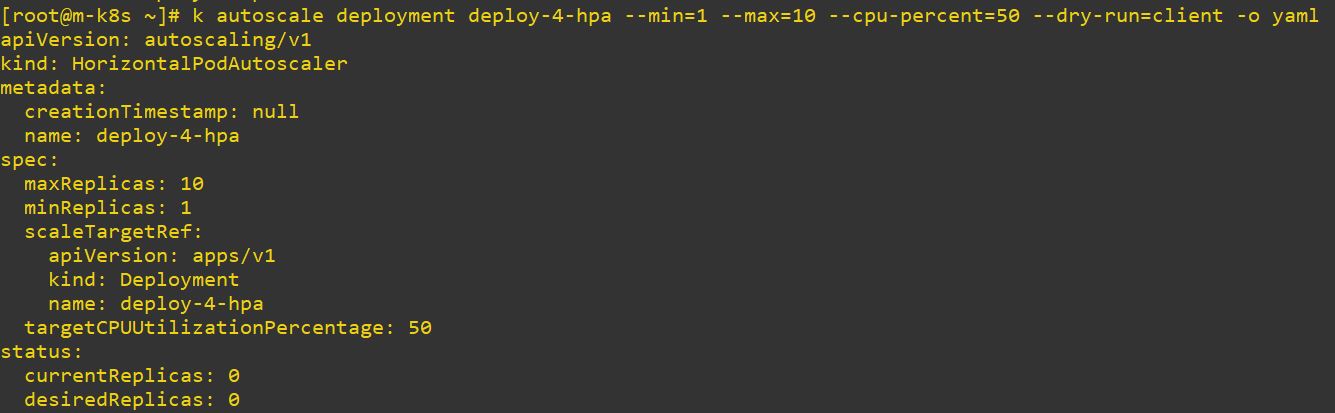
- Set load
while true
do
COUNTER=$((COUNTER + 1))
echo -ne "$COUNTER - " ; curl $1
