Tree Traversal
- Tree Traversal techniques include various ways to visit all the nodes of the tree.
- Unlike linear data structures (Array, Linked List, Queues, Stacks, etc) which have only one logical way to traverse them, trees can be traversed in different ways.
- Tree Traversal refers to the process of visiting or accessing each node of the tree exactly once in a certain order.
- Tree traversal algorithms help us to visit and process all the nodes of the tree.
- Since tree is not a linear data structure, there are multiple nodes which we can visit after visiting a certain node.
- There are multiple tree traversal techniques which decide the order in which the nodes of the tree are to be visited.
Depth First Search(DFS)
- Inorder Traversal
- Preorder Traversal
- Postorder Traversal
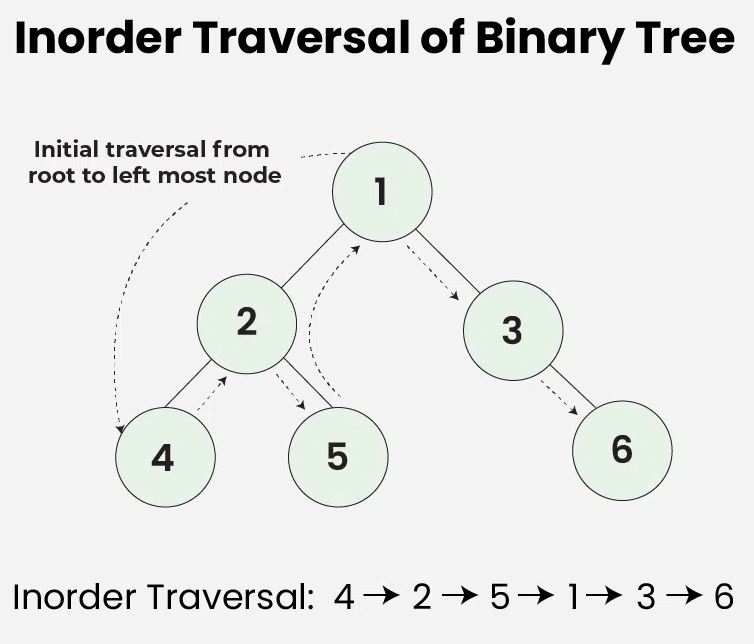
Inorder Traversal
- Inorder traversal visits the node in the order: Left -> Root -> Right
- Algorithm for Inorder Traversal:
- Traverse the left subtree(left -> subtree)
- Visit the root
- Traverse the right subtree(right -> subtree)
- Usage of Inorder Traversal:
- Inorder traversal can be used to evaluate arithmetic expressions stored in expression trees.
Code
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public static class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
inorderTraversal(root);
}
// Function to perform inorder traversal
static void inorderTraversal(Node node)
{
// Base case
if (node == null)
return;
// Recur on the left subtree
inorderTraversal(node.left);
// Visit the current node
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
// Recur on the right subtree
inorderTraversal(node.right);
}
}
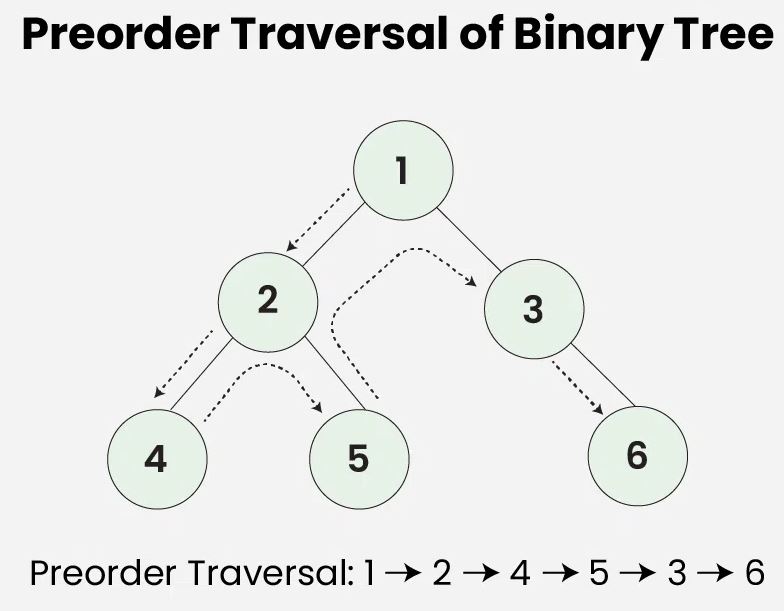
Preorder Traversal
- Preorder traversal visits the node in the order: Root -> Left -> Right
- Algorithm for Preorder Traversal:
- Visit the root
- Traverse the left subtree(left -> subtree)
- Traverse the right subtree(right -> subtree)
- Usage of Preorder Traversal:
- Preorder traversal is used to create a copy of the tree.
- Preorder traversal is also used to get prefix expressions on an expression tree.
