Data Analysis
Download Northwind Database
- GITHUB
- DOWNLOAD Northwind

EXEC
- EXEC sp_helpdb
- show information of databse
EXEC sp_helpdb 'Northwind';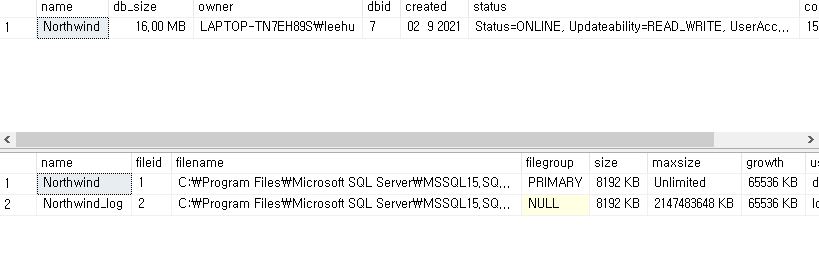
INDEX
- FILLFACTOR
- use only 1% of leaf page space
- PAD_INDEX
- apply to FILLFACTOR middle page
CREATE INDEX Test_Inde ON Test(LastName)
WITH (FILLFACTOR = 1, PAD_INDEX = ON)
- sys.indexes
- help to search index number
SELECT index_id, name
FROM sys.indexes
WHERE object_id = object_id('Test');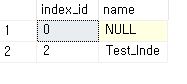
DBCC
- DBCC
- show database data that match with the condition
- IND
- show index data
DBCC IND('Northwind', 'Test', 2);