doneExcersice
- Apply deployment and autoscale.

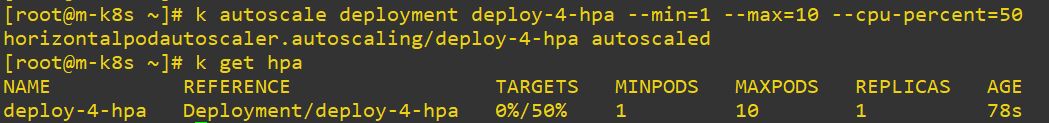
- Monitor pods by
watch kubectl top pods --use-protocol-buffers - Monitor HPA by
watch kubectl get hpa
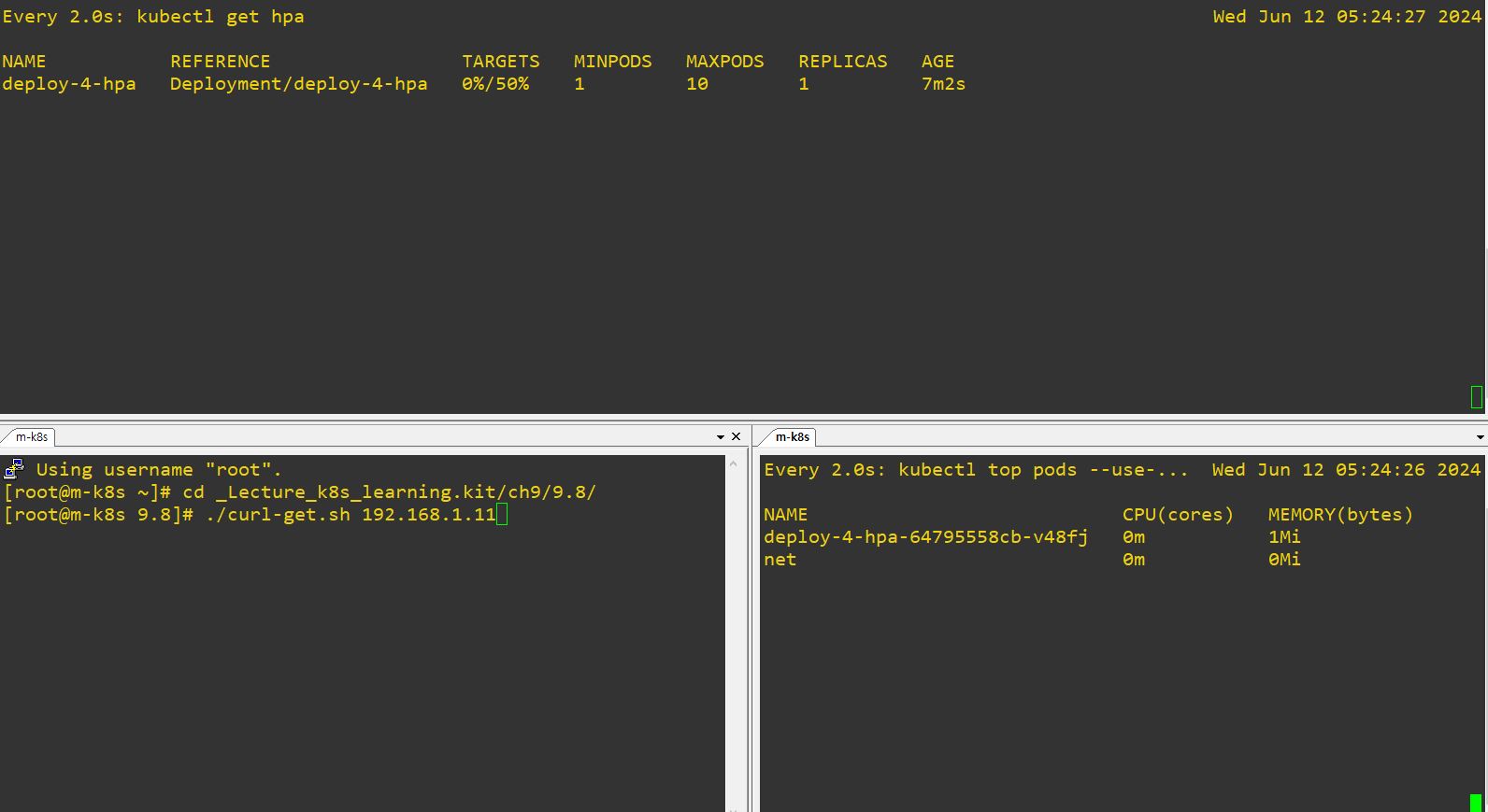
- Set load