Code
class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item) {
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public static class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
PreorderTraversal(root);
}
// Function to perform preorder traversal
static void PreorderTraversal(Node node)
{
// Base case
if (node == null)
return;
// Visit the current node
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
// Recur on the left subtree
PreorderTraversal(node.left);
// Recur on the right subtree
PreorderTraversal(node.right);
}
}
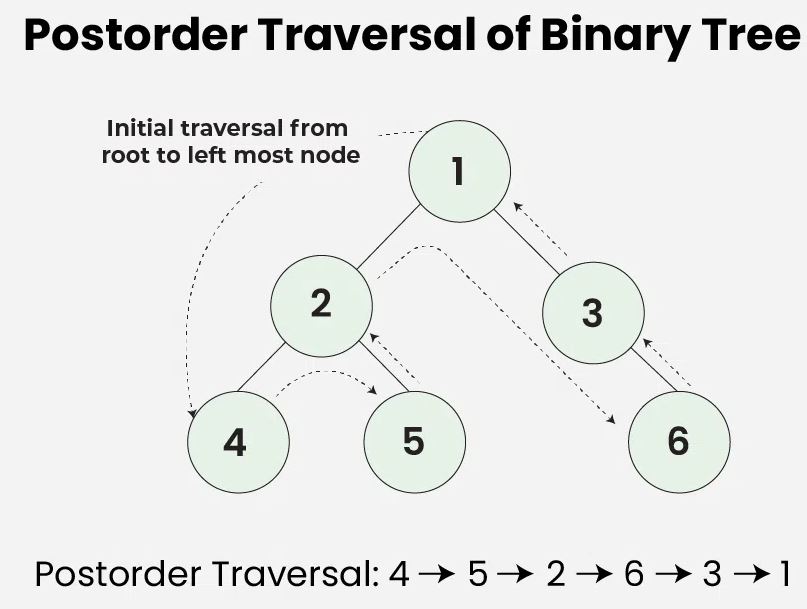
Postorder Traversal
- Postorder traversal visits the node in the order: Left -> Right -> Root
- Algorithm for Postorder Traversal:
- Traverse the left subtree(left -> subtree)
- Traverse the right subtree(right -> subtree)
- Visit the root
- Usage of Postorder Traversal:
- Postorder traversal is used to delete the tree.
- Postorder traversal is also useful to get the postfix expression of an expression tree.
- Postorder traversal can help in garbage collection algorithms, particularly in systems where manual memory management is used.
Code
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public static class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
PostorderTraversal(root);
}
// Function to perform postorder traversal
static void PostorderTraversal(Node node) {
// Base case
if (node == null)
return;
// Recur on the left subtree
PostorderTraversal(node.left);
// Recur on the right subtree
PostorderTraversal(node.right);
// Visit the current node
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
}
}
Breadth First Search(BFS)
- Level Order Traversal
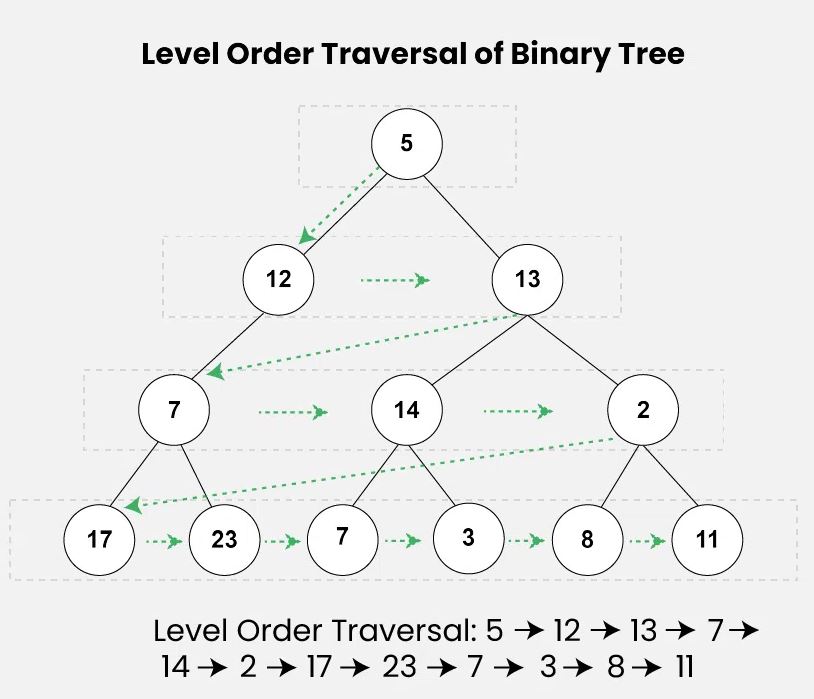
Level Order Traversal
- Level Order Traversal visits all nodes present in the same level completely before visiting the next level.
- Algorithm for Level Order Traversal:
- Create an empty queue Q
- Enqueue the root node of the tree to Q
- Loop while Q is not empty
- Dequeue a node from Q and visit it
- Enqueue the left child of the dequeued node if it exists
- Enqueue the right child of the dequeued node if it exists
- Usage of Level Order:
- Level Order Traversal is used for not only Breadth First Search to search or process nodes level-by-lebel, but also Tree Serialization and Deserialization.
Code
public class TreeNode
{
public int Value;
public TreeNode Left;
public TreeNode Right;
public TreeNode(int x) { Value = x; }
}
public static class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
// Example usage
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);
root.Left = new TreeNode(2);
root.Right = new TreeNode(3);
root.Left.Left = new TreeNode(4);
root.Left.Right = new TreeNode(5);
root.Right.Right = new TreeNode(6);
Console.Write("Level Order Traversal: ");
LevelOrder(root);
}
// Function to perform postorder traversal
public static void LevelOrder(TreeNode root)
{
if (root == null) return;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new Queue<TreeNode>();
queue.Enqueue(root);
while (queue.Count > 0)
{
TreeNode node = queue.Dequeue();
Console.Write(node.Value + " ");
if (node.Left != null) queue.Enqueue(node.Left);
if (node.Right != null) queue.Enqueue(node.Right);
}
}
}