- PAGE
- ref: [Database], [File Number], [Page Number], [Print Option]
- HEAD_RID
- ref: Page Address, File ID, Slot Number
DBCC PAGE('Northwind', 1, 840, 3);
DBCC PAGE('Northwind', 1, 848, 3);
DBCC PAGE('Northwind', 1, 849, 3);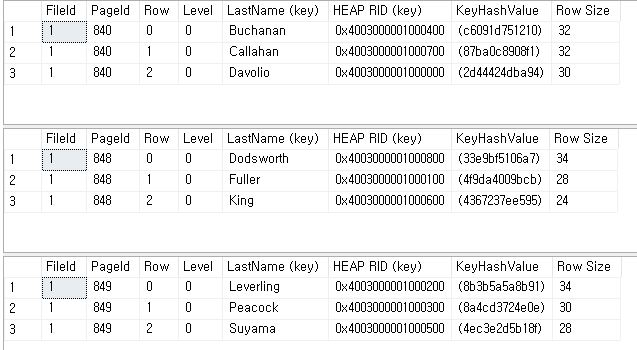
DBCC PAGE('Northwind', 1, 872, 3);
DBCC PAGE('Northwind', 1, 848, 3);
DBCC PAGE('Northwind', 1, 849, 3);
- Random Access
- Access one page by one page to read
- Bookmark Lookup
- search row by RID
Multiple Index
Copy table to new table
- SELECT INTO
- copy the table and paste in a new table
SELECT *
INTO TestOrderDetails
FROM [Order Details];
EXEC
- EXEC sp_helpindex
- show information of index
CREATE INDEX Index_TestOrderDetails
ON TestOrderDetails(OrderID, ProductID);
EXEC sp_helpindex 'TestOrderDetails';
Index performance
- Multiple Index
- when you use multiple index(A, B), the index order is A and B is next level of A
- So, if you want to use index, you have to start A
- if you start B, then the process cannot use index
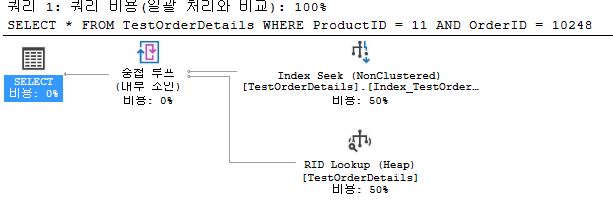
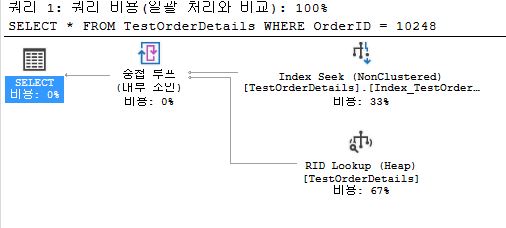
- SEEK
- process speed is good
- use index when searching
SELECT *
FROM TestOrderDetails
WHERE OrderID = 10248 AND ProductID = 11;
SELECT *
FROM TestOrderDetails
WHERE ProductID = 11 AND OrderID = 10248;
SELECT *
FROM TestOrderDetails
WHERE OrderID = 10248;
SELECT LastName
INTO TestEmployees
FROM Employees;
CREATE INDEX Index_TestEmployees
ON TestEmployees(LastName);
SELECT *
FROM TestEmployees
WHERE LastName LIKE 'Bu%';
- SCAN
- process speed is bad
- do not use index when searching
SELECT *
FROM TestOrderDetails
WHERE ProductID = 11;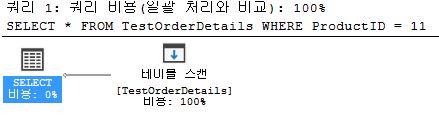
- when you use data processing, all of data will be scanned even it is index
SELECT *
FROM TestEmployees
WHERE SUBSTRING(LastName, 1, 2) = 'Bu';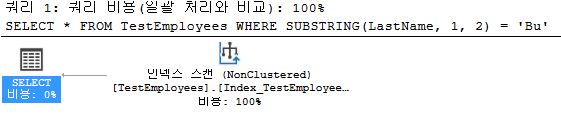
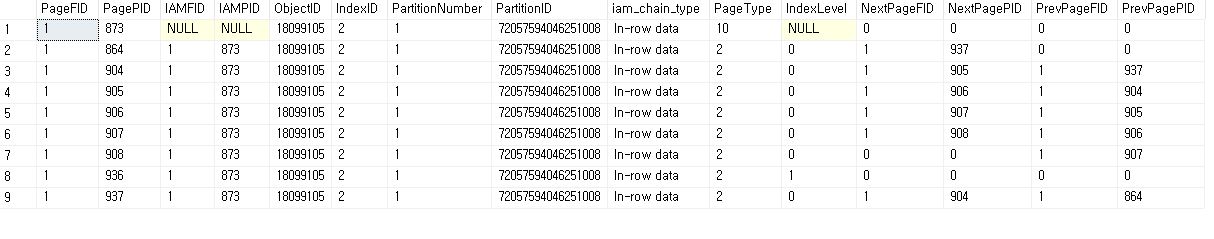
Page Split
- Page Split
- if page is full, make a new page and insert in specific position
DECLARE @i INT = 0;
WHILE @i < 50
BEGIN
INSERT INTO TestOrderDetails
VALUES(10248, 100 + @i, 10, 1, 0);
SET @i = @i +1;
END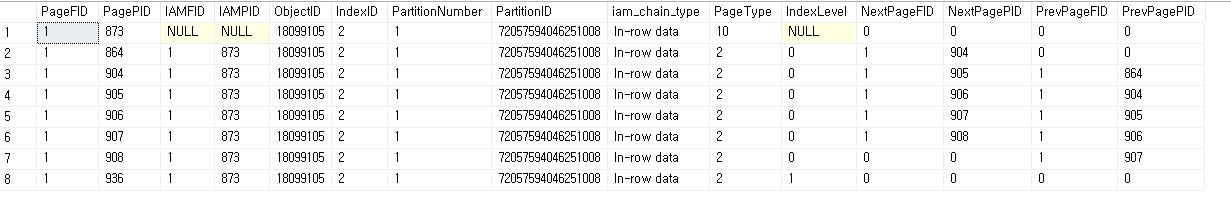