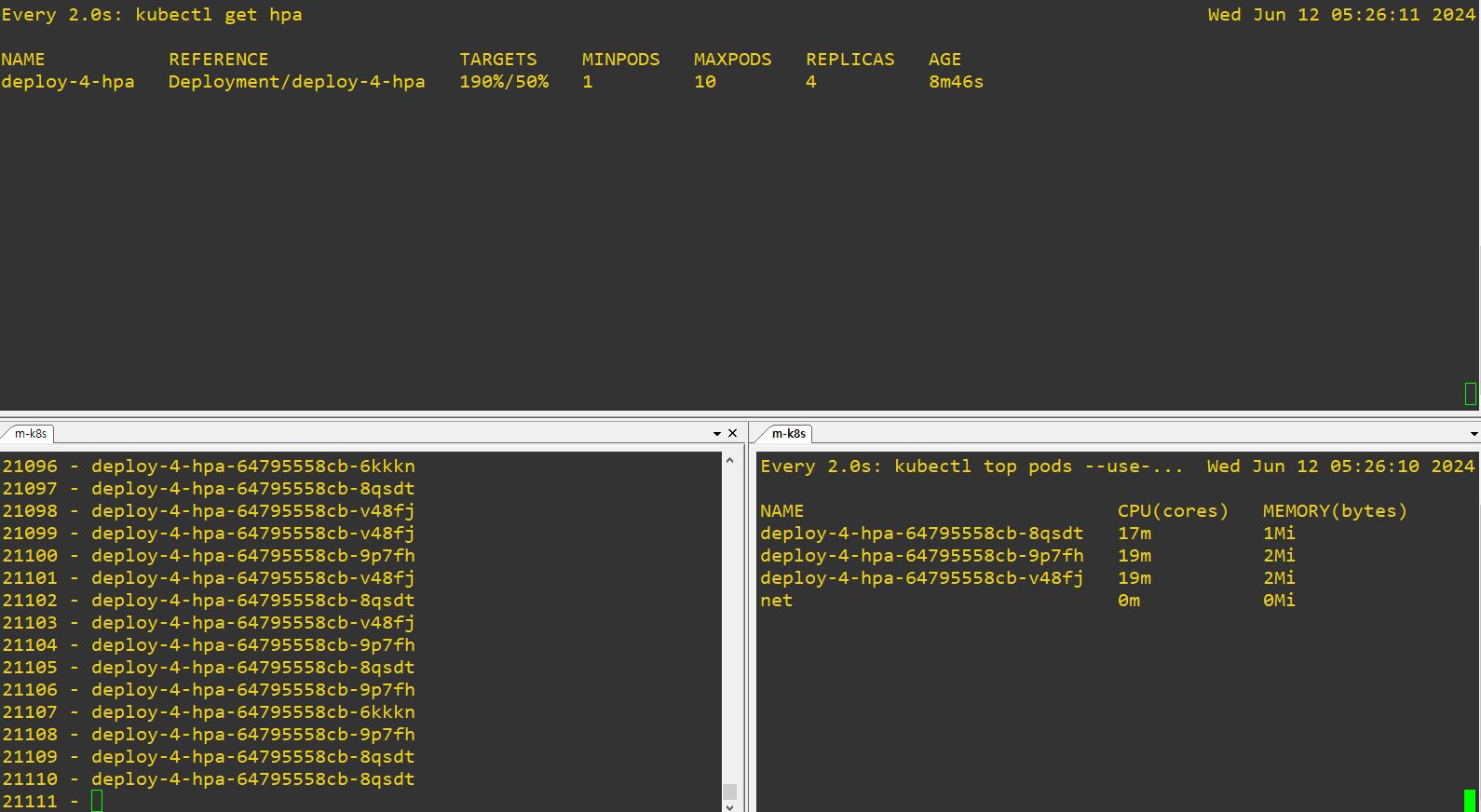
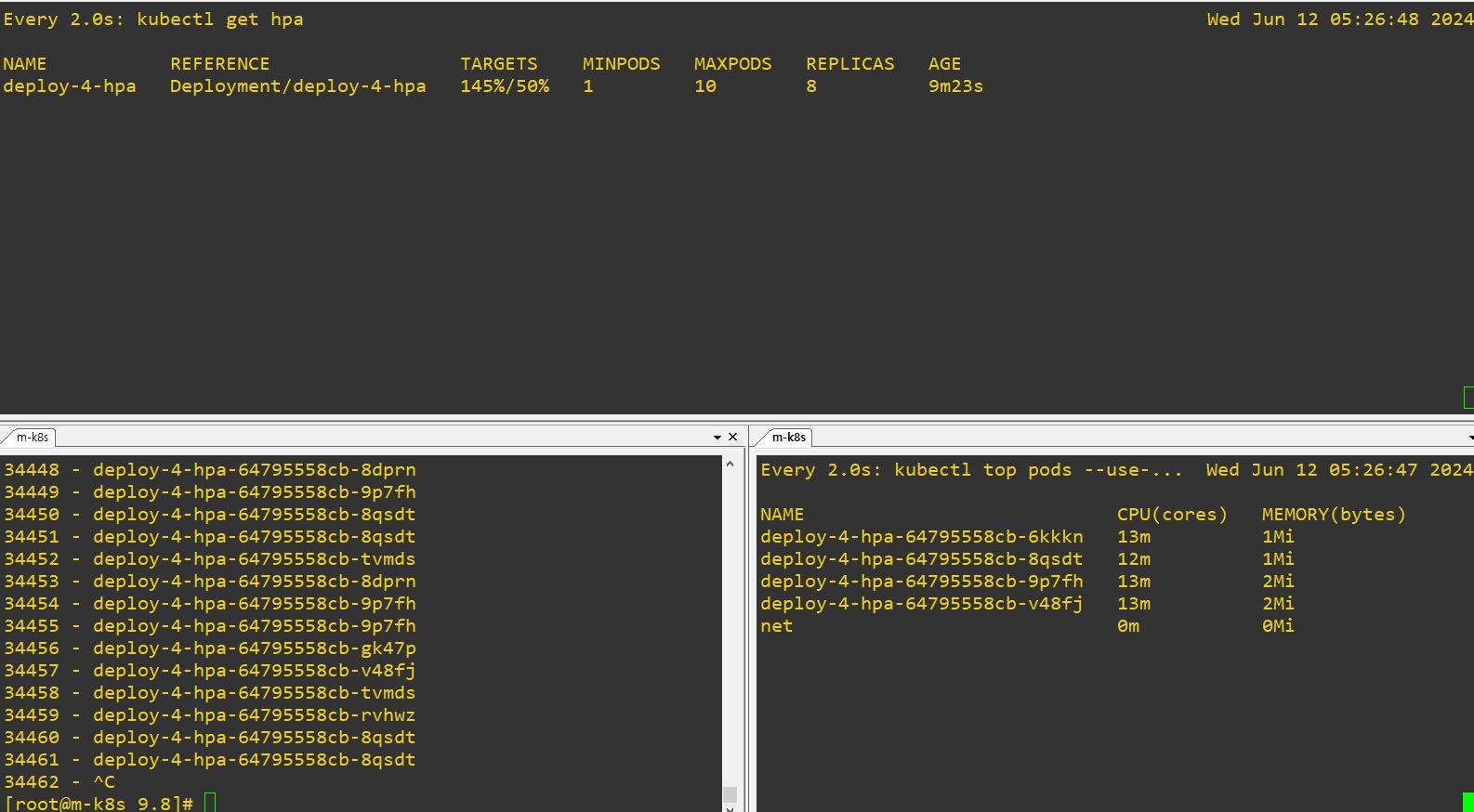
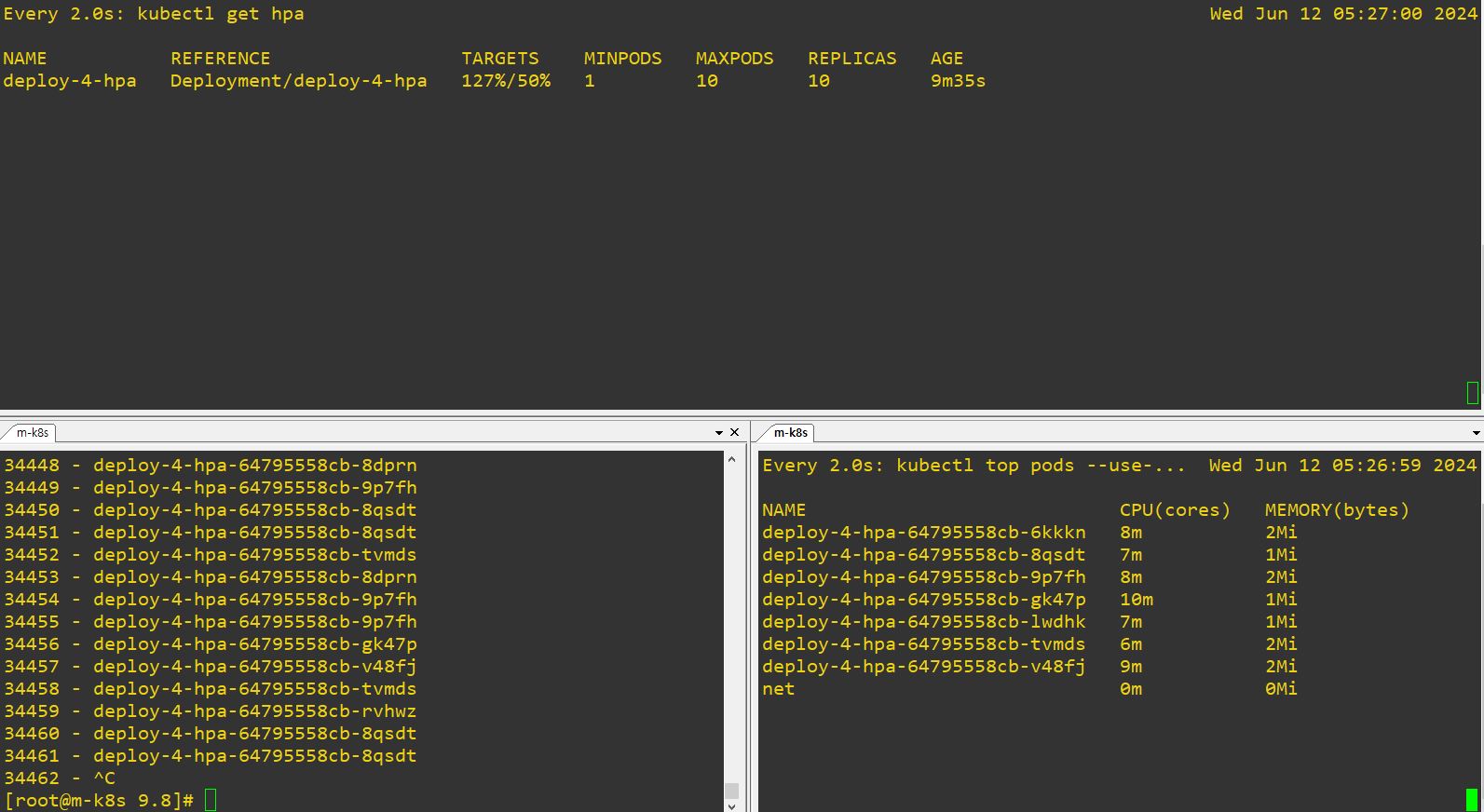
- Stop load
