Quick Sort
- Quick sort is a widely used sorting algorithm known for its efficiency and effectiveness.
- It follows the “divide and conquer” approach to sort elements.
Concept
Partitioning
- Choose a pivot element from the array.
- Usually, this can be the first, last, or middle element of the array.
- The goal of partitioning is to rearrange the elements of the array so that all elements less than the pivot are placed before it, and all elements greater than the pivot are placed after it.
Recursion
- Recursively apply the above process to the sub-arrays formed by partitioning until the entire array is sorted.
Combine
- Since each partitioning step places one element (the pivot) into its final sorted position, after all partitions are done, the array is sorted.
Implementation
- Program.cs
namespace QuickSort;
class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 1, 10, 5, 8, 7, 6, 4, 3, 2, 9 };
Console.WriteLine("Original array : ");
Common.Print(arr);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Choose pivot: ");
Console.WriteLine("[1] First as pivot");
Console.WriteLine("[2] Middle as pivot");
Console.WriteLine("[3] Last as pivot");
var choice = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine();
switch (choice)
{
case "1":
FirstAsPivot.Run(arr);
break;
case "2":
MiddleAsPivot.Run(arr);
break;
case "3":
LastAsPivot.Run(arr);
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Choose 1 to 3");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Sorted array : ");
Common.Print(arr);
}
}- Common.cs
namespace QuickSort
{
public class Common
{
public static void Swap(int[] arr, int a, int b)
{
var temp = arr[a];
arr[a] = arr[b];
arr[b] = temp;
}
public static void Print(int[] arr)
{
foreach(var item in arr)
{
Console.Write(item + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}First element as pivot
- FirstAsPivot.cs
namespace QuickSort
{
public class FirstAsPivot
{
public static int[] Run(int[] arr)
{
QuickSort(arr, 0, arr.Length - 1);
return arr;
}
private static void QuickSort(int[] arr, int start, int end)
{
if (start >= end) return;
int pivot = start;
int left = start + 1;
int right = end;
int temp;
while(left <= right)
{
while (left <= end && arr[left] < arr[pivot] ) left++;
while (right > start && arr[right] > arr[pivot] ) right--;
if (left > right) Common.Swap(arr, pivot, right);
else Common.Swap(arr, left, right);
Common.Print(arr);
}
QuickSort(arr, start, right - 1);
QuickSort(arr, right + 1, end);
}
}
}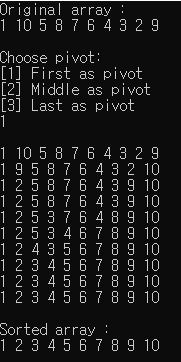
- Round 1
- Index
pivotis 0 andpivotvalue 1. Indexleftis 1 andleftvalue is 10. Indexrightis 9 andrightvalue is 9. - Compare 1 and 10. 10 is bigger then 1. So, index
leftis 1 andleftvalue is 10 for swapping. - Compare 1 and 9. Honestly, 1 is smaller then every elements. So, we should move index
rightuntil 0 and resultrightvalue is 1 for swapping. -
It will swap 1 to 1. So, nothing ganna be changed.
- Round 2
-
In first recursive,
startis 1 andendis -1. So, it will return directly. - Round 3
- In second recursive,
startis 1 andendis 9. - Index
pivotis 1 andpivotvalue is 10. Indexleftis 2 andleftvalue is 5. Indexrightis 9 andrightvalue is 9. - Compare 10 and 5. Honestly, 10 is bigger then every elements. So, we should move index
leftuntil 10. - Compare 10 and 9. 9 is smaller then 10. So, index
rightis 9 andrightvalue is 9 for swapping. - Compare index
leftandright. I mean, compare 10 and 9. 10 is bigger then 9. So, swappivotandright. -
Now our array is
1, 9, 5, 8, 7, 6, 4, 3, 2, 10. - Round 4
- In third recursive,
startis 1 andendis 8. - After continuing quick sort, you will get
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10as a result of quick sort.
Middle element as pivot
- MiddleAsPivot.cs
namespace QuickSort
{
public class MiddleAsPivot
{
public static int[] Run(int[] arr)
{
QuickSort(arr, 0, arr.Length - 1);
return arr;
}
private static void QuickSort(int[] arr, int start, int end)
{
if (start >= end) return;
int left = start;
int right = end;
int pivot = (start + end)/2;
while (left < right)
{
while (arr[left] < arr[pivot]) left++;
while (arr[right] > arr[pivot]) right--;
if (left < right)
{
Common.Swap(arr, left, right);
Common.Print(arr);
}
}
QuickSort(arr, start, pivot);
QuickSort(arr, pivot + 1, end);
}
}
}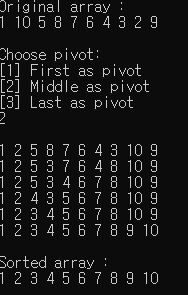
- Round 1
- Index
pivotis 4 andpivotvalue 7. Indexleftis 0 andleftvalue is 1. Indexrightis 9 andrightvalue is 9. - Compare 7 and 1. 1 is smaller then 7. So, move
left. Now, indexleftis 1 andleftvalue is 10. - Compare 7 and 10. 10 is bigger then 7. So, index
leftis 1 andleftvalue is 10 for swapping. - Compare 7 and 9. 9 is bigger then 7. So, move
right. Now, indexrightis 8 andleftvalue is 2. - Compare 7 and 2. 2 is smaller then 7. So, index