Clustered vs Non-Clustered
Clustered
- Clustered
- Leaf Page = Data Page
- data is ordered by Clustered index
Non-Clustered
- not exist Clustered Index
- data is saved in Heal Table
- Heap RIP → Heap Table To exract data
SELECT *
INTO TestOrderDetails2
FROM [Order Details];
SELECT *
FROM TestOrderDetails2;
CREATE INDEX Index_OrderDetails
ON TestOrderDetails2(OrderID, productID);
EXEC sp_helpindex 'TestOrderDetails2';
SELECT index_id, name
FROM sys.indexes
WHERE object_id = object_id('TestOrderDetails2');
DBCC IND('Northwind', 'TestOrderDetails2', 2);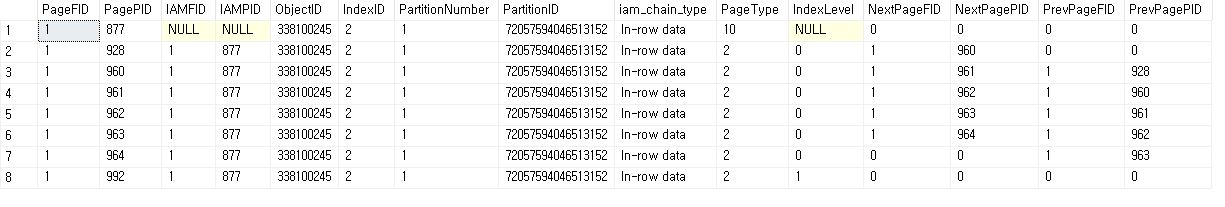
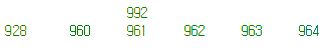
- HEAP RID
- Heap RID([Page Address(4)] [File ID(2)][Slot(2)] ROW)
- Heap Table[{Page} {Page} {Page} {Page}]
DBCC PAGE('Northwind', 1, 928, 3);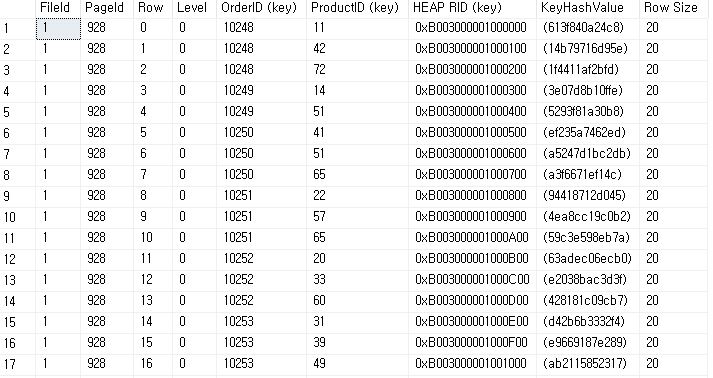
- exist Clustered Index
- no Heap Table. Real data is in Leaf Table
- has real Key value of Clustered Index
- Previous index can be changed
- no Heap Table. Real data is in Leaf Table
CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX Index_OrderDetails_Clustered
ON TestOrderDetails2(OrderID);
SELECT index_id, name
FROM sys.indexes
WHERE object_id = object_id('TestOrderDetails2');
DBCC IND('Northwind', 'TestOrderDetails2', 1);
DBCC IND('Northwind', 'TestOrderDetails2', 2);
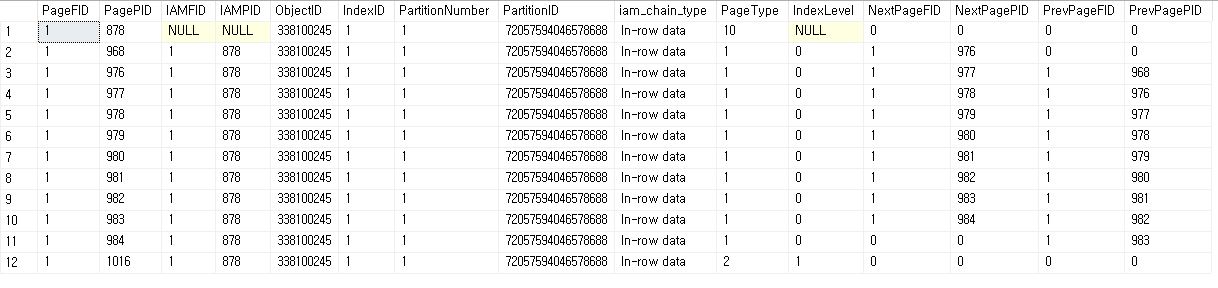
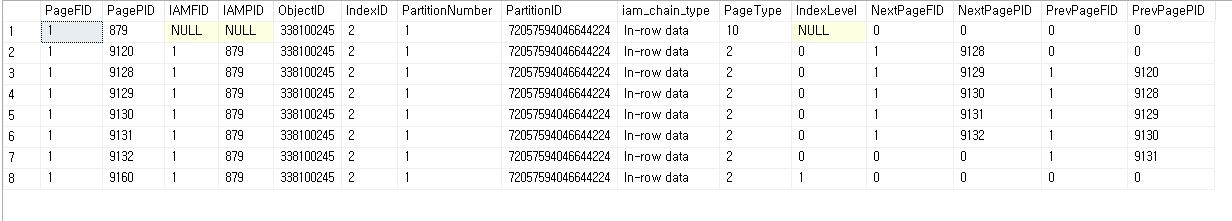
DBCC PAGE('Northwind', 1, 9120, 3);