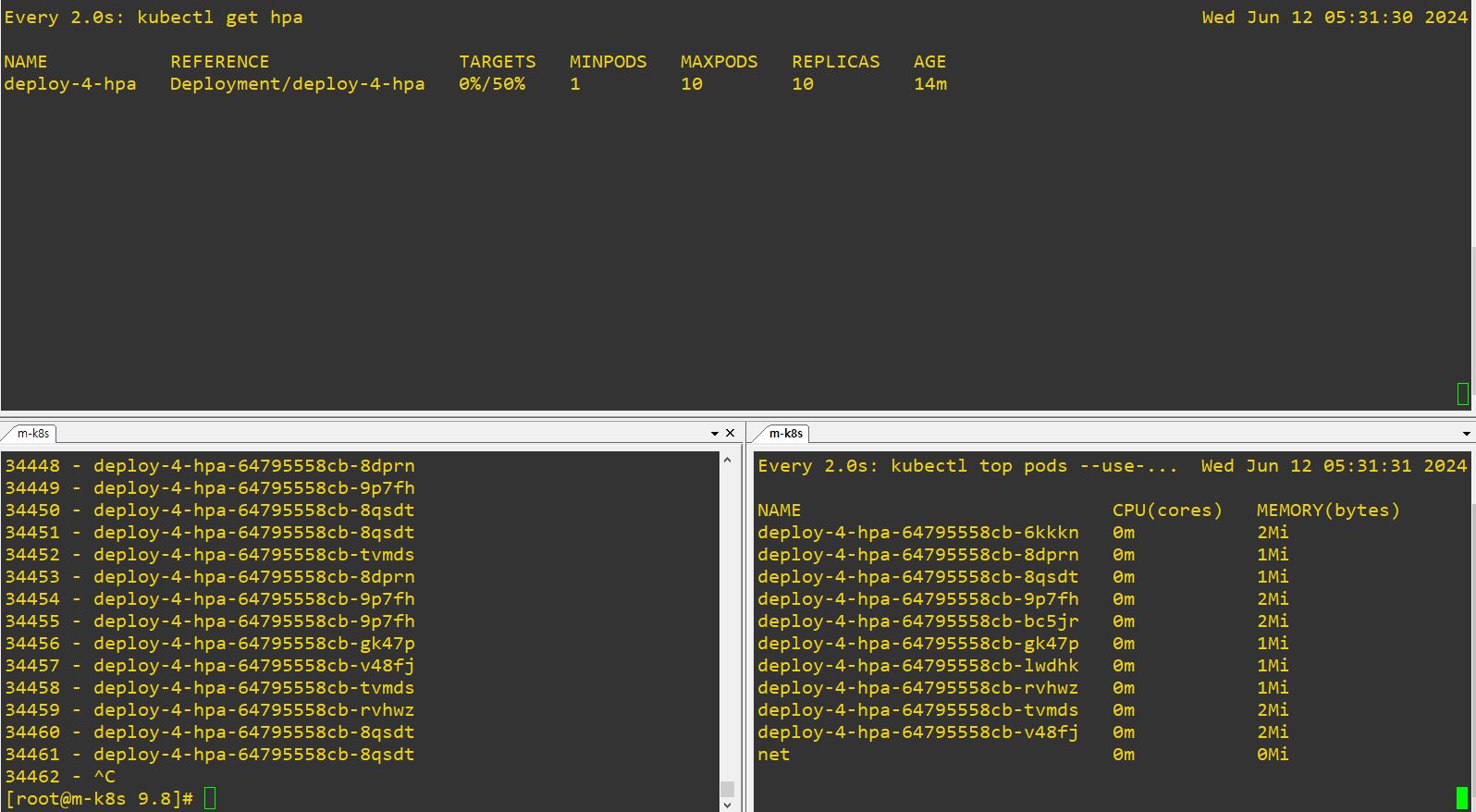
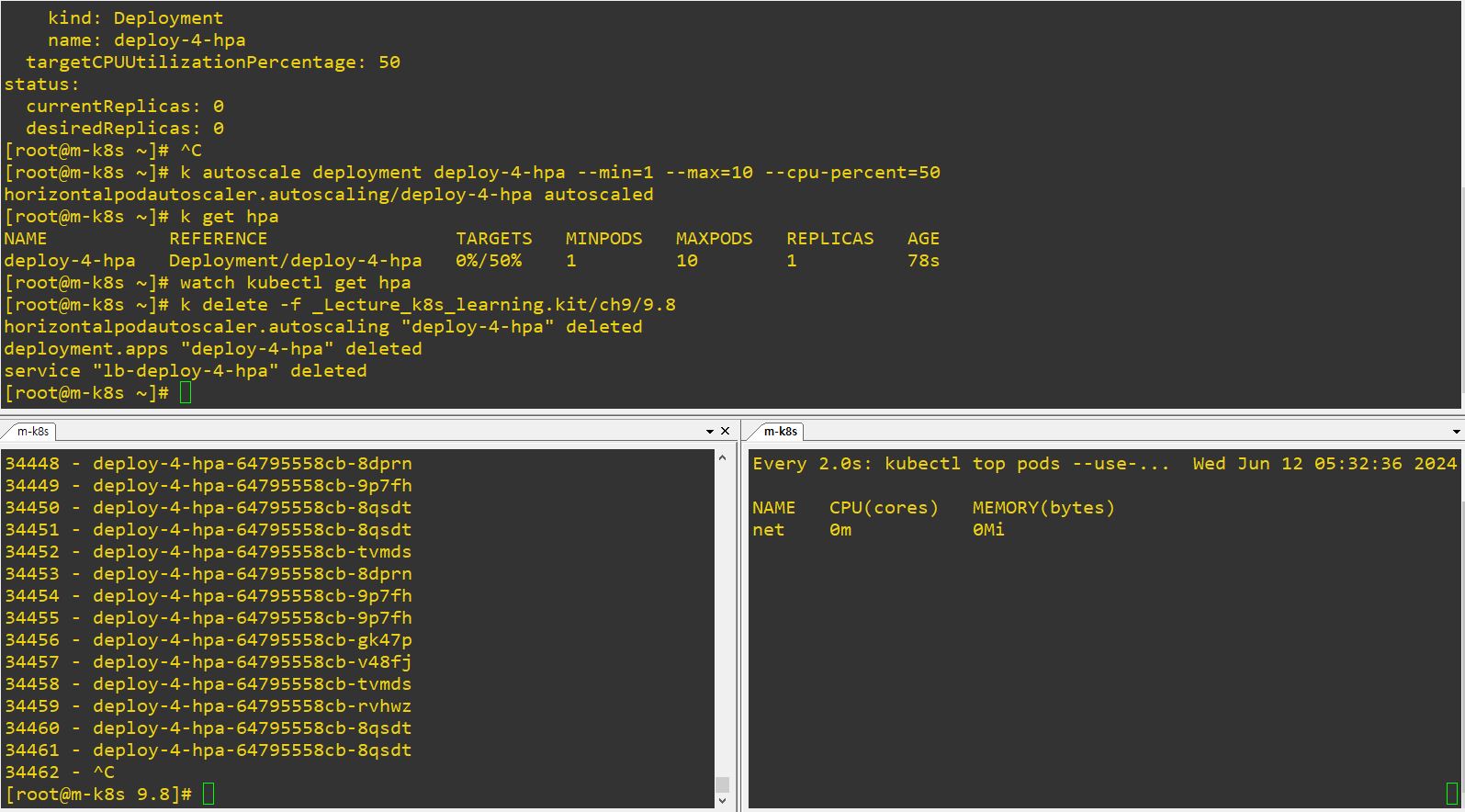
kube-dashboard
- You can do all commands on Web UI.