rightis 8 andrightvalue is 2 for swapping. - Swap 10 and 2. Our current array is
1, 2, 5, 8, 7, 6, 4, 3, 10, 9. - Compare 7 and 2. 2 is smaller then 7. So, move
left. Now, indexleftis 2 andleftvalue is 5. - Compare 7 and 5. 5 is smaller then 7. So, move
left. Now, indexleftis 3 andleftvalue is 8. - Compare 7 and 8. 8 is bigger then 7. So, index
leftis 3 andleftvalue is 8 for swapping. - Compare 7 and 10. 10 is bigger then 7. So, move
right. Now, indexrightis 7 andleftvalue is 3. - Compare 7 and 3. 3 is smaller then 7. So, index
rightis 7 andrightvalue is 3 for swapping. - Swap 8 and 3. Our current array is
1, 2, 5, 3, 7, 6, 4, 8, 10, 9. - Compare 7 and 3. 3 is smaller then 7. So, move
left. Now, indexleftis 4 andleftvalue is 7. - Compare 7 and 7. It’s same. So, index
leftis 4 andleftvalue is 7 for swapping. - Compare 7 and 8. 8 is bigger then 7. So move
right. Now, indexrightis 6 andrightvalue is 4. - Compare 7 and 4. 4 is smaller then 7. So, index
rightis 6 andrightvalue is 4 for swapping. - Swap 7 and 4. Our current array is
1, 2, 5, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 10, 9. -
Move
leftandright. Current indexleftis 5 and indexrightis also 5. Therefore, while loops are finished here. - Round 2
- In first recursive,
startis 0 andendis 4. - Index
pivotis 2 andpivotvalue 5. Indexleftis 0 andleftvalue is 1. Indexrightis 4 andrightvalue is 4. - Compare 5 and 1. 1 is smaller then 5. So, move
left. Now, indexleftis 1 andleftvalue is 2. - Compare 5 and 2. 2 is smaller then 5. So, move
left. Now, indexleftis 2 andleftvalue is 5. - Compare 5 and 5. It’s same. So, index
leftis 2 andleftvalue is 5 for swapping. - Compare 5 and 4. 4 is smaller then 5. So, index
rightis 4 andrightvalue is 4 for swapping. - Swap 5 and 4. Our current array is
1, 2, 4, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 9. - Compare 4 and 4. It’s same. So, index
leftis 2 andleftvalue is 4 for swapping. - Compare 4 and 5. 5 is bigger then 4. So, move
right. Now, indexrightis 3 andrightvalue is 3. -
Swap 4 and 3. Our current array is
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 9. - Round 3
-
In second recursive,
startis 0 andendis 2. But, every elemtns are already sorted. - Round 4
- In third recursive,
startis 0 andendis 1. But, every elemtns are already sorted. - After continuing quick sort, you will get
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10as a result of quick sort.
Last element as pivot
- LastAsPivot.cs
namespace QuickSort
{
public class LastAsPivot
{
public static int[] Run(int[] arr)
{
QuickSort(arr, 0, arr.Length - 1);
return arr;
}
private static void QuickSort(int[] arr, int start, int end)
{
if (start > end) return;
int pivot = end;
int left = start;
int right = end - 1;
while (left < right)
{
while (left < end && arr[left] < arr[pivot]) left++;
while (right > start && arr[right] > arr[pivot]) right--;
if(left > right) Common.Swap(arr, pivot, left);
else Common.Swap(arr, left, right);
Common.Print(arr);
}
QuickSort(arr, start, left - 1);
QuickSort(arr, left + 1, end);
}
}
}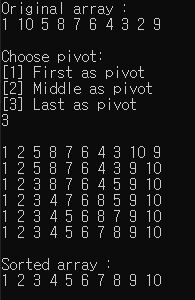
- Round 1
- Index
pivotis 9 andpivotvalue 9. Indexleftis 0 andleftvalue is 1. Indexrightis 8 andrightvalue is 2. - Compare 9 and 1. 1 is smaller then 9. So, move
left. Now, indexleftis 1 andleftvalue is 10. - Compare 9 and 10. 10 is bigger then 9. So, index
leftis 1 andleftvalue is 10 for swapping. - Compare 9 and 2. 2 is smaller then 9. So, index
rightis 8 andrightvalue is 2 for swapping. - Swap 10 and 2. Our current array is
1, 2, 5, 8, 7, 6, 4, 3, 10, 9. - Compare and continue to move. Index
leftis 8 andleftvalue is 10 for swapping. - Compare 9 and 10. 10 is bigger then 9. So, move
right. Now, indexrightis 7 andrightvalue is 3. - Compare 9 and 3. 3 is smaller then 9. So, index
rightis 7 andrightvalue is 3 for swapping. -
However, index
leftis bigger then indexright. Swap 9 and 10. Our current array is1, 2, 5, 8, 7, 6, 4, 3, 9, 10. - Round 2
- In first recursive,
startis 0 andendis 7. - Index
pivotis 7 andpivotvalue 3. Indexleftis 0 andleftvalue is 1. Indexrightis 6 andrightvalue is 4. - Compare 3 and 1. 1 is smaller then 3. So, move
left. Now, indexleftis 1 andleftvalue is 2. - Compare 3 and 2. 2 is smaller then 3. So, move
left. Now, indexleftis 2 andleftvalue is 5. - Compare 3 and 5. 5 is bigger then 3. So, index
leftis 2 andleftvalue is 5 for swapping. - Compare 3 and continue to move until 2. Index
rightis 1 andrightvalue is 2 for swapping. -
However, index
leftis bigger then indexright. Swap 5 and 3. Our current array is1, 2, 3, 8, 7, 6, 4, 5, 9, 10. - Round 3
-
In second recursive,
startis 0 andendis 1. But, every elemtns are already sorted. - Round 4
- In third recursive,
startis 0 andendis -1. It will be directly returned.