Index Scan VS Index Seek
Index Scan vs Index Seek
- Index Access Process
- Index Scan: Search LEAF PAGE sequentially
- Index Seek: Search with index
CONVERT
- CONVERT
- change type of variable
CREATE TABLE TestAccess
(
id INT NOT NULL,
name NCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
dummy NCHAR(1000) NULL
);
CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX TestAccess_CI
ON TestAccess(id);
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX TestAccess_NCI
ON TestAccess(name);
DECLARE @i INT;
SET @i = 1;
DECLARE @i INT;
SET @i = 1;
WHILE(@i <= 500)
BEGIN
INSERT INTO TestAccess
VALUES(@i, 'Name' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @i), 'Hello World' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @i));
SET @i = @i + 1;
END
EXEC sp_helpindex 'TestAccess';
SELECT index_id, name
FROM sys.indexes
WHERE object_id = object_id('TestAccess');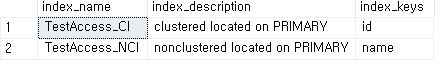
Clustered
DBCC IND('Northwind', 'TestAccess', 1);

Non-Clustered
DBCC IND('Northwind', 'TestAccess', 2);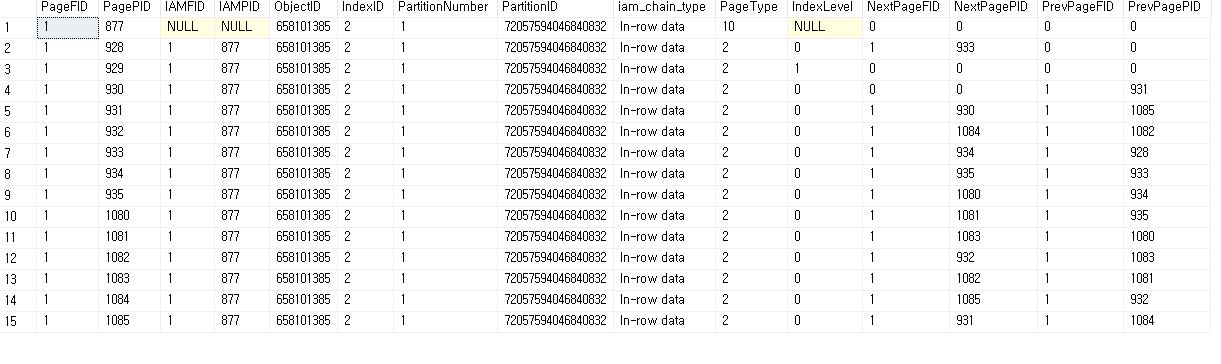