Excercise
- Check kubernetes-dashboard service IP.
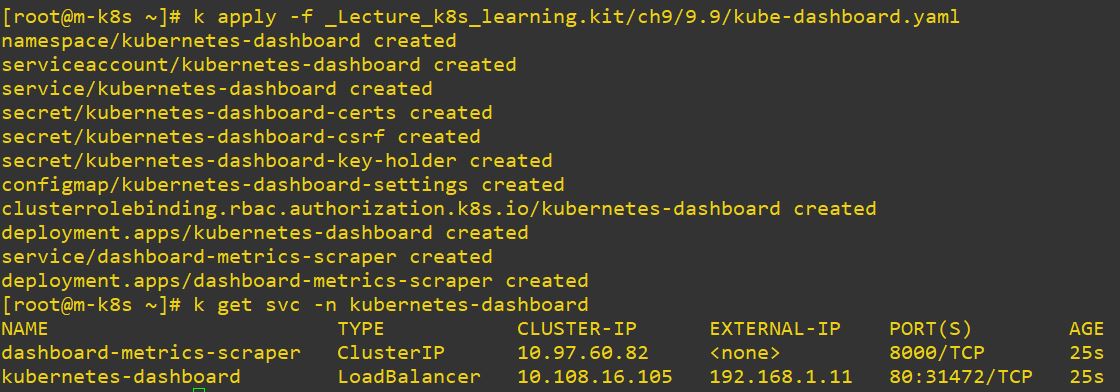
- Open Web UI with kubernetes-dashboard service IP.
- Click skip for authorization.