SET STATISTICS
- TIME
- Time for Logical read
- IO
- Number of pages read to find actual data
SET STATISTICS TIME ON;
SET STATISTICS IO ON;Scan Process
- All table
- INDEX SCAN
SELECT *
FROM TestAccess;

- Non-Clustered
- INDEX SCAN + KEY LOOKUP
- N is number of rows which you want to search
- 2 is for root → page stesp in Non-Clustered
SELECT TOP 5 *
FROM TestAccess
ORDER BY name;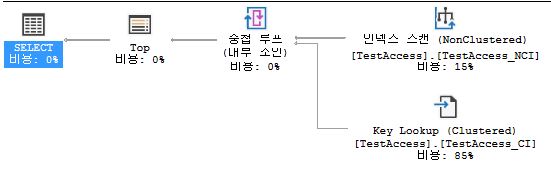

Seek Process
- Clustered
- INDEX SEEK
- root → page
- 2 steps
SELECT *
FROM TestAccess
WHERE id = 104;

- Non-Clustered
- INDEX SEEK + KEY LOOKUP
- root → page → clustered root → page
- page has Key of clustered index
- 4 steps
SELECT *
FROM TestAccess
WHERE name = 'name5';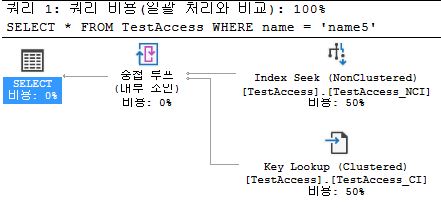

Bookmark Lookup
SET STATISTICS
- PROFILE
- show the actual order in which it was executed
SELECT *
INTO TestOrders
FROM Orders;
SELECT *
FROM TestOrders;
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX Orders_Index01
ON TestOrders(CustomerID);
SELECT index_id, name
FROM sys.indexes
WHERE object_id = object_id('TestOrders');
DBCC IND('Northwind', 'TestOrders', 2);
SET STATISTICS TIME ON;
SET STATISTICS IO ON;
SET STATISTICS PROFILE ON;WITH INDEX
- WITH INDEX
- force index usage
- Database choose whether index usage or not
- if it is more better index not usage, database can choose
SCAN
SELECT *
FROM TestOrders
WHERE CustomerID = 'QUICK';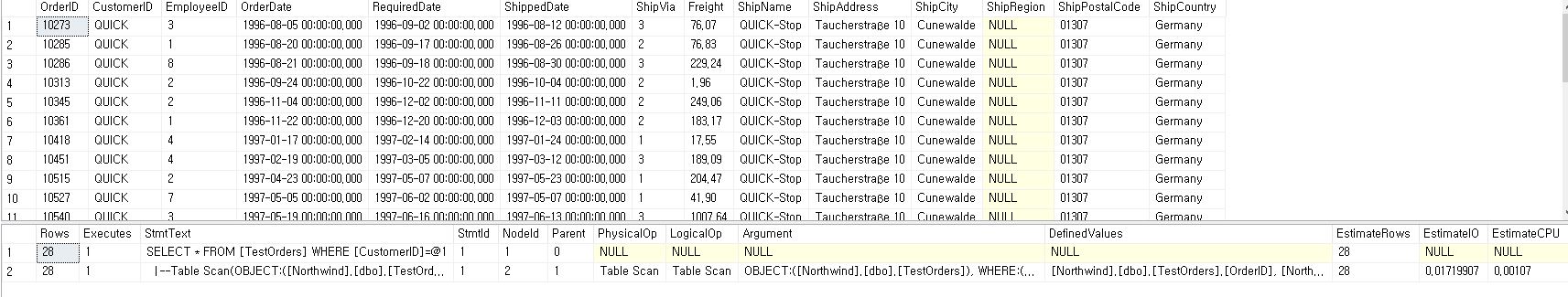


SELECT *
FROM TestOrders WITH(INDEX(Orders_Index01))
WHERE CustomerID = 'QUICK';

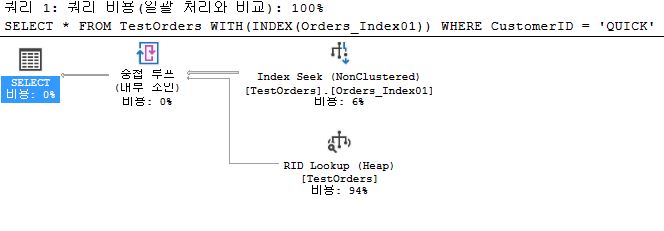
Decrease Lookup
- Covered Index
- include all column to search in index
- but it can putsa load on the DML(CREATE, DELETE, UPDATE)
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX Orders_Index02
ON TestOrders(CustomerID, ShipVia);
SELECT *
FROM TestOrders WITH(INDEX(Orders_Index02))
WHERE CustomerID = 'QUICK' AND ShipVia = 3;


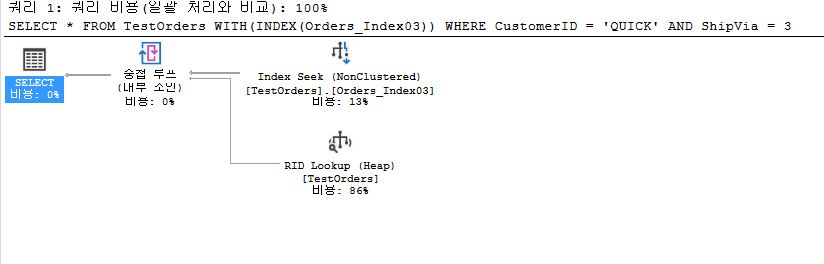
- INCLUDE
- give a hint to index by
INCLUDE
- give a hint to index by
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX Orders_Index03
ON TestOrders(CustomerID) INCLUDE (ShipVia);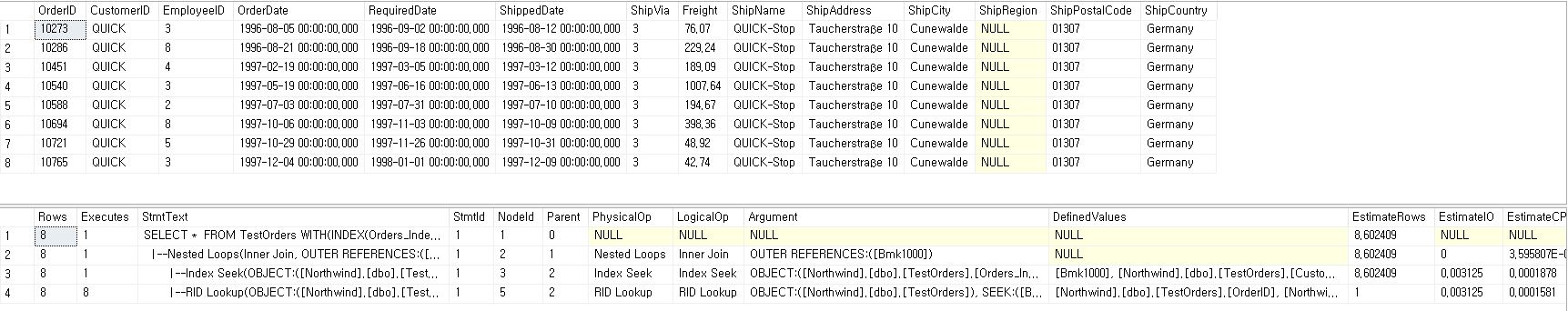