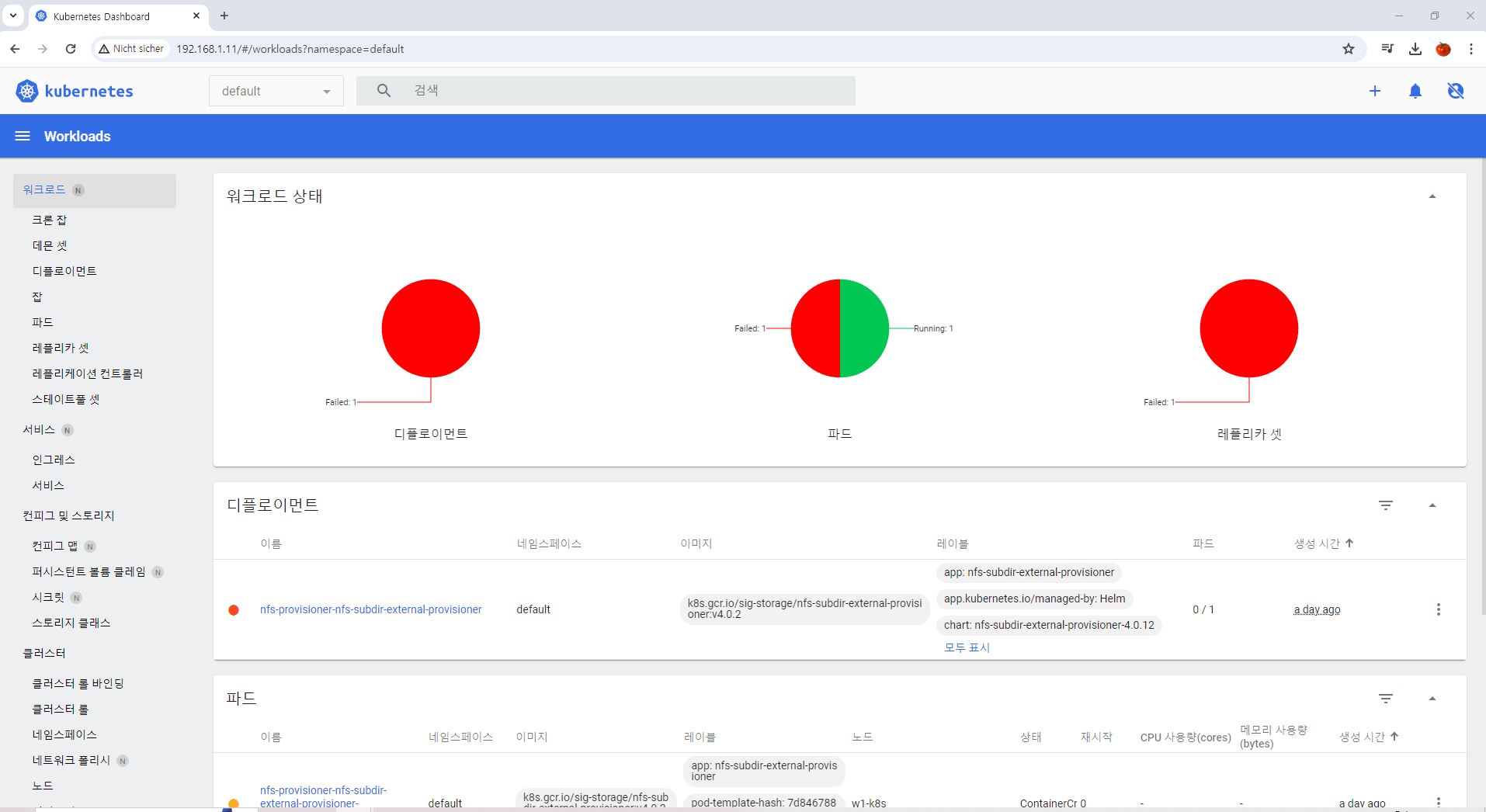
- Create a pod with left-top
+button. - Click deploy button.
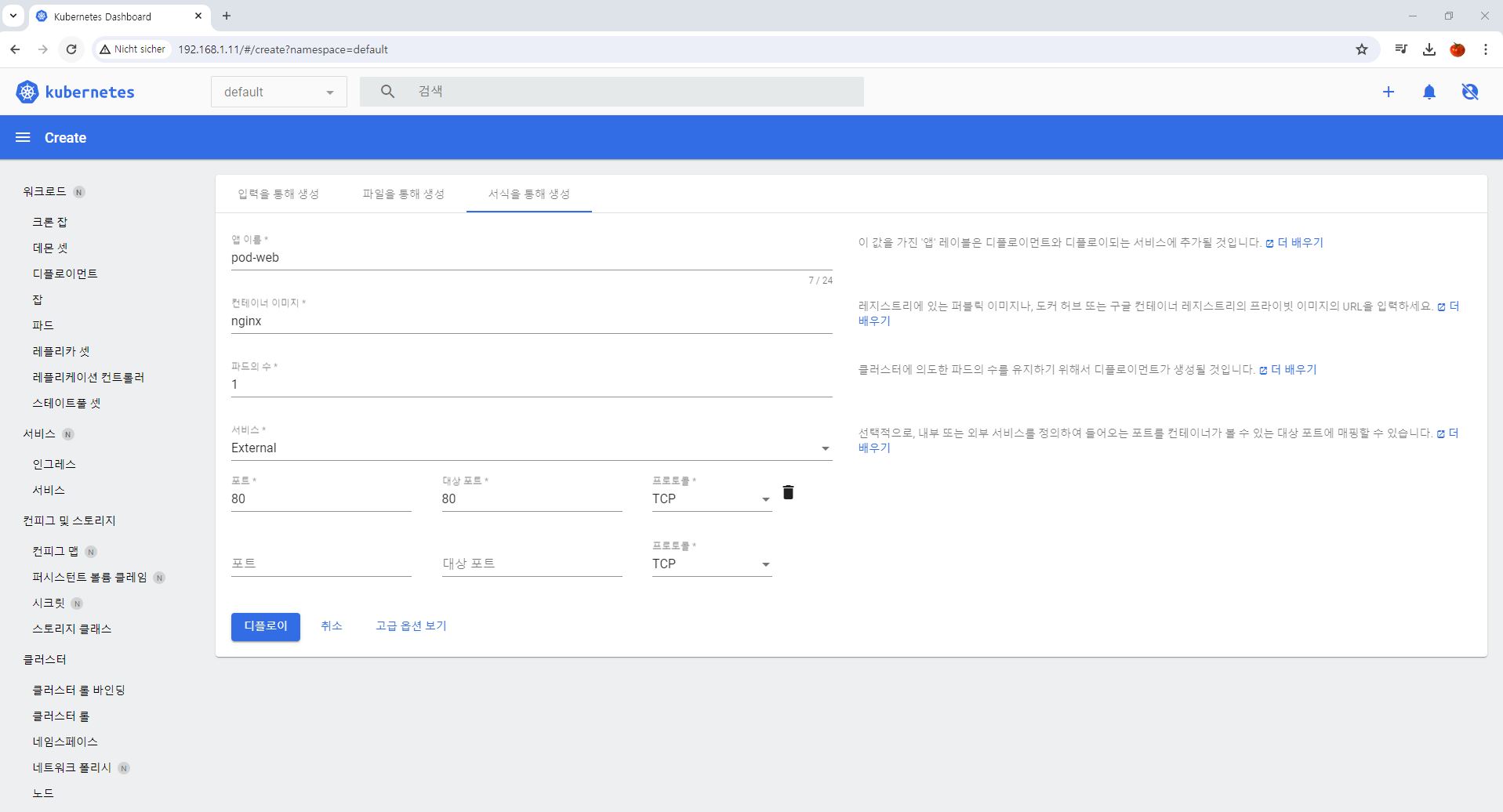
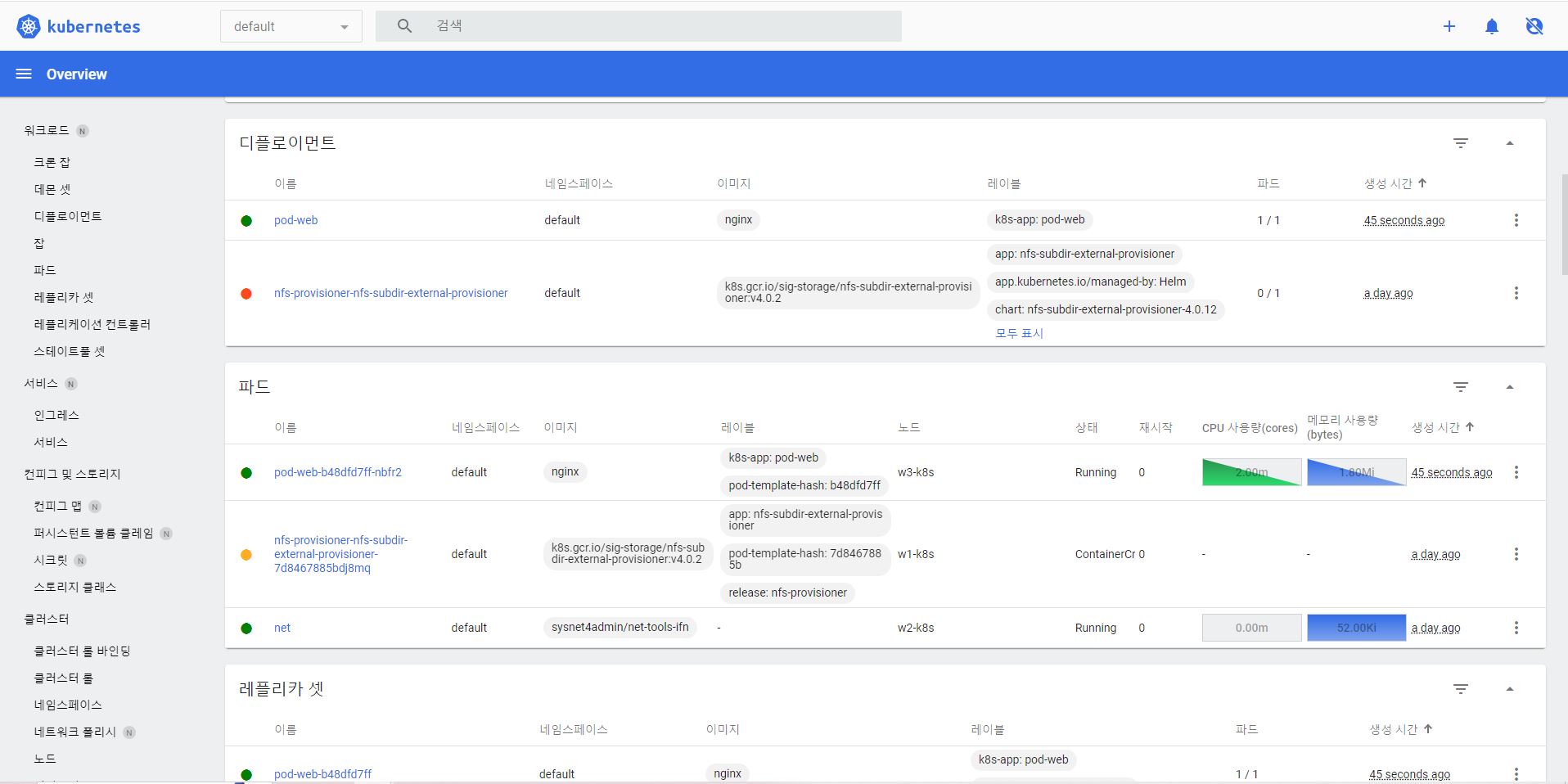
- Click Pods in bread.
- Click three dots button to see information of pod-web.
- Click deployment
- Delete pod-web deployment with three dots button.