- Clustered
- Only one column
- it can put a load if there is Non-Clustred
Index Column Order
Create dummy data
USE Northwind;
SELECT *
INTO TestOrders
FROM Orders;
DECLARE @i INT = 1;
DECLARE @emp INT;
SELECT @emp = MAX(EmployeeID)
FROM Orders;
SELECT *
FROM TestOrders;
WHILE(@i < 1000)
BEGIN
INSERT INTO TestOrders(CustomerID, EmployeeID, OrderDate)
SELECT CustomerID, @emp + @i, OrderDate
FROM Orders;
SET @i = @i + 1;
END
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM TestOrders;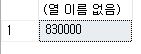
Create Index
idx_emp_ordcreates index byEmployeeIDat first, and then byOrderDateidx_ord_empcreates index byOrderDateat first, and then byEmployeeID
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX idx_emp_ord
ON TestOrders(EmployeeID, OrderDate);
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX idx_ord_emp
ON TestOrders(OrderDate, EmployeeID);
SET STATISTICS TIME ON;
SET STATISTICS IO ON;Compare
- Case 1: no range in search
- there is same logiacal read time
- and both use index to search
SELECT *
FROM TestOrders WITH(INDEX(idx_emp_ord))
WHERE EmployeeID = 1 AND OrderDate = CONVERT(DATETIME, '19970101');

SELECT *
FROM TestOrders WITH(INDEX(idx_ord_emp))
WHERE EmployeeID = 1 AND OrderDate = CONVERT(DATETIME, '19970101');

- first, database searches the page which have a real data matching with condition
- and check the next row
- if the next row is not matched with condition, then return
- So,
idx_emp_ordandidx_emp_ordsearched same count of row - this is because their search order did not affect to search
SELECT *
FROM TestOrders
ORDER BY EmployeeID, OrderDate;
SELECT *
FROM TestOrders
ORDER BY OrderDate, EmployeeID;
- Case 2: range in search
- both use index also
- but both of logical read time are different
-- Same with next SELECT statement ---------------
SELECT *
FROM TestOrders WITH(INDEX(idx_emp_ord))
WHERE EmployeeID = 1 AND OrderDate >= '19970101' AND OrderDate <= '19970103';
--------------------------------------------------
SELECT *
FROM TestOrders WITH(INDEX(idx_emp_ord))
WHERE EmployeeID = 1 AND OrderDate BETWEEN '19960701' AND '19970103';

SELECT *
FROM TestOrders WITH(INDEX(idx_ord_emp))
WHERE EmployeeID = 1 AND OrderDate BETWEEN '19960701' AND '19970103';
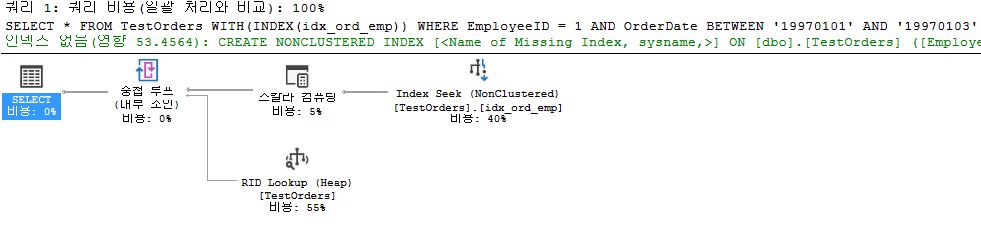
- in
idx_emp_ord, database searches the page which match with1inEmployeeID, and then match with between19970101and19970103inOrderDate - and check next row
- it is ordered by
EmployeeIDfirst, so next row must have same or biggerEmployeeID - So,
idx_emp_ordsearched only 3 rows
SELECT *
FROM TestOrders
ORDER BY EmployeeID, OrderDate;
- in
idx_ord_emp, database searches the page wich match with between19970101and19970103inOrderDate, and then match with1inEmployeeID - and check next row
- it is ordered by
OrderDatefirst, So if theOrderDateis in between19970101and19970103, then database have to checkEmployeeIDin the rows - So
idx_ord_empsearched more then 3 rows
SELECT *
FROM TestOrders
ORDER BY OrderDate, EmployeeID;
IN-LIST
- IN()
- if between range is small, then change the range to
IN()
- if between range is small, then change the range to
SET STATISTICS PROFILE ON;
SELECT *
FROM TestOrders WITH(INDEX(idx_ord_emp))
WHERE EmployeeID = 1 AND OrderDate IN('19960101','19970102', '19970103');
SELECT *
FROM TestOrders WITH(INDEX(idx_emp_ord))
WHERE EmployeeID = 1 AND OrderDate IN('19960101','19970102', '19970103');
Join
Hash Join
- Hash Join does not need to sort → The more data to Merge, The better to Hash
- not be infected by Index
- Hash is better than NL/Merge(depends on situation)
- But you have to concider the cost of hash table(process time become bigger → Index)
- Random Access X
- smaller data is good to make Hash Table
SELECT *
FROM TestOrders AS o
INNER JOIN TestCustomers AS c
ON o.CustomerID = c.CustomerID;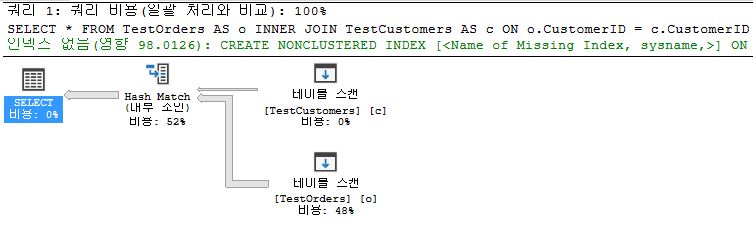
- Hash Join in C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace HashJoin
{
class Player
{
public int playerId;
}
class Salary
{
public int playerId;
}
class HashTable
{
int _bucketCount;
List<int>[] _buckets;
public HashTable(int bucketCount = 100)
{
_bucketCount = bucketCount;
_buckets = new List<int>[bucketCount];
for (int i = 0; i < bucketCount; i++)
_buckets[i] = new List<int>();
}
public void Add(int value)
{
int key = value % _bucketCount;
_buckets[key].Add(value);
}
public bool Find(int value)
{
int key = value % _bucketCount;
// _buckets[key].Contains(value);
foreach(int v in _buckets[key])
{
if (v == value)
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Random rand = new Random();
List<Player> players = new List<Player>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
if (rand.Next(0, 2) == 0)
continue;
players.Add(new Player() { playerId = i });
}
List<Salary> salaries = new List<Salary>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
if (rand.Next(0, 2) == 0)
continue;
salaries.Add(new Salary() { playerId = i });
}
// TEMP HashTable
/*Dictionary<int, Salary> hash = new Dictionary<int, Salary>();
foreach (Salary s in salaries)
hash.Add(s.playerId, s);
List<int> result = new List<int>();
foreach(Player p in players)
{
if (hash.ContainsKey(p.playerId))
result.Add(p.playerId);
}*/
HashTable hash = new HashTable();
foreach (Salary s in salaries)
hash.Add(s.playerId);
List<int> result = new List<int>();
foreach(Player p in players)
{
if (hash.Find(p.playerId))
result.Add(p.playerId);
}
}
